Manufacturing and Analytical Characterization - Chemical
Category: Poster Abstract
(M1330-08-54) Amorphous Solid Dispersion Physical Stability: Historical Examples and Shelf-Life Assessment
Monday, October 23, 2023
1:30 PM - 2:30 PM ET

Patrick J. Marroum, PhD
Distinguished Research Fellow
AbbVie, Inc.
North Chicago, Illinois, United States
Frank Theil, PhD (he/him/his)
Principal Research Scientist
Abbvie
Ludwigshafen, Rheinland-Pfalz, Germany
Presenter (non-author)(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Poor aqueous solubility and therefore scarcity of bioavailability of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is one of the main challenges in the development of solid oral dosage forms during the last few decades in the pharmaceutical industry.[1, 2] Formulating the API as an amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) has been proven to successfully enhance bioavailability of many APIs classified as biopharmaceutical classification system (BCS) class II and class IV.[3, 4] Many ASD formulations are thermodynamically unstable but kinetically stabilized due to low molecular mobility in the glassy ASD formulation.[5, 6] Accelerated API crystallization at high drug loads (DL) in kinetically stabilized ASDs is considered a potential risk for both, patients and pharmaceutical companies.[7] In this work the long-term physical stability of two kinetically stabilized ASDs is presented: a 15 %DL ASD of Fenofibrate was investigated after 15 years of storage under uncontrolled ambient conditions, and a 20 %DL ASD of Nifedipine even after 25 years.[8, 9] Those observations show that even kinetically stabilized ASDs can be crystal free way beyond the desired pharmaceutical shelf-life. Additionally, a strategy for crystallization risk assessment of ASD products, based on monitoring crystal growth in ASDs using transmission Raman spectroscopy (TRS), is discussed. Our approach classifies the crystallization risk in the drug product (DP) based on accelerated open dish studies. Depending on the observed data, proper mitigation steps are advised. In case of an anticipated crystallization in the packaged DP over shelf-life, the actual crystal growth in the DP is estimated. For this step, open dish crystallization rates obtained at accelerated conditions are combined with modeling of the glass transition temperature Tg and water content of the packaged DP during storage.
Methods: The starting point of the risk assessment is the standard open dish stress test at 40 °C / 75% RH. Ifcrystallization is detected in this study within 14 days of storage, an investigation of the crystallization risk is indicated. As in this stage of development crystallization is usually detected qualitatively by polarized light microscopy, the next step is to quantify the crystal growth and assign a rate constant. This investigation is performed in a Tier I investigation, preferably using TRS. In our experience, the non-destructive nature, inherent sample averaging, and chemometric data evaluation make this technology more than suited to quantify crystal growth in ASD samples. From our work on long term stability, we can assume that an ASD taking 14 days or longer to show complete API crystallization in an open dish experiment at 40 °C / 75% RH will not present a crystallization risk during shelf-life storage of the packaged material.[9] In cases where the ASD under investigation shows a considerable crystallization rate, the physical stability of alternate formulations can be compared in a Tier II study. A Tier III investigation is indicated if no alternate formulation with sufficient stability is found, or other reasons, like bioavailability or manufacturability, indicate the usage of a formulation considered not physically stable. In the Tier III investigation, the crystallization rate constant is measured for several storage conditions above Tg. The rate constants can be correlated with the ratio of Tg over T. Calculations of the moisture dependence of the Tg in the ASD and moisture content of the packaged DP can be used to determine the Tg of the product during storage.
Results: The risk assessment strategy is now routinely applied to AbbVies ASD development candidates. The application of the complete risk assessment strategy on a model compound will be presented in this talk. After crystallization of the lead formulation candidate was observed in an open dish study, the rate of crystallization was determined and compared to alternate formulations (Figure 3). As the lead formulation had shown complete API crystallization within 3 days at 40 °C / 75% RH open dish condition, an estimation of the physical shelf-life was indicated. Based on predicted water content of the blister packaged DP and calculated impact of water on the products Tg, a shelf-life till crystallinity limit of 67 months could be estimated.
Conclusion: With the results presented in this work, crystallization observed in open-dish studies is no longer a showstopper in ASD development. Using historical examples, the possibility of long-term stability in kinetically stabilized ASDs even if stored only a few degrees below Tg could be shown. Utilizing recent results of the investigation of glass physics in ASDs and combining them with physical modeling tools, a risk assessment and mitigation framework for API crystallization in ASD formulation could be developed. The framework enables drug development teams to conduct rational risk-based actions in ASD development. It allows to successfully bring ASD formulations to market that were just a couple of years ago discontinued due to perceived stability issues.
References: 1. Thayer, A.M., FINDING SOLUTIONS. Chemical & Engineering News Archive, 2010. 88(22): p. 13-18.
2. Waring, M.J., et al., An analysis of the attrition of drug candidates from four major pharmaceutical companies. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2015. 14(7): p. 475-486.
3. Schittny, A., J. Huwyler, and M. Puchkov, Mechanisms of increased bioavailability through amorphous solid dispersions: a review. Drug Delivery, 2020. 27(1): p. 110-127.
4. Pandi, P., et al., Amorphous solid dispersions: An update for preparation, characterization, mechanism on bioavailability, stability, regulatory considerations and marketed products. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2020. 586: p. 119560.
5. Lehmkemper, K., et al., Long-Term Physical Stability of PVP- and PVPVA-Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol Pharm, 2017. 14(1): p. 157-171.
6. Zhou, D., et al., Assessing Physical Stability Risk Using the Amorphous Classification System (ACS) Based on Simple Thermal Analysis. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2019. 16(6): p. 2742-2754.
7. Yu, L., Amorphous pharmaceutical solids: preparation, characterization and stabilization. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2001. 48(1): p. 27-42.
8. Theil, F., et al., Frozen in Time: Kinetically Stabilized Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Nifedipine Stable after a Quarter Century of Storage. Mol Pharm, 2017. 14(1): p. 183-192.
9. Theil, F., et al., Extraordinary Long-Term-Stability in Kinetically Stabilized Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Fenofibrate. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2017. 14(12): p. 4636-4647.
10. Mudie, D.M., et al., A novel architecture for achieving high drug loading in amorphous spray dried dispersion tablets. International Journal of Pharmaceutics: X, 2020. 2: p. 100042.
11. Gupta, P., V.K. Kakumanu, and A.K. Bansal, Stability and Solubility of Celecoxib-PVP Amorphous Dispersions: A Molecular Perspective. Pharmaceutical Research, 2004. 21(10): p. 1762-1769.
12. Zhou, D., et al., Thermodynamics, molecular mobility and crystallization kinetics of amorphous griseofulvin. Mol Pharm, 2008. 5(6): p. 927-36.
13. Amharar, Y., et al., Solubility of crystalline organic compounds in high and low molecular weight amorphous matrices above and below the glass transition by zero enthalpy extrapolation. Int J Pharm, 2014. 472(1-2): p. 241-7.
14. Kothari, K., V. Ragoonanan, and R. Suryanarayanan, Influence of molecular mobility on the physical stability of amorphous pharmaceuticals in the supercooled and glassy States. Mol Pharm, 2014. 11(9): p. 3048-55.
15. Hancock, B.C., S.L. Shamblin, and G. Zografi, Molecular mobility of amorphous pharmaceutical solids below their glass transition temperatures. Pharm Res, 1995. 12(6): p. 799-806.
16. Amidon, G.L., et al., A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm Res, 1995. 12(3): p. 413-20.
17. Liu, B., et al., Crystallization Risk Assessment of Amorphous Solid Dispersions by Physical Shelf-Life Modeling: A Practical Approach. Mol Pharm, 2021. 18(6): p. 2428-2437.
Acknowledgements: Numerous AbbVie employees were involved in developing, producing and analyzing the presented examples. Their contributions are highly appreciated. We’d like to especially thank Jörg Rosenberg for having the foresight to store ASD samples over decades for later analysis and Sankaran Anantharaman as well as Holger van Lishaut for initiating the development of the risk assessment and mitigation approach.
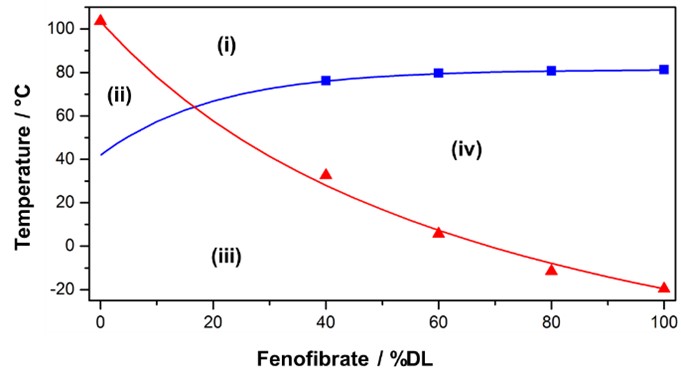 Figure 1: Exemplary phase diagram of a polymer-fenofibrate system.[9] The solubility temperature at different compositions is depicted in blue. The measured Tg values of different compositions are depicted in red. The symbols reflect measured data and the curves show modeling results. Different regions can be identified in the phase diagram: (i) thermodynamically stable melt, (ii) thermodynamically stable glass, (iii) kinetically stable glass and (iv) the undercooled or unstable melt, respectively.
Figure 1: Exemplary phase diagram of a polymer-fenofibrate system.[9] The solubility temperature at different compositions is depicted in blue. The measured Tg values of different compositions are depicted in red. The symbols reflect measured data and the curves show modeling results. Different regions can be identified in the phase diagram: (i) thermodynamically stable melt, (ii) thermodynamically stable glass, (iii) kinetically stable glass and (iv) the undercooled or unstable melt, respectively.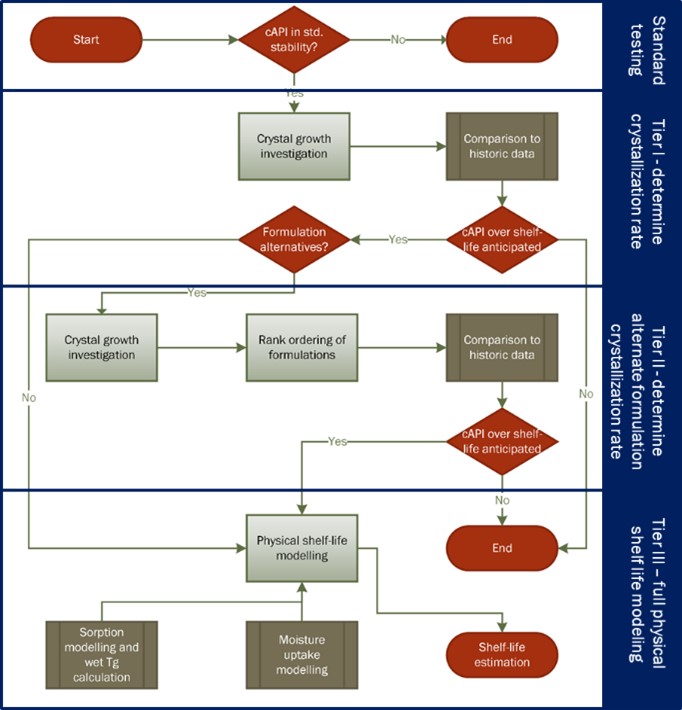 Figure 2: Workflow of the physical shelf life modelling risk assessment strategy for crystallization in ASD formulations. An investigation of the physical stability is indicated if API crystallization is observed in the standard open dish stability investigation at 40 °C / 75% RH within two weeks. In a Tier I investigation, the rate of crystallization in the ASD is determined. If crystallization is sufficiently fast to indicate a shelf life risk, the crystal growth rate in alternate formulations is determined in a Tier II investigation. If no sufficiently stable formulation can be used, a Tier III investigation is indicated and the crystal growth of the DP in the primary packaging container is approximated.
Figure 2: Workflow of the physical shelf life modelling risk assessment strategy for crystallization in ASD formulations. An investigation of the physical stability is indicated if API crystallization is observed in the standard open dish stability investigation at 40 °C / 75% RH within two weeks. In a Tier I investigation, the rate of crystallization in the ASD is determined. If crystallization is sufficiently fast to indicate a shelf life risk, the crystal growth rate in alternate formulations is determined in a Tier II investigation. If no sufficiently stable formulation can be used, a Tier III investigation is indicated and the crystal growth of the DP in the primary packaging container is approximated.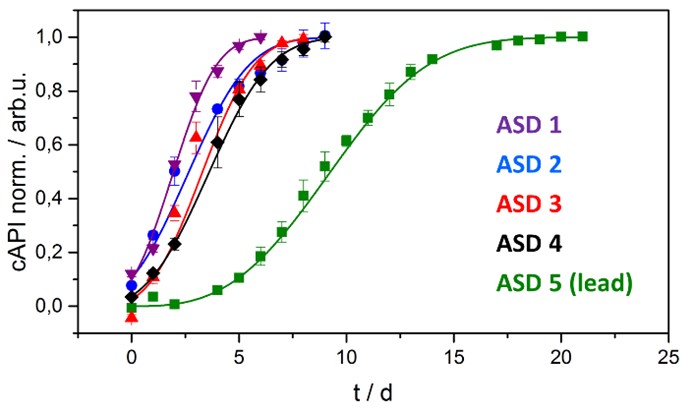 Figure 3: Crystal growth in five different ASD formulation candidates of an AbbVie internal compound. The crystal growth was recorded in samples stored at 30 °C / 75 %RH (open dish) using TRS. The fraction of crystallized API normalized to total API is shown in dependence of time.
Figure 3: Crystal growth in five different ASD formulation candidates of an AbbVie internal compound. The crystal growth was recorded in samples stored at 30 °C / 75 %RH (open dish) using TRS. The fraction of crystallized API normalized to total API is shown in dependence of time.