Formulation and Delivery - Biomolecular
Category: Poster Abstract
(W1030-02-12) Pain-Free Alternatives for Vaccinating against the Zika Virus Using 3D Printed Orally Dissolving Films (ODF) and Intranasal Drops
- SS
Sarthak Shah, MS (he/him/his)
PhD Student
Mercer University
atlanta, Georgia, United States - SS
Sarthak Shah, MS (he/him/his)
PhD Student
Mercer University
atlanta, Georgia, United States - PP
Parth Patel, BA
Mercer University
atlanta, Georgia, United States - PB
Priyal Bagwe, BS (she/her/hers)
Mercer University
Atlanta, Georgia, United States - AK
Akanksha Kale, Ph.D.
Mercer University
atlanta, Georgia, United States .jpg)
Sharon Vijayanand, B.Pharm. (she/her/hers)
Ph.D. Candidate
Mercer University
Atlanta, Georgia, United States
Smital Rajan Patil, BS in Pharmacy (she/her/hers)
PhD Candidate
Mercer University
atlanta, Georgia, United States- MU
Mohammad Nasir Uddin, Ph.D. (he/him/his)
Mercer University
Atlanta, Georgia, United States - MD
Martin J. D'Souza, Ph.D.
Mercer University
Atlanta, Georgia, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: The recent pandemic has shown us the importance of a robust preparedness plan, and the need to develop a safe and widely deliverable vaccine product. The Zika virus is still an ongoing threat to humans. Although this virus is considered a travel-related infectious disease in the United States, the virus results in severe irreversible consequences for humans. Once the virus has transferred from the pregnant mother to the fetus, the baby may develop microcephaly. In addition, this viral infection causes Guillain-Barré syndrome, in which patients experience muscle paralysis due to the demyelination of the myelin sheath. Currently, there is no FDA approved treatment or vaccine available. This leaves the door open for Zika to reemerge globally. The omphalos of this research is to limit the reemergence of Zika by developing a microparticulate inactivated Zika vaccine that can be administered to patients via pain-free routes such as intranasal drops or by using our patented 3D printed Orally Dissolving Films (ODF) which can be easily placed in the buccal cavity.
Methods: We developed microparticles (MPs) using Poly(lactic)-co-glycolic acid polymer (PLGA) encapsulating inactivated Zika virus through the double emulsion solvent evaporation method. In-vitro, we characterized the MP for size, morphology, polydispersity index, and zeta potential. We characterized the ODFs for diameter, weight variation, thickness, disintegration, and pH. The immunogenicity of adjuvanted MP Zika vaccine in ODFs was observed via Griess’s assay by measuring the release of nitric oxide (NO) release by dendritic cells. Encapsulation efficiency and cytotoxicity were measured via the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay and MTT assay. In-vivo, Swiss Webster mice received a prime dose and two boosters, each two weeks apart. Alhydrogel (Alum, Th2) and MPLA (Th1) were used as adjuvants. Serum was collected every two weeks and analyzed using ELISA for mucosal IgA, IgG, IgM, and IgG subtypes (IgG1, IgG2a, IgG3). After sacrifice, the spleen and lymph nodes were collected and analyzed for CD4+ helper and CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell cellular response via flow cytometry.
Results: In vitro, the microparticles were immunogenic and non-cytotoxic in murine dendritic cells. The size of MP was 573.4 ± 10.18 nm, the polydispersity index was 0.294 ± 0.133, and the zeta potential was -22.6 ± 0.503 mV. Morphologically, the MPs were spherical with a donut-like configuration. The average diameter of the ODFs was 4.08 ± 0.07 mm. The average thickness of adjuvanted Zika MP ODF was 0.27 ± 0.07 mm. The average weight was 8.98 ±1.37 mg. The film disintegrated in 203.4 ± 75.6 s. The average pH was 7.89 ± 0.12. The disintegration time of the ODFs showed desirable results, indicating that this ODF formulation allows the film to disintegrate faster. The film's pH was neutral, indicating that the ODFs may not irritate the mucosal lining of the oral cavity. The Griess’s assay demonstrated a significantly higher (p < 0.01) release of nitric oxide, a hallmark of the innate immune response, by dendritic cells upon exposure to adjuvanted Zika virus ODF MP vaccine than the control, blank ODFs. In-vivo, the MP vaccine with or without adjuvant MP was administered via intranasal and ODFs routes to Swiss Webster Mice. Vaccinated mice produced significantly higher mucosal IgA, IgM, IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG3 antibody titers than the control mice. 3D printed Orally dissolving films and intranasal drops adjuvanted groups displayed robust humoral and balanced Th1/Th2 responses. A significant CD4+ helper and CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell cellular response were seen for both IN and ODF adjuvant groups compared to the control mice in spleenocytes and lymph nodes. This study evaluated the potential of developing a pain-free vaccination route for administering the Zika virus to deter the reemergence of the virus.
Conclusion: We successfully developed an inactivated microparticulate lyophilized Zika virus vaccine. This MP vaccine was safe and immunogenic in-vitro. The MP vaccine in ODFs was safe to use on the buccal mucosa. The intranasal and ODFs showed excellent humoral response compared to unvaccinated mice. The vaccinated groups displayed a significant cellular CD4+ helper and CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell response than the untreated groups. Mucosal (IgA) and long-term (IgG) humoral response for the ODF route was higher than the intranasal drops. Adding adjuvants to our MP vaccine aided our approach to produce a balanced Th1 and Th2 helper T-cell response. This inactivated vaccine can be administered by pain-free alternative routes and produce a significant humoral and cellular response. This ‘proof-of-concept' study is a crucial step in developing an effective vaccination program that could curb the spread of the Zika virus and prevent a large-scale spread.
References: 1. Kale, A.; Joshi, D.; Menon, I.; Bagwe, P.; Patil, S.; Vijayanand, S.; Braz Gomes, K.; Uddin, M.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Zika Vaccine Microparticles (MPs)-Loaded Dissolving Microneedles (MNs) Elicit a Significant Immune Response in a Pre-Clinical Murine Model. Vaccines 2023, 11, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030583.
2. Kale A, Joshi D, Menon I, Bagwe P, Patil S, Vijayanand S, Braz Gomes K, D'Souza M. Novel microparticulate Zika vaccine induces a significant immune response in a preclinical murine model after intramuscular administration. Int J Pharm. 2022 Aug 25;624:121975. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121975. Epub 2022 Jul 3. PMID: 35787459.
Acknowledgements: Zika strain PRVABC59 was provided by Brandy Russell, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Colorado. Figure 1 was made using biorender.com.
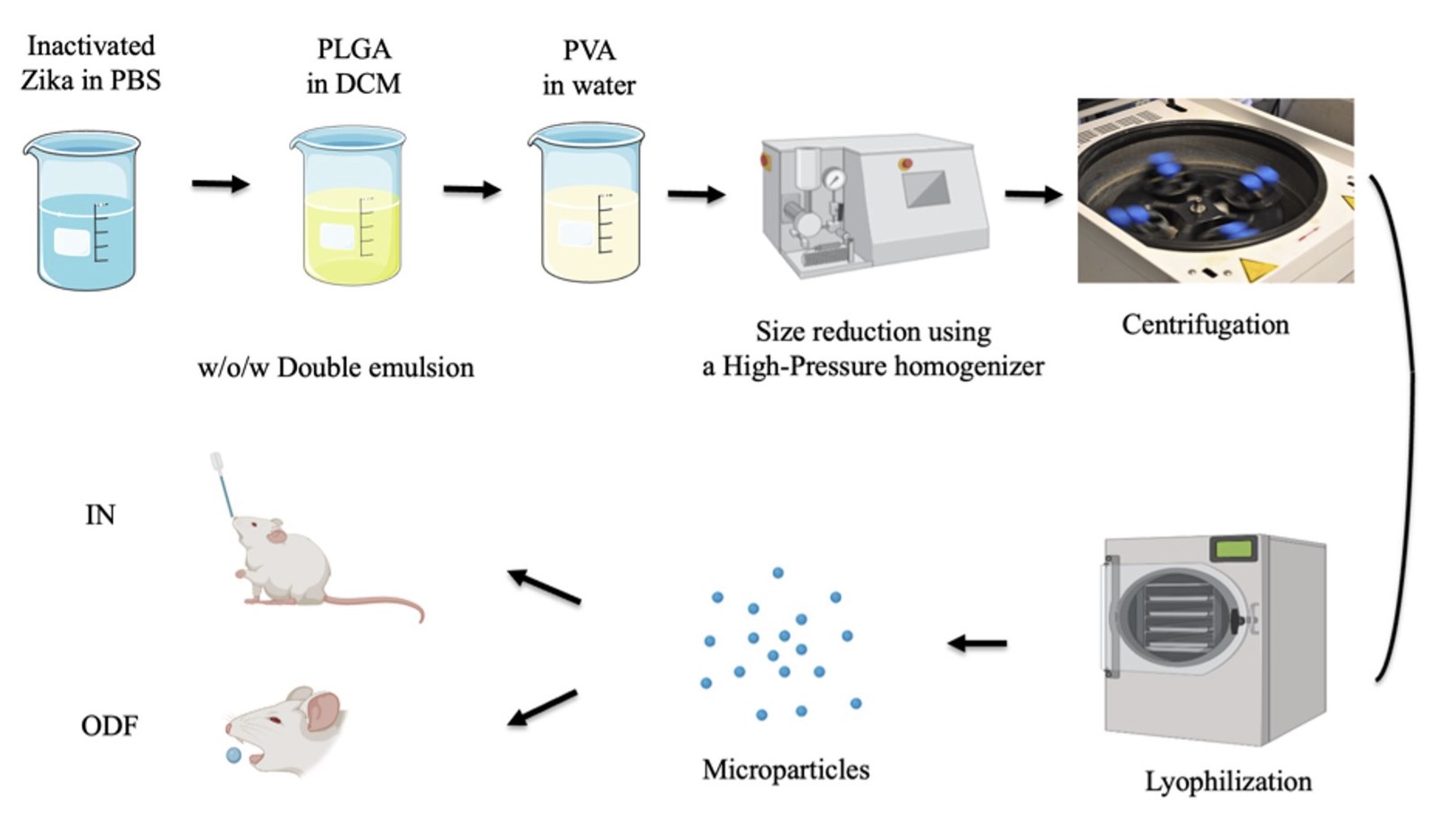 Figure 1: Formulation of microparticles by the double emulsion evaporation method.
Figure 1: Formulation of microparticles by the double emulsion evaporation method. 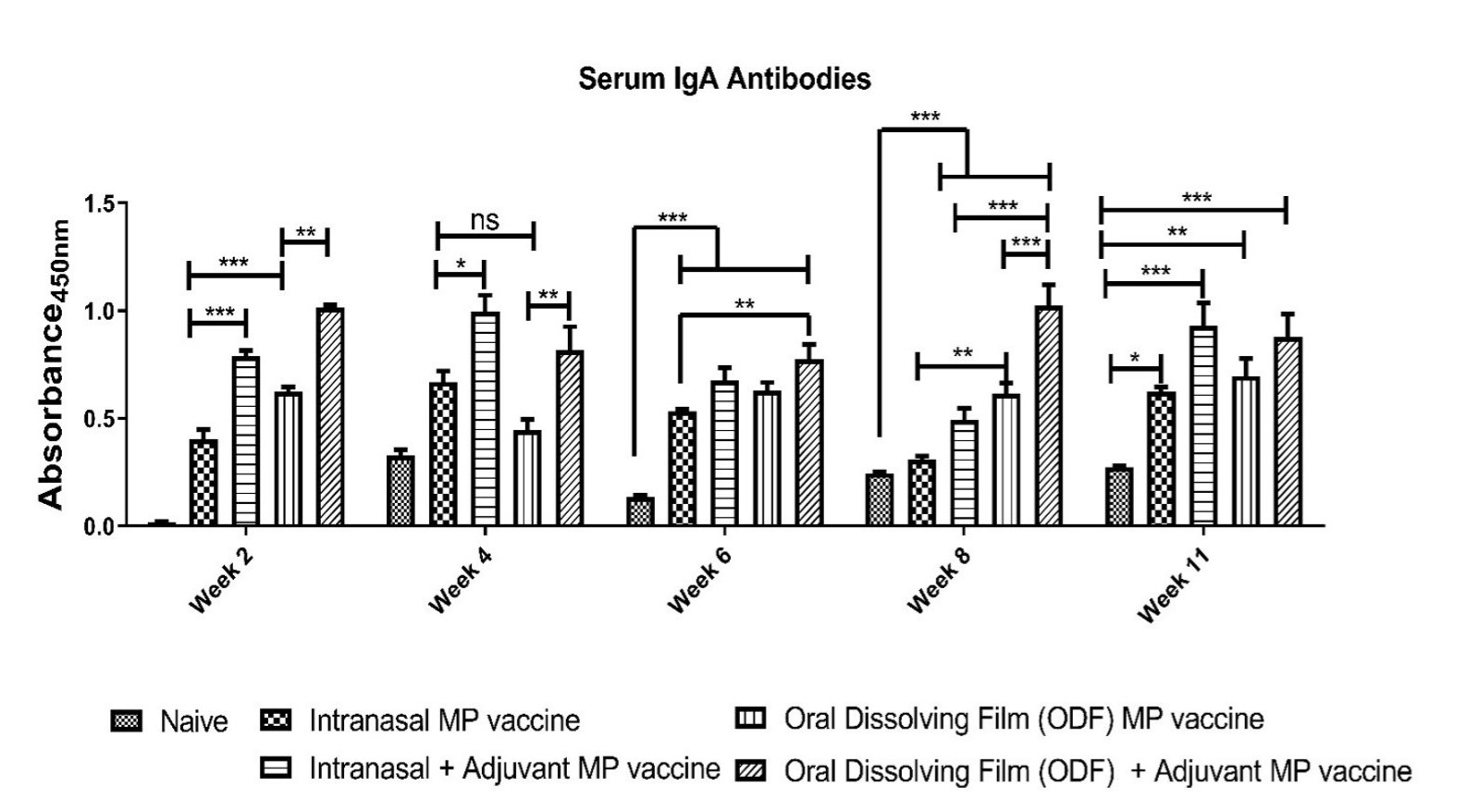 Figure 2: Zika virus-specific secretory IgA antibodies. p > 0.05 (ns, non-significant), p ≤ 0.05 (*), p ≤ 0.01 (**), p ≤ 0.001 (***), and p ≤ 0.0001 (****). In all experiments, a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Figure 2: Zika virus-specific secretory IgA antibodies. p > 0.05 (ns, non-significant), p ≤ 0.05 (*), p ≤ 0.01 (**), p ≤ 0.001 (***), and p ≤ 0.0001 (****). In all experiments, a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. 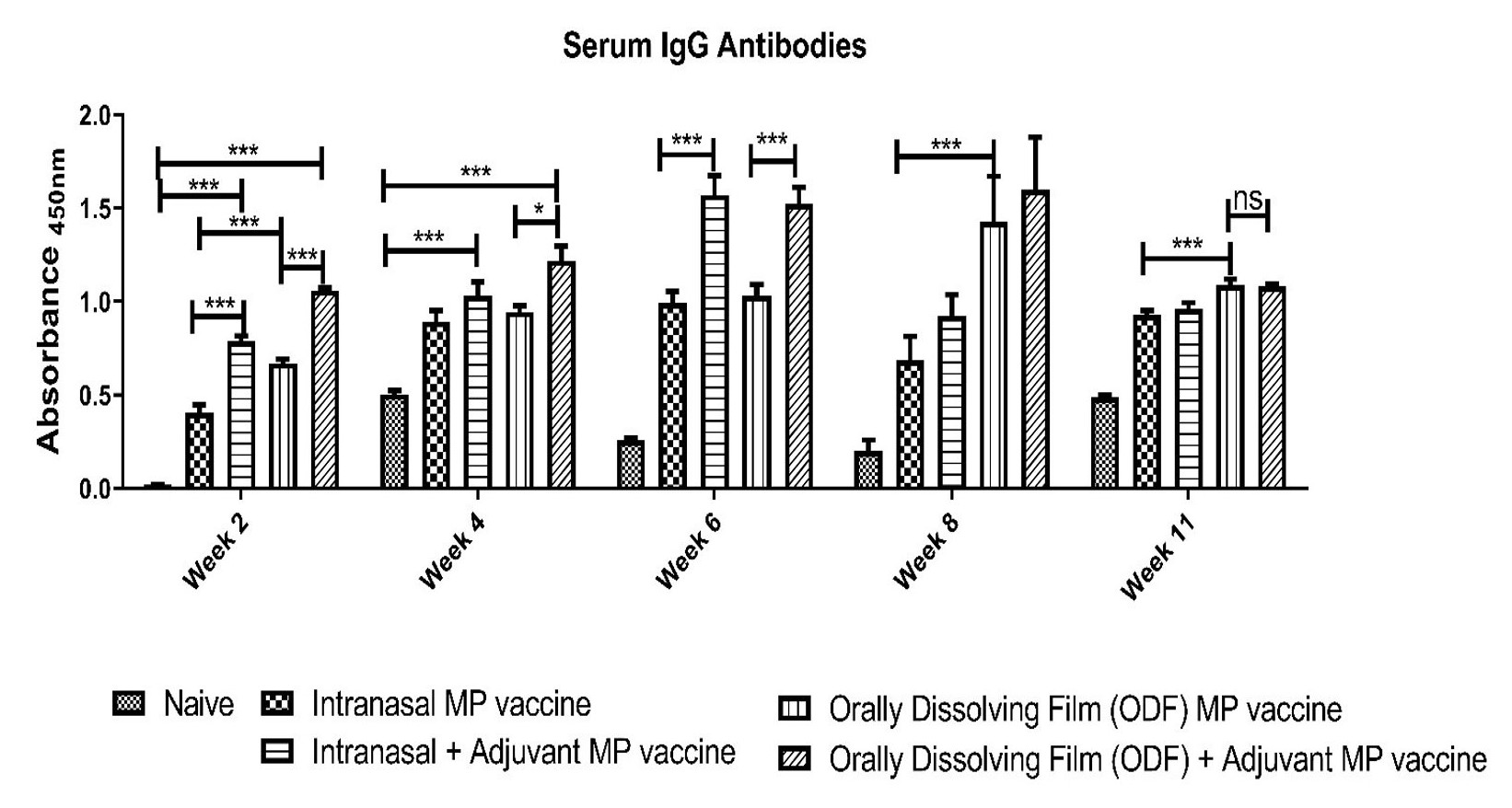 Figure 3: Zika virus-specific IgG antibodies. p > 0.05 (ns, non-significant), p ≤ 0.05 (*), p ≤ 0.01 (**), p ≤ 0.001 (***), and p ≤ 0.0001 (****). In all experiments, a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Figure 3: Zika virus-specific IgG antibodies. p > 0.05 (ns, non-significant), p ≤ 0.05 (*), p ≤ 0.01 (**), p ≤ 0.001 (***), and p ≤ 0.0001 (****). In all experiments, a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.