Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Poster Abstract
(T0930-01-03) Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Improved Ocular Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
9:30 AM - 10:30 AM ET

Suraj Fanse, MS (he/him/his)
PhD Graduate Student
University of Connecticut
Storrs Mansfield, Connecticut, United States
Suraj Fanse, MS (he/him/his)
PhD Graduate Student
University of Connecticut
Storrs Mansfield, Connecticut, United States- KM
Kellen Maurus, BS (he/him/his)
University of Connecticut
Storrs, Connecticut, United States - SB
Saurabh Bhorkade, MS (he/him/his)
University of Connecticut
Storrs, Connecticut, United States 
Diane J. Burgess, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Distinguished Professor
University of Connecticut
Storrs, Connecticut, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Cataract is the leading cause of vision loss among people worldwide. Loteprednol etabonate (LE) is a hydrophobic corticosteroid approved for topical management of inflammation and post-operative pain in the eye following cataract surgery. Unfortunately, the existing marketed formulations (ophthalmic suspensions and ointment) exhibit short pre-corneal residence, high drug loss, ocular irritation, and poor bioavailability which necessitates frequent drug administration (up to 8 times a day) and compromises patient compliance. Thus, the key objective of the present work was to develop a novel nanoparticulate-based delivery to improve the treatment efficacy by enhancing the transcorneal permeation and bioavailability of LE. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) are a new generation of lipid nanoparticles which comprise of a solid lipid matrix incorporated with a liquid lipid to generate crystal imperfections in the matrix. This facilitates higher drug loading, minimal drug expulsion over storage, controlled release, and improved bioavailability1. The current research aimed at formulation development and QbD-based optimization of topical loteprednol etabonate nanostructured lipid carrier (LE-NLC) formulations; and to assess the impact of NLCs loaded with ocular permeation enhancers and in situ gelling agents.
Methods: Screening of various excipients (solid lipid, liquid lipid, and surfactants) was carried out based on the miscibility and compatibility studies with LE (solubility, DSC, and particle size). LE-NLCs were prepared using melt emulsification and hot homogenization. A Box-Behnken Design response surface methodology (DoE) was utilized for formulation optimization. Three formulations (F1, F2, and F3) were prepared based on the design space obtained using the DoE study. F1 comprised of LE-loaded NLCs, F2 contained transcutol (permeation enhancer with rapidly reversible changes in corneal epithelial tissues) in LE-NLCs, and F3 contained gellan gum (ion-sensitive in situ gelling polymer) in LE-NLCs. The formulation compositions are detailed in Fig. 1A. Particle size, zeta potential, and PDI were measured using dynamic light scattering (DLS). Drug loading and encapsulation efficiency were determined using UPLC. The microstructure and molecular properties were characterized via TEM, confocal laser scanning microscopy, PLM, DSC, and TGA. Rheological behavior was investigated using ARES-G2 rheometer. In vitro drug release testing method was developed using a USP IV apparatus. Cell cytotoxicity, cellular uptake and uptake mechanisms were investigated using human corneal epithelial cells. Trans-corneal permeation studies were performed using rabbit cornea.
Results: Gelucire 44/14 and Miglyol 829 had the highest miscibility with the drug, lowest particle size of NLCs, and good stability. Thus, they were selected for the optimization of NLCs. The multifactorial interactions between %lipids, %surfactants, homogenization speed and time were investigated using DoE and a robust design space was identified (Fig.1B). Formulation F3 showed higher particle size, lower zeta potential, and a slightly higher PDI due to the formation of gellan gum corona on the surface of NLCs. All three formulations showed good stability for 3 weeks, had acceptable pH and osmolarity. F3 showed gelation in the presence of artificial tear fluid within 40 seconds. The absence of melting endotherm for LTP in the formulations (via DSC) suggests that the drug exists in an amorphous or molecularly dispersed state in the lipid matrix. All three formulations had high storage modulus over a broad range of oscillatory stress. Formulation F3 had the highest viscosity due to the presence of a gelling polymer. The pseudoplastic behavior of all NLCs was investigated using the Power law (Ostwald-de-Waele equation) modeling and the significantly lower viscosities ( < 1 Pa.s) at a shear rate of 103 1/s provides confidence that the NLCs will not cause discomfort to the eye on application. In vitro drug release profiles of all NLCs followed first-order release kinetics. The drug release rates of F1 and F2 were higher while F3 showed a lower release rate (Fig.2B). Formulation F2 had the highest transcorneal flux and permeability (Peff) through rabbit eye cornea. A good in vitro-ex vivo correlation was established (Fig.2E). Cell cytotoxicity studies exhibited >90% viability of human corneal epithelial cells for all the formulations (Fig.3A). Quantitative cellular uptake studies revealed the following rank order of decreasing rate of uptake: F2 > F1 >F3 (Fig.3B) which was also corroborated using confocal imaging. Overall, F3 showed higher retention to corneal epithelium but slower drug release rate as well as cellular uptake. The formulations did not show vascular lysis or coagulation (compared to positive control) as evident from the chorioallantoic membrane test (Fig.3D). The inhibition study suggested that the uptake mechanism was energy-dependent and primarily occurred via clathrin-mediated pathway.
Conclusion: Correlations between the critical quality attributes and both the formulation and processing parameters through QbD guide the rational formulation design of NLCs. The approach of using a permeation enhancer with NLCs showed the highest uptake, sustained release, desired particle size and stability compared to traditional nanoformulations and the use of in situ gelling agents. Overall, the present study successfully reports the ocular bioavailability enhancement of LTP providing a promising potential of reducing dosing frequency and improving treatment outcomes.
References: 1. Lakhani P., Patil A., and Majumdar S. Recent advances in topical nano drug delivery systems for the anterior ocular segment. Therapeutic Delivery. 2018, 9(2), 137-153.
Acknowledgements: Funding for this project was made possible by the Pfizer Distinguished Chair in Pharmaceutical Technology fund and the Office of Undergraduate Research at the University of Connecticut.
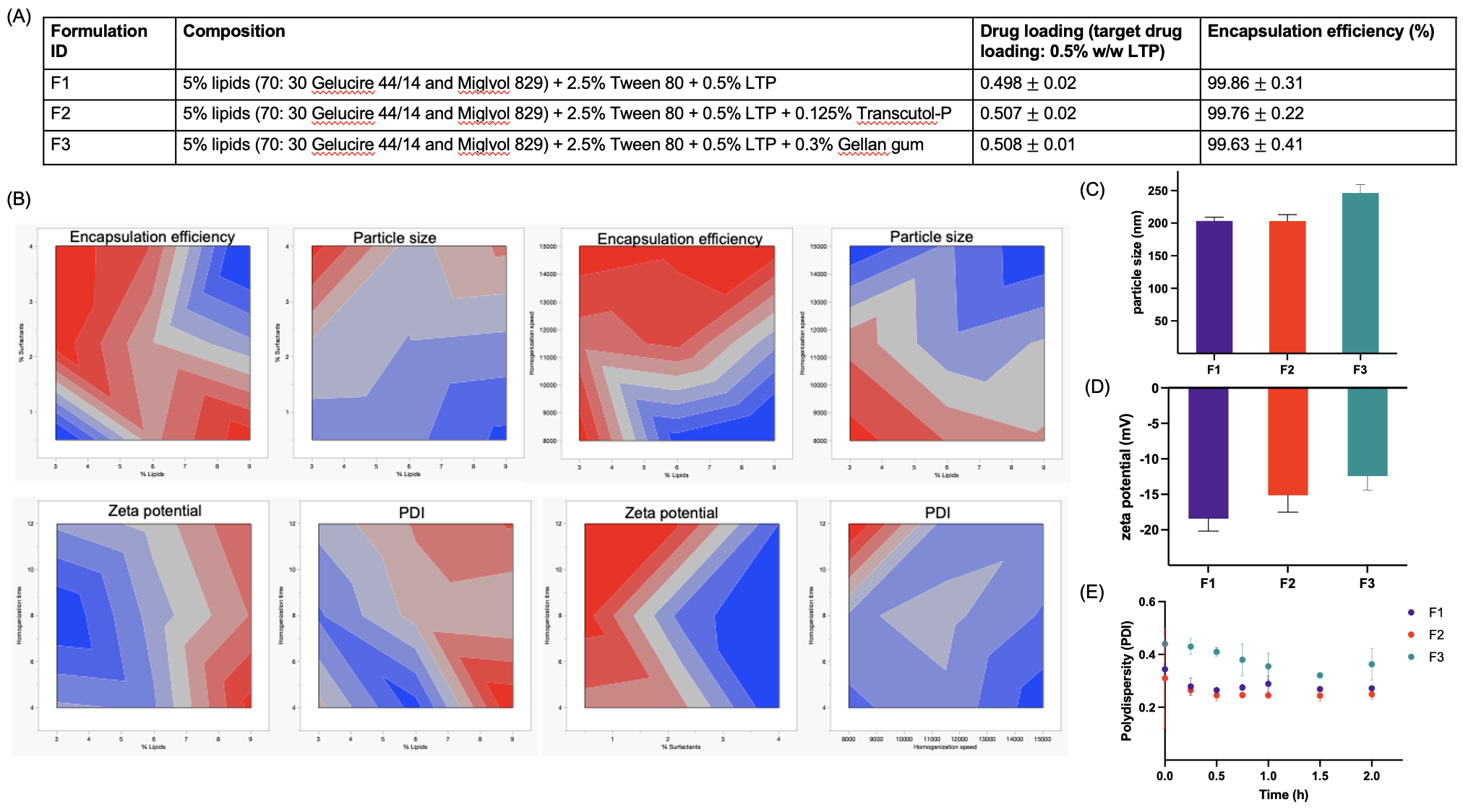 Fig. 1. A) Composition of different NLC formulations, their drug loading and encapsulation efficiency (mean±SD, n=3); B) contour plots for interactions between different dependent and independent, formulation and processing variables; C) hydrodynamic particle size (nm) of NLC formulations (mean±SD, n=3); D) zeta potential (mV) of NLC formulations (mean±SD, n=3); E) polydispersity index (PDI) of various NLC formulations (mean±SD, n=3).
Fig. 1. A) Composition of different NLC formulations, their drug loading and encapsulation efficiency (mean±SD, n=3); B) contour plots for interactions between different dependent and independent, formulation and processing variables; C) hydrodynamic particle size (nm) of NLC formulations (mean±SD, n=3); D) zeta potential (mV) of NLC formulations (mean±SD, n=3); E) polydispersity index (PDI) of various NLC formulations (mean±SD, n=3).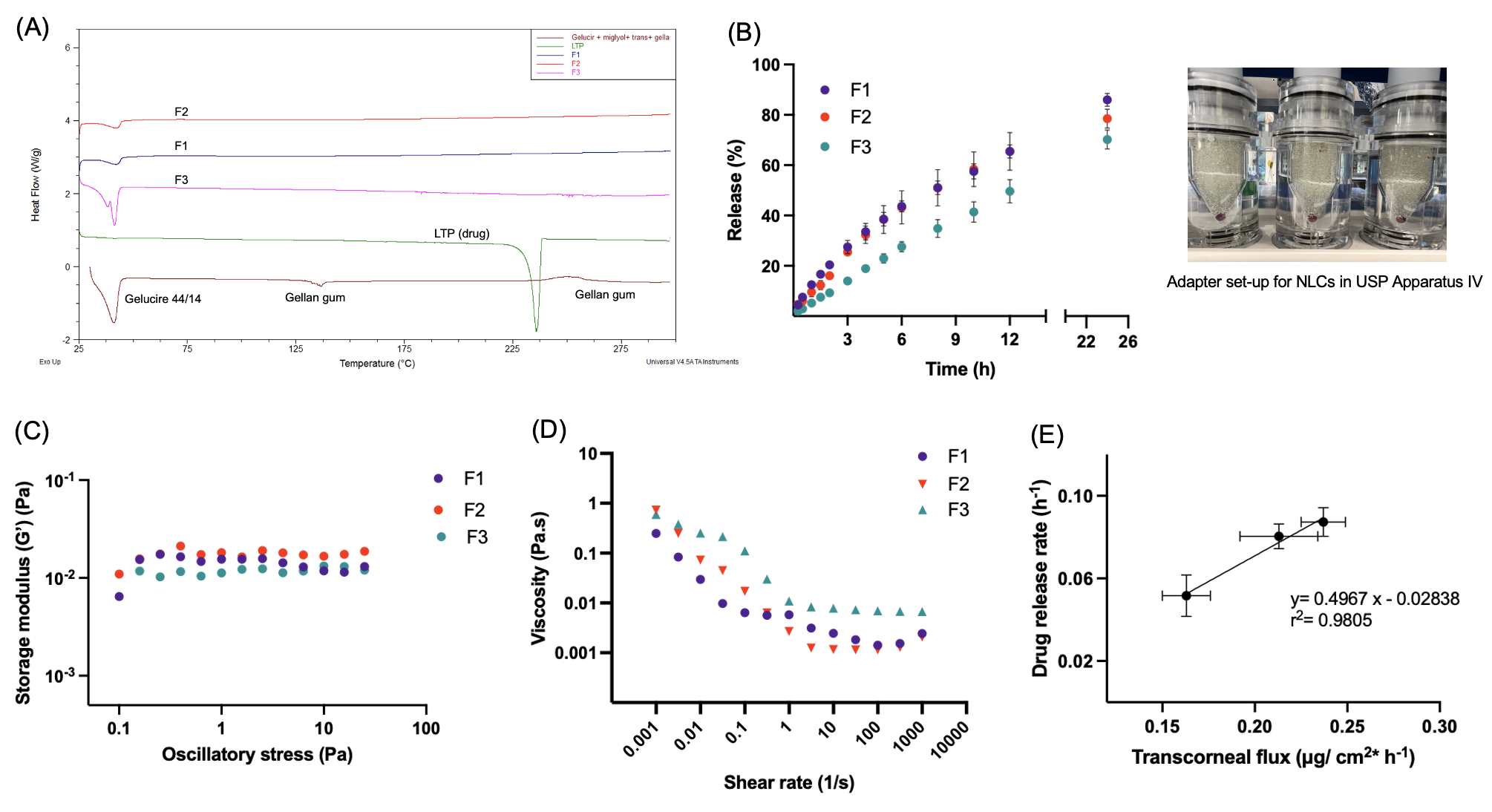 Fig. 2. A) Representative DSC thermograms of the prepared NLC formulations, drug, lipid mixture and polymer; B) in vitro drug release profiles of formulations using USP IV apparatus (formulations on a cellulose membrane holder sandwiched within glass beads along with a 50 nm PTFE filter in the filter head) (mean±SD, n=3); C) storage moduli (G’, Pa) of the NLC formulations as a function of oscillatory stress (mean±SD, n=3); D ) viscosity (η, Pa.s) of the NLC formulations as a function of shear rate (mean±SD, n=3); and E) in vitro-ex vivo correlation between drug release and transcorneal flux (mean±SD, n=3).
Fig. 2. A) Representative DSC thermograms of the prepared NLC formulations, drug, lipid mixture and polymer; B) in vitro drug release profiles of formulations using USP IV apparatus (formulations on a cellulose membrane holder sandwiched within glass beads along with a 50 nm PTFE filter in the filter head) (mean±SD, n=3); C) storage moduli (G’, Pa) of the NLC formulations as a function of oscillatory stress (mean±SD, n=3); D ) viscosity (η, Pa.s) of the NLC formulations as a function of shear rate (mean±SD, n=3); and E) in vitro-ex vivo correlation between drug release and transcorneal flux (mean±SD, n=3). 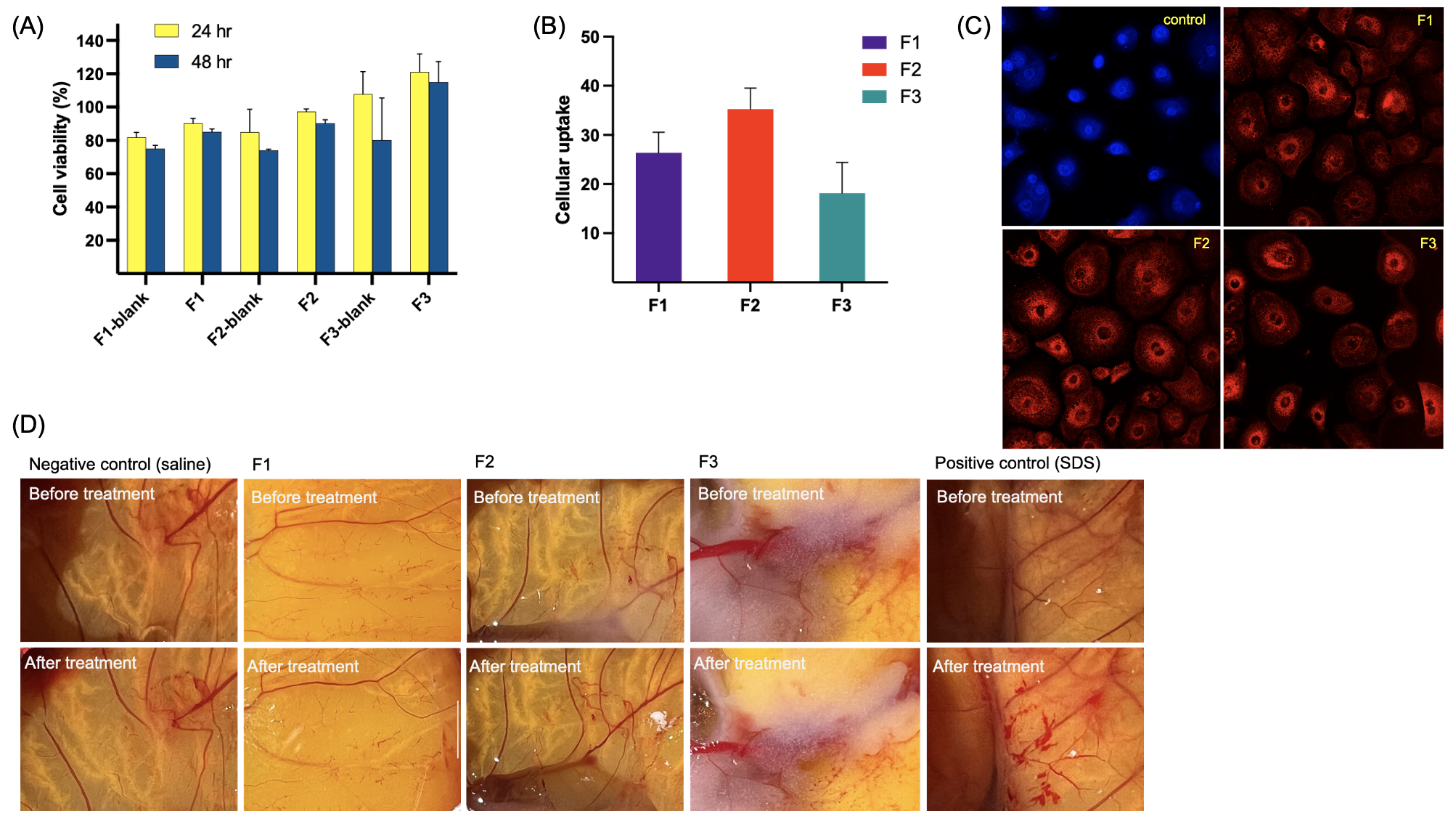 Fig. 3. A) Cell cytotoxicity study represented as %cell viability with respect to untreated cells determined using the CCK8 test at 24h and 48h incubation (mean±SD, n=6); B) quantitative cellular uptake studies using Nile red as the fluorescence marker determined using a fluorescence plate reader (incubation for 4h) (mean±SD, n=6); C) qualitative cellular uptake imaging of NLC formulations using confocal laser scanning microscope; and D) representative images of the ocular irritation test using hen’s egg-chorioallantoic membrane test for all the NLC formulations, negative control (saline), and positive control (SDS).
Fig. 3. A) Cell cytotoxicity study represented as %cell viability with respect to untreated cells determined using the CCK8 test at 24h and 48h incubation (mean±SD, n=6); B) quantitative cellular uptake studies using Nile red as the fluorescence marker determined using a fluorescence plate reader (incubation for 4h) (mean±SD, n=6); C) qualitative cellular uptake imaging of NLC formulations using confocal laser scanning microscope; and D) representative images of the ocular irritation test using hen’s egg-chorioallantoic membrane test for all the NLC formulations, negative control (saline), and positive control (SDS).