Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(W1230-03-20) Development of a Novel, Semi-mechanistic In Vitro Dissolution Model to Inform Physiology-Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling Frameworks
Wednesday, October 25, 2023
12:30 PM - 1:30 PM ET
- PV
Paul Vrenken, M.S. (he/him/his)
PhD candidate Systems Pharmacology
Bayer AG
Leverkusen, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany - PV
Paul Vrenken, M.S. (he/him/his)
PhD candidate Systems Pharmacology
Bayer AG
Leverkusen, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany 
Maria Vertzoni, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Associate Professor
National and Kapodistrian University of Athens
Zografou, Attiki, Greece- SF
Sebastian Frechen, Ph.D. (he/him/his)
Bayer AG
Leverkusen, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany - AD
Andre Dallmann, Ph.D. (he/him/his)
Bayer AG
Loos, Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: To develop and assess a novel, semi-mechanistic dissolution model describing the in vitro dissolution kinetics of poorly soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) formulated as immediate release formulations using the Open Systems Pharmacology (OSP) suite.
Methods: A modular approach to PBBM was taken by implementing a versatile Noyes-Whitney-type dissolution equation into MoBi® (part of the OSP suite, version 11.1), where the sub-models describing solubility and dissolution can be applied based on physicochemical properties of the API, the formulation type and available in vitro dissolution data. The aqueous solubility-pH profile for ionizable APIs is described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation where the effect of medium pH on solubility is modulated by the solubility gain per charge (SG). This parameter is fitted to aqueous solubility data measured across different pH values. Furthermore, ionizable APIs can significantly alter the pH at the particle surface from the bulk fluid pH during dissolution. This effect was explored by calculating the surface pH and compare the predicted dissolution profiles with using the bulk pH [1]. The developed dissolution equation explicitly models two separate flows for surfactant bound (SDS or bile salt micelles) and unbound API from the dissolving drug particle surface to the bulk fluid [2]. Partitioning into bile salt micelles is accounted for by a semi-mechanistic model accounting for bile salt concentration and medium pH [3, 4]. For ionizable APIs, separate partition coefficients (Km:w,neutral and Km:w,ionized) can be predicted based on lipophilicity, or can be informed using measured solubilities in media containing bile salts (e.g., FaSSIF and FeSSIF). Micelle diffusion coefficients are calculated based on the respective radius of the API or bile salt micelles using the Stokes-Einstein equation. The diffusion layer thickness (h) in the USP2 apparatus for bound and unbound API are calculated using a previously published semi-mechanistic model that considers the effect of medium volume, viscosity, and agitation rate on h [1]. Together, the described models are used to fit a formulation-specific product-particle size distribution (P-PSD) to one in vitro dissolution assay which is subsequently and confirmed or rejected using dissolution assays where the conditions differ with respect to hydrodynamics or buffer properties [1]. The ability of the developed dissolution model to extrapolate to different in vitro dissolution conditions was explored using two formulations of poorly soluble compounds, Acalabrutinib (Calquence®) and Glibenclamide (Euglucon N®) [see Table 1].
Results: For acalabrutinib, using the bulk pH or surface pH model at a medium pH of 6.8 leads to comparable simulation results. The effects of increasing agitation rate and adding surfactant (0.2 and 0.5% SDS) on dissolution rate were captured (Fig. 1 A-B). At a medium with pH 4.5, the prediction accuracy, as indicated by the average and absolute average fold error (AFE and AAFE, respectively), was higher when using the surface pH than bulk pH in the dissolution model (AFE: 1.31 vs. 2.96; AAFE: 1.42 vs. 2.96). When acidity increased further, instant dissolution was predicted by the bulk pH model, while the surface pH model predicted dissolution curves that matched the observed data closely (Fig. 1 C-E). At pH 1, the observed dissolution data were not sufficiently informative to assess the advantage of the surface over the bulk pH model (Fig. 1 F). For glibenclamide, predictions were deemed adequate in pH 6 phosphate buffer (AFE: 0.90; AAFE: 1.29) and accurate in FaSSIF versions 1-3 (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: A novel in vitro dissolution model was implemented in OSP and evaluated with two case studies. The results show that the semi-mechanistic dissolution model can adequately predict in vitro dissolution profiles when the medium and/or hydrodynamic conditions are altered. For acalabrutinib, predictions obtained from the surface pH model were accurate. However, at pH 1, no conclusions can be drawn due to missing sampling time points within the first 10 minutes. In this case, the limiting step might not be the dissolution rate but e.g., capsule rupture or particle deaggregation. Additional case studies are needed to examine the performance of the presented model. Once thoroughly evaluated, this model can be seamlessly integrated into the whole-body PBPK framework in PK-Sim®. Such a physiologically-based biopharmaceutics model (PBBM) might then be used to predict drug dissolution and absorption in vivo.
References: [1] Pepin et al., Pharm. Sci., 111 (2022)
[2] Gamsiz et al., Pharm. Res., 27 (2010)
[3] Sugano, Exp. Opinion drug Met. & Tox., 5 (2009)
[4] Pathak et al., Mol. Pharm., 14 (2017)
[5] Löbenberg et al., Pharm. Res., 17 (2000)
[6] Klumpp et al., Eur J Pharm Sci, 142 (2020)
Acknowledgements: This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No. 955756. Conflict of Interest - A.D. and S.F. use Open Systems Pharmacology software, tools, and models in their professional roles. S.F. is a member of the Open Systems Pharmacology Sounding Board. The other authors declared no competing interests for this work.
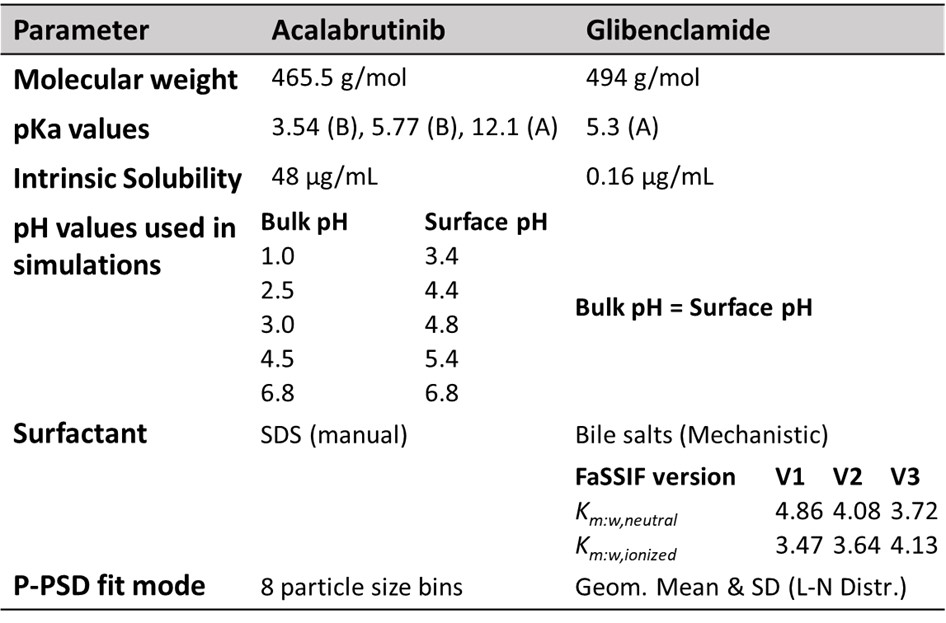 Table 1. Overview of input parameters used for model APIs acalabrutinib [1] and glibenclamide [5, 6]
Table 1. Overview of input parameters used for model APIs acalabrutinib [1] and glibenclamide [5, 6]Abbreviations: A: acid; B: base; FaSSIF: Fasted state simulated intestinal fluid; L-N: lognormal; P-PSD: product particle size distribution; SD: standard deviation; SDS: sodium dodecyl sulfate
.jpg) Figure 1. Acalabrutinib (Calquence® 100 mg capsules) model predictions in various dissolution conditions in the USP2 apparatus, using bulk pH (dashed lines, AFE: 1.40, AAFE: 1.40) or surface pH (solid lines, AFE: 1.01, AAFE: 1.13) [1]
Figure 1. Acalabrutinib (Calquence® 100 mg capsules) model predictions in various dissolution conditions in the USP2 apparatus, using bulk pH (dashed lines, AFE: 1.40, AAFE: 1.40) or surface pH (solid lines, AFE: 1.01, AAFE: 1.13) [1]Abbreviations: RPM: rounds per minute; SDS: sodium dodecyl sulfate; AFE: average fold error; AAFE: absolute average fold error
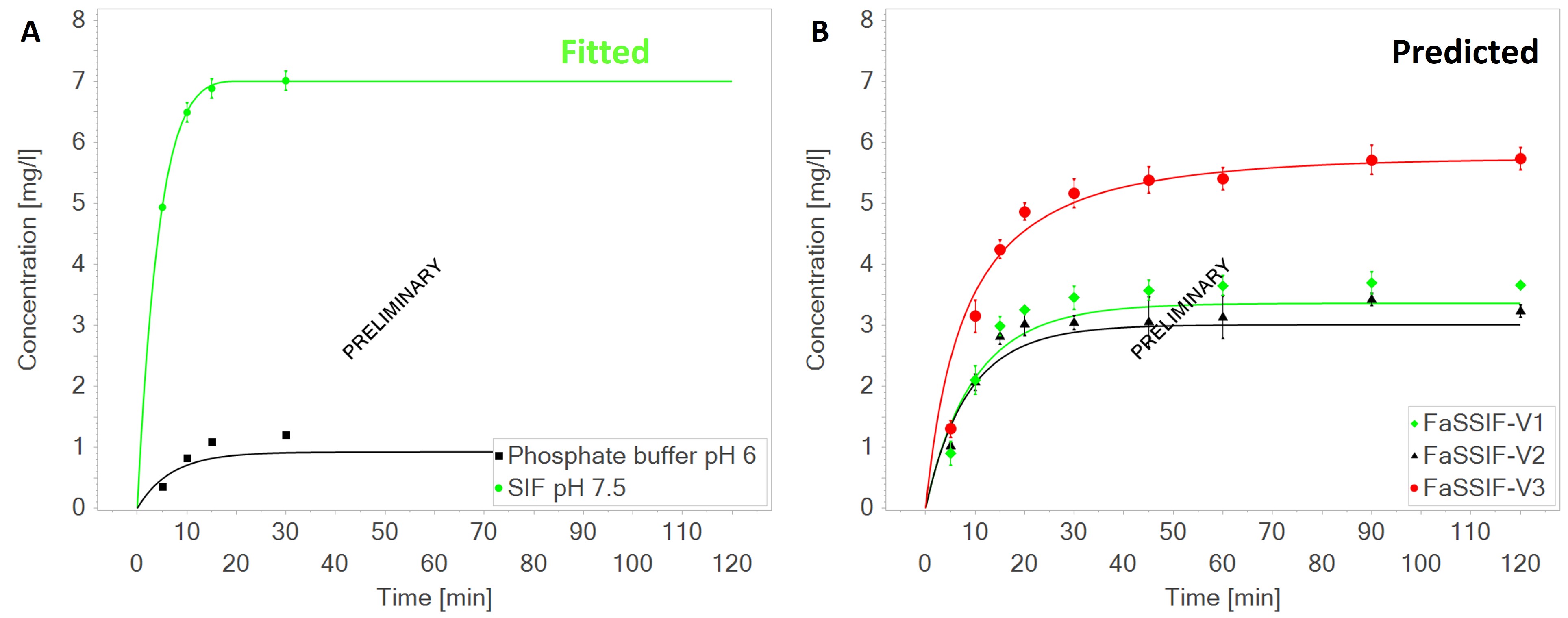 Figure 2. Glibenclamide (Euglucon N® 3.5 mg tablets) dissolution profiles in various media in the USP2 apparatus (500 mL, 75 RPM), with in A: fitted dissolution curve in SIF pH 7.5 (light green) and predicted dissolution in phosphate buffer pH 6 (black, AFE: 0.90, AAFE: 1.29) [5], and in B: Predicted dissolution curves in FaSSIF-V1 (light green, AFE: 0.97, AAFE: 1.13), FaSSIF-V2 (black, AFE: 0.97, AAFE: 1.10) and FaSSIF-V3 (red, AFE: 1.04, AAFE: 1.08) [6]
Figure 2. Glibenclamide (Euglucon N® 3.5 mg tablets) dissolution profiles in various media in the USP2 apparatus (500 mL, 75 RPM), with in A: fitted dissolution curve in SIF pH 7.5 (light green) and predicted dissolution in phosphate buffer pH 6 (black, AFE: 0.90, AAFE: 1.29) [5], and in B: Predicted dissolution curves in FaSSIF-V1 (light green, AFE: 0.97, AAFE: 1.13), FaSSIF-V2 (black, AFE: 0.97, AAFE: 1.10) and FaSSIF-V3 (red, AFE: 1.04, AAFE: 1.08) [6]Abbreviations: RPM: rounds per minute; SIF: simulated intestinal fluid; AFE: average fold error; AAFE: absolute average fold error; FaSSIF: (fasted state) simulated intestinal fluid; V1-3: version one to three.
