Formulation and Delivery - Biomolecular
Category: Poster Abstract
(T1330-02-12) Novel Bio-Active Peroxisomal Proliferator Activating Receptor Gamma (PPARγ) Hydrogel for Periodontitis Management
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
1:30 PM - 2:30 PM ET
- XK
Xuejia Kang, MS (she/her/hers)
Auburn University
Auburn, Alabama, United States - XK
Xuejia Kang, MS (she/her/hers)
Auburn University
Auburn, Alabama, United States - JR
Jayachandra Ramapuram, Ph.D.
Auburn University
auburn, Alabama, United States - RA
Raj Amin, Ph.D.
Auburn University
auburn, Alabama, United States - JS
Jianzhong Shen, Ph.D.
Auburn University
Auburn, Alabama, United States - MA
Manjusha Annaji, MS
PhD student
Auburn University
auburn, Alabama, United States - PB
Prorok Barton, Ph.D.
Auburn University
auburn, Alabama, United States - Pc
Pengyu chen, Ph.D.
Auburn University
auburn, Alabama, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that is widespread and can lead to systemic diseases, including cancer (1). Bacteria-accumulated lipopolysaccharides (LPS) activate macrophages as M1 phenotype, resulting in an inflammatory microenvironment that generates inflammatory factors, oxidative stress, matrix metalloproteinase, and alveolar bone dysfunction(2-3). Full agonists of insulin-sensitizing peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ) mitigate the activation of inflammatory macrophages, but they have side effects, such as heart disease(4). To treat periodontitis without these side effects, a novel partial agonist was synthesized, which can be delivered at an effective dose by using a ROS-scavenging viscous hydrogel as a carrier. The hydrogel is designed to address the four pathogenic aspects of the disease and to manage periodontitis effectively. The primary goal of this study is to develop an innovative hydrogel that can treat periodontitis by targeting the above pathogenic factors.
Methods: The novel compound AU9 was encapsulated in a micelle and then incorporated into the hydrogel, in which polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was cross-linked by a ROS-responsive linker TPA via vortex methods. The formulation was characterized using scanning electronic microscopy and rheology assays. To simulate the in-vitro inflammatory microenvironment, Murine macrophage cells RAW 264.7 was treated with Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and the formulation's ability to regulate the interaction of macrophages with alveolar bone cells (osteoclasts and osteoblasts) was studied using transwell co-culture assays. The formulation's effects on the consecutive regeneration of soft tissues were evaluated via detection of matrix metalloproteinase activities. In vivo, a ligature-induced periodontitis mice model was established, and the formulation's efficacy in treating peritonitis was evaluated using computed tomography (CT). Various biochemical assays, including flow cytometry, ELISA, and qPCR were used to determine relevant inflammatory factors (5-6). Bone regeneration-associated markers were determined using biomarker staining kits and solutions.
Results: The working mechanism of the novel hydrogel can be explained through a schematic illustration. This innovative hydrogel has been designed to alleviate inflammatory factors, decrease oxidative stress, and downregulate matrix metalloproteinases, ultimately preventing tooth loss by regenerating periodontal soft and bone tissues (Fig. 1A). The polymer TPA, which contains phenylboronic acid groups, reacts quickly with the alcohol hydroxyl groups of PVA, forming PVA-TPA hydrogels immediately upon mixing (Fig. 1B-C). The hydrogel is loaded with the compound AU9, which downregulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory factors and alleviates oxidative stress, including reactive oxygen species, malondialdehyde (MDA), and nitric oxide levels (Fig. 1E-H). M1 macrophages promote osteoclast activity, which is indicated by elevated tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) activity. However, the AU9 hydrogel inhibits M1 macrophages and promotes M2 macrophages, leading to the downregulation of TRAP activity. LPS-activated M1 macrophages inhibit osteoblast calcium deposition, but the addition of the AU9 hydrogel reverses this trend. The increase of MMPs due to NF-kβ activation is responsible for the degradation of consecutive periodontal soft tissue. However, the decrease of MMP1, MMP3, and MMP9 suggests the potential of the AU9 hydrogel in preventing the impairment of periodontal tissue (Fig. 2). These results were confirmed in in vivo ligature models, where the holes of the ligature-established mice showed damaged holes, bone loss, and an increased CEJ-AB distance in CT results. The relevant inflammatory markers and alveolar bone markers were increased in ligature models but showed a decreasing trend in the AU9 hydrogel treated group. Furthermore, RANKL stimulates osteoclast formation and activity, while OPG acts as a decoy receptor for RANKL in the RANK/RANKL/OPG axis, thus downregulating osteoclast genesis and bone resorption. Ligature mimicking bacterial accumulation increases RANKL while decreasing OPG. However, the AU9 hydrogel reverses the ratio of RANKL and OPG (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: In this study, a local bioactive hydrogel was developed to scavenge ROS and loaded with a novel compound AU9 to alleviate periodontal inflammation. The hydrogel effectively modulated macrophage phenotype and downregulated oxidative stress, mitigating pathogenic factors and promoting periodontal soft and hard tissue regeneration. By targeting macrophages and bone-associated cells such as osteoclasts and osteoblasts, the novel AU9 hydrogel showed great potential as an alternative therapy for chronic periodontitis. Overall, this study highlights the promising therapeutic potential of the innovative AU9-loaded hydrogel for the treatment of periodontal diseases
References: 1. Cardoso, Elsa Maria, Cátia Reis, and Maria Cristina Manzanares-Céspedes. "Chronic periodontitis, inflammatory cytokines, and interrelationship with other chronic diseases." Postgraduate medicine 130.1 (2018): 98-104.
2. Shapouri‐Moghaddam, Abbas, et al. "Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease." Journal of cellular physiology 233.9 (2018): 6425-6440.
3. Usui, Michihiko, et al. "Mechanism of alveolar bone destruction in periodontitis—Periodontal bacteria and inflammation." Japanese Dental Science Review 57 (2021): 201-208.
4. Steinke, Ian, et al. "Selective PPAR-Delta/PPAR-Gamma Activation Improves Cognition in a Model of Alzheimer’s Disease." Cells 12.8 (2023): 1116.
5. Kang, Xuejia, et al. "Diethyldithiocarbamate copper nanoparticle overcomes resistance in cancer therapy without inhibiting P-glycoprotein." Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine 47 (2023): 102620.
6. Kang, Xuejia, et al. "Near-infrared light-triggered activation of pro-drug combination cancer therapy and induction of immunogenic cell death." International Journal of Pharmaceutics 607 (2021): 120972.
Acknowledgements: I would like to thank Dr.Amin and his lab members for the synthesis of the novel compound AU9 and Dr.Jianzhong Shen for the facility support. The contribution of Dr.Huang, Dr.Zhang, Dr.Bart, and their lab members in the animal study is highly appreciated. The mentor of Dr.Jay and Dr.Chen is appreciated. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) MIRA R35GM133795 (P. Chen). The IACUC ID is 2021-3955.
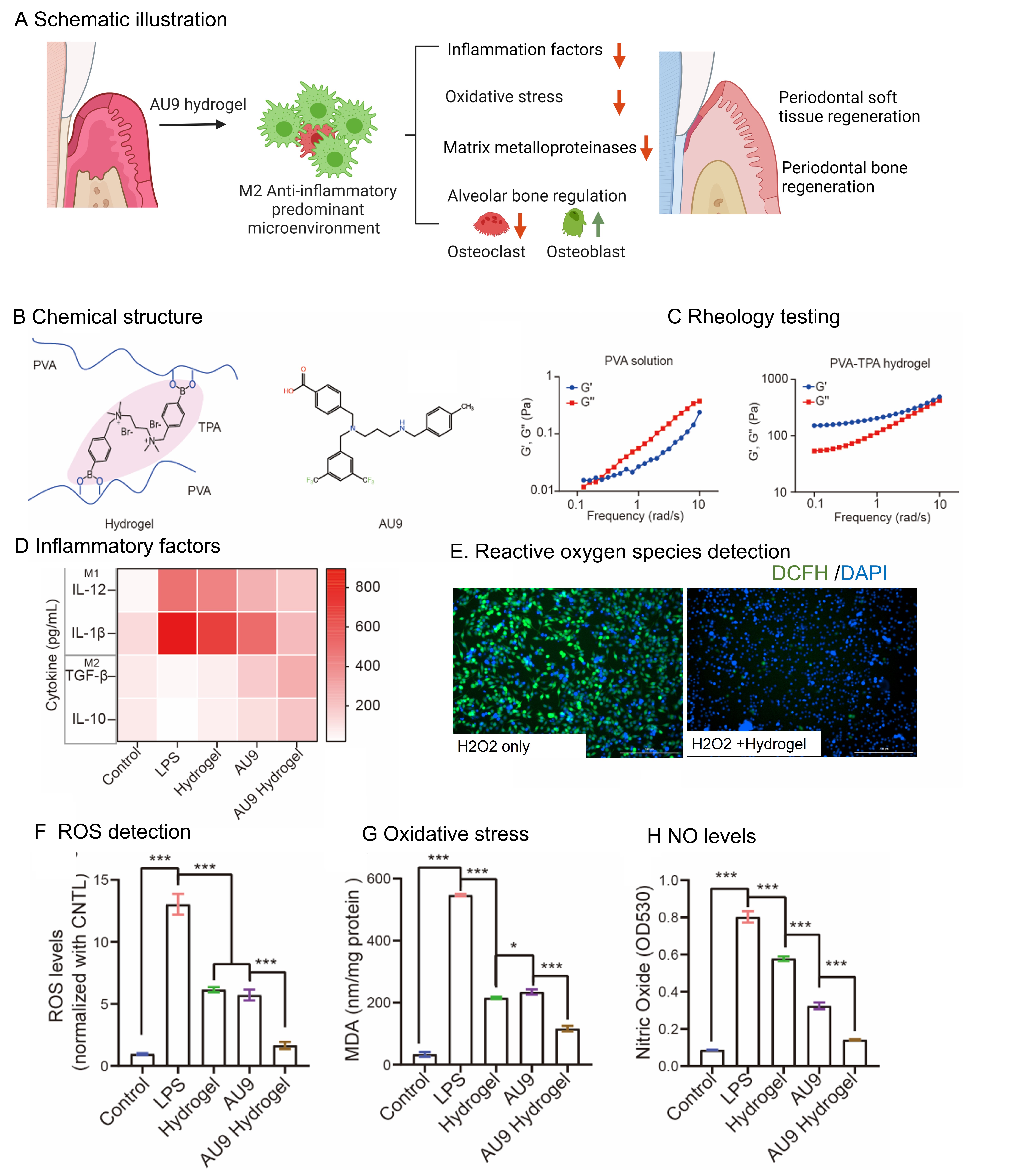 Fig1. (A)schematic of AU9 hydrogel in anti-periodontitis. (B)The chemical structure of hydrogel and AU9. (C) Frequency spectra of G’ and G’’ moduli of the PVA solution and hydrogel. (D) The ROS scavenging ability of hydrogel. DCFH for ROS detection green. DAPI for nuclear-Blue (E)&(F) Effective inhibition of LPS-induced ROS production and MDA levels. (G) AU9 hydrogel inhibits nitric oxide.
Fig1. (A)schematic of AU9 hydrogel in anti-periodontitis. (B)The chemical structure of hydrogel and AU9. (C) Frequency spectra of G’ and G’’ moduli of the PVA solution and hydrogel. (D) The ROS scavenging ability of hydrogel. DCFH for ROS detection green. DAPI for nuclear-Blue (E)&(F) Effective inhibition of LPS-induced ROS production and MDA levels. (G) AU9 hydrogel inhibits nitric oxide. .jpg) Fig2. AU9 regulates the interaction of macrophage, osteoclast, and osteoblast in the periodontal microenvironment. (A)Schematic illustration of the interaction of macrophage and bone cells (osteoclast and osteoblast) ;(B) Cellular pathogenesis in periodontitis: Firstly, LPS activates NF-Kb, thereby activating M1 macrophage, promoting osteoclast (OC), inhibiting osteoblast (OB). Secondly, reactive oxygen species (ROS) also facilitate the activation of NF-kB and the activated M1 further aggravates the ROS cascade. Thirdly, the matrix metalloproteinases generated by M1 degrade the periodontal soft tissues; AU9 hydrogel promotes beneficial cell markers: anti-inflammatory M2 marker (D) and osteoblast marker (F); AU9 hydrogel inhibits the NF-kB activation (G), thus inhibiting M1 markers (C), osteoclast (E), and increased matrix metalloproteinases MMPs(H-J).
Fig2. AU9 regulates the interaction of macrophage, osteoclast, and osteoblast in the periodontal microenvironment. (A)Schematic illustration of the interaction of macrophage and bone cells (osteoclast and osteoblast) ;(B) Cellular pathogenesis in periodontitis: Firstly, LPS activates NF-Kb, thereby activating M1 macrophage, promoting osteoclast (OC), inhibiting osteoblast (OB). Secondly, reactive oxygen species (ROS) also facilitate the activation of NF-kB and the activated M1 further aggravates the ROS cascade. Thirdly, the matrix metalloproteinases generated by M1 degrade the periodontal soft tissues; AU9 hydrogel promotes beneficial cell markers: anti-inflammatory M2 marker (D) and osteoblast marker (F); AU9 hydrogel inhibits the NF-kB activation (G), thus inhibiting M1 markers (C), osteoclast (E), and increased matrix metalloproteinases MMPs(H-J).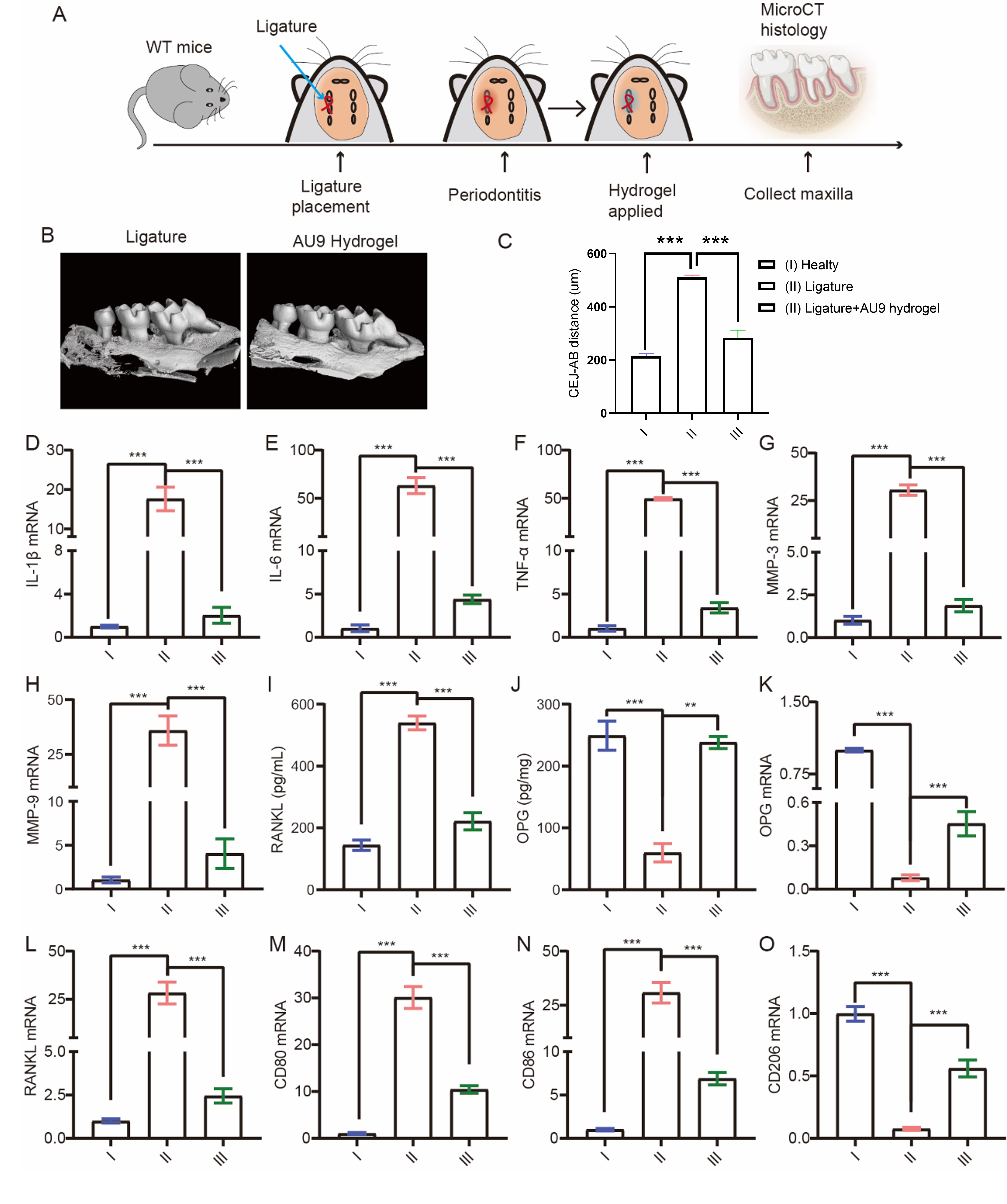 Figure 3. Anti-periodontitis effects of AU9 hydrogel in vivo. (A) Illustration of treatment.AU9 hydrogel inhibits the tooth loss determined by the CT picture (B) and (C) the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) to alveolar bone crest (ABC) distance of mice tooth. AU9-hydrogel inhibits the ligature-induced inflammatory factors(D-F); AU9-hydrogel inhibits the ligature-induced soft tissue degradation markers MMPs genes(G-H); AU9-hydrogel inhibits the ligature-induced osteoclast marker (I &L) and promotes (J&K) osteoblast marker. AU9-hydrogel inhibits the ligature-induced proinflammatory M1 macrophage markers(M-N) and improves anti-inflammatory M2 markers(O) in mice periodontal models.
Figure 3. Anti-periodontitis effects of AU9 hydrogel in vivo. (A) Illustration of treatment.AU9 hydrogel inhibits the tooth loss determined by the CT picture (B) and (C) the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) to alveolar bone crest (ABC) distance of mice tooth. AU9-hydrogel inhibits the ligature-induced inflammatory factors(D-F); AU9-hydrogel inhibits the ligature-induced soft tissue degradation markers MMPs genes(G-H); AU9-hydrogel inhibits the ligature-induced osteoclast marker (I &L) and promotes (J&K) osteoblast marker. AU9-hydrogel inhibits the ligature-induced proinflammatory M1 macrophage markers(M-N) and improves anti-inflammatory M2 markers(O) in mice periodontal models.