Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Poster Abstract
(M1230-11-72) Encapsulation of Zidovudine via Spray-Drying for Taste-Masking for Incorporation into an Orally Dispersible Film
Monday, October 23, 2023
12:30 PM - 1:30 PM ET

Mikayla M. Smith, MS (she/her/hers)
Graduate Research Assistant
University of Kansas
Lawrence, Kansas, United States
Mikayla M. Smith, MS (she/her/hers)
Graduate Research Assistant
University of Kansas
Lawrence, Kansas, United States- MH
Michael J. Hageman, Ph.D.
University of Kansas
Lawrence, Kansas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: One in three children around the world infected with HIV perinatally will die before their first birthday if they do not receive any treatment.1 For this reason, adherence and sufficient access to HIV prophylactic treatment for infants and children is a critical matter. Our purpose is to increase adherence to zidovudine (ZDV) and other anti-retroviral agents used to prevent perinatal transmission of HIV from mother to infant by overcoming the extremely bitter taste of ZDV through polymeric encapsulation. Additionally, we plan to incorporate our formulation into much more discreet packaging, by including the formulation in an orally dispersible film (ODF) as opposed to the large, cumbersome bottles the current liquid syrup form of ZDV is packaged in.
Methods: Encapsulation of ZDV was done by spray drying a suspension of ZDV in a polymer solution. A suspension is necessary for encapsulation, as it is only the soluble components of the solution, i.e. polymer, which will be atomized by the atomizing nozzle of the spray dryer. Therefore, the atomized polymer particles will be able to coat the insoluble, non-atomized ZDV particles. An encapsulation efficiency study was performed on the resulting spray-dried material. A novel oral dissolution apparatus was adapted from Thi et al., since accurate in vitro oral dissolution apparatuses have not been well established.2 This model allowed for small volume (2.4 mL) and controlled flow-through, simulating the flow of saliva in the mouth (1 mL/min). Additionally, simulated salivary fluid (SSF) at pH 7.0 was used as the chosen medium for in vitro oral release studies. Finally, in vitro gastric dissolution studies were performed to ensure enough ZDV was released in the gastric environment.
Results: Using the taste recognition threshold (TRT) for ZDV (1.89 mM or 4.3% released at 5 min) reported by Schiffman et al. as the benchmark for taste masking, we determined that the best encapsulating polymer for our encapsulated ZDV (eZDV) would be a combination of ethylcellulose (EC), a nonionic polymer, and Eudragit E PO (EPO), a cationic polymer.3 The formulation containing both of these polymers at a ratio of 1:4 (EC:EPO) was able to create a synergistic effect and reduce the percent release of ZDV in SSF to only 1.4x greater than the acceptable percent release using the TRT. The impact of EC:EPO ratio and drug load on ZDV release were explored, and it was discovered that slightly decreasing the ratio of EC:EPO to approximately 1:7 had no impact on ZDV release. However, maintaining the ratio of EC:EPO while increasing the drug load from 75% to 80% w/w resulted in miniscule increases in ZDV release. This indicates the ability to achieve even higher drug loads, while remaining close to the TRT, allowing for a smaller dosage form, which typically leads to increased adherence. Nevirapine (NVP) was also explored as a possible inhibitor of ZDV release in SSF as it is completely insoluble at physiological pH. NVP is an additional anti-retroviral agent typically given with ZDV for perinatal HIV prophylaxis, so inclusion of NVP in the formulation would further reduce the number of physical medications the patient would have to take. The quaternary formulation containing 2:8:15:75 (EC:EPO:NVP:ZDV) performed similarly to the ternary 5:20:75 (EC:EPO:ZDV) formulation, which reduced release of ZDV in SSF to only 1.4x greater than the TRT. We also developed a quaternary 4:16:20:60 (EC:EPO:NVP:ZDV) formulation, which was able to further reduce the release of ZDV to a value below the TRT. Although the drug load of ZDV in this formulation is much lower than all the others, the ratio of NVP to ZDV is the same as the ratio of the recommended dose of each drug per the WHO guidelines for HIV prophylaxis of infants 6-12 weeks old. This quaternary formulation was chosen as the primary eZDV formulation moving forward with inclusion of eZDV into an orally dispersible film (ODF). Finally, since EC is a nonionic polymer and may not as readily dissolve in the gastric fluid as EPO will, in vitro gastric dissolution was explored to ensure ZDV release was not being inhibited in the stomach. The results from this study indicate that all formulations released at least 80% of ZDV from the formulations within 60 minutes.
Conclusion: Inclusion of ZDV in an encapsulated form using both cationic and nonionic polymers, as well as NVP, prevented release of ZDV in SSF above the TRT, theoretically masking the taste of ZDV for patients. This is incredibly important for increasing adherence of infants to the medication regimen and reducing HIV infections worldwide. Additionally, inclusion of the eZDV formulation in an ODF will allow for more accurate dosing and increased adherence due to the smaller size being much more discreet for parents to carry home to their infants and children.
References: 1. Lallemant M, Chang S, Cohen R, Pecoul B. Pediatric HIV - A Neglected Disease? The New England Journal of Medicine. 2011; 365(7): 581-583.
2. Thi THH, Morel S, Ayouni F, Flament M. Development and evaluation of taste-masked drug for paediatric medicines - Application to acetaminophen. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2012; 434: 235-242.
3. Schiffman SS, Zervakis J, Shaio E, Heald A. Effect of the Nucleoside Analogs Zidovudine, Didanosine, Stavudine, and Lamivudine on the Sense of Taste. Nutrition. 1999; 15: 854-859.
Acknowledgements:Madison & Lila Self Graduate Fellowship; Oak Therapeutics; George Wang, Ph. D, at Bristol Myers Squibb for running scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
.jpg) (A) This diagram illustrates ZDV particles suspended in a polymer solution for encapsulation via spray drying. Once the suspension reaches the atomizing nozzle, the solubilized polymer particles will become atomized and will coat the insoluble ZDV particles as they are cooled flowing down the spray dryer. These encapsulated ZDV (eZDV) particles will be collected in the collection chamber. (B) The novel oral in vitro dissolution apparatus adapted from Thi et al. allows for a more accurate representation of the oral environment. The empty column tube allows for a small volume (2.4 mL), as the syringe pump pushes buffer or SSF through the flow-through tubing at 1 mL/min. Collection occurs after the buffer or SSF has completely flowed through the drug-containing column.
(A) This diagram illustrates ZDV particles suspended in a polymer solution for encapsulation via spray drying. Once the suspension reaches the atomizing nozzle, the solubilized polymer particles will become atomized and will coat the insoluble ZDV particles as they are cooled flowing down the spray dryer. These encapsulated ZDV (eZDV) particles will be collected in the collection chamber. (B) The novel oral in vitro dissolution apparatus adapted from Thi et al. allows for a more accurate representation of the oral environment. The empty column tube allows for a small volume (2.4 mL), as the syringe pump pushes buffer or SSF through the flow-through tubing at 1 mL/min. Collection occurs after the buffer or SSF has completely flowed through the drug-containing column. 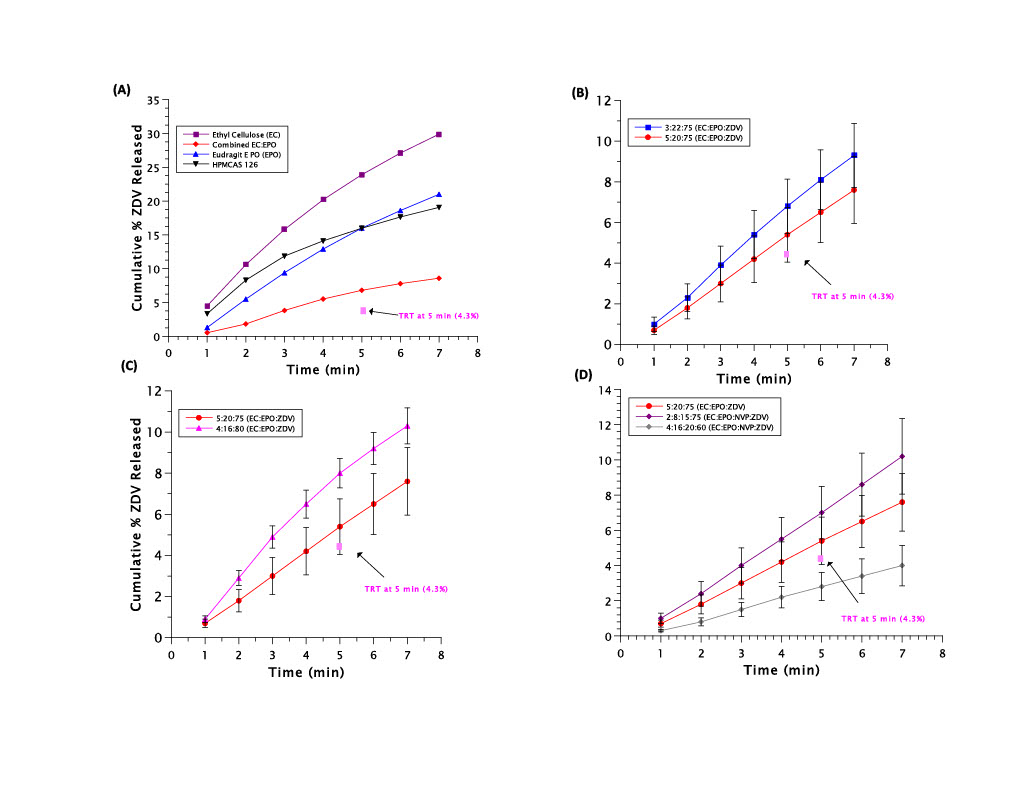 (A) Polymer selection for the encapsulant of ZDV was evaluated by assessing the % release of ZDV from the formulation in 50 mM pH 6.8 phosphate buffer. (B) This figure conveys the impact of changing the polymer ratio, while maintaining drug load, on the % release of ZDV in SSF at pH 7.0. The formulation containing 3:22:75 (EC:EPO:ZDV) represents a polymer ratio of 1:7 (EC:EPO), and the formulation containing 5:20:75 (EC:EPO:ZDV) represents a polymer ratio of 1:4 (EC:EPO). (C) Figure C conveys the impact of drug load on the % release of ZDV in SSF, while maintaining constant polymer ratio. (D) This figure illustrates the impact of NVP addition to create a quaternary formulation on the % release of ZDV in SSF. Polymer ratio is held constant at 1:4 (EC:EPO) for all three of these formulations.
(A) Polymer selection for the encapsulant of ZDV was evaluated by assessing the % release of ZDV from the formulation in 50 mM pH 6.8 phosphate buffer. (B) This figure conveys the impact of changing the polymer ratio, while maintaining drug load, on the % release of ZDV in SSF at pH 7.0. The formulation containing 3:22:75 (EC:EPO:ZDV) represents a polymer ratio of 1:7 (EC:EPO), and the formulation containing 5:20:75 (EC:EPO:ZDV) represents a polymer ratio of 1:4 (EC:EPO). (C) Figure C conveys the impact of drug load on the % release of ZDV in SSF, while maintaining constant polymer ratio. (D) This figure illustrates the impact of NVP addition to create a quaternary formulation on the % release of ZDV in SSF. Polymer ratio is held constant at 1:4 (EC:EPO) for all three of these formulations.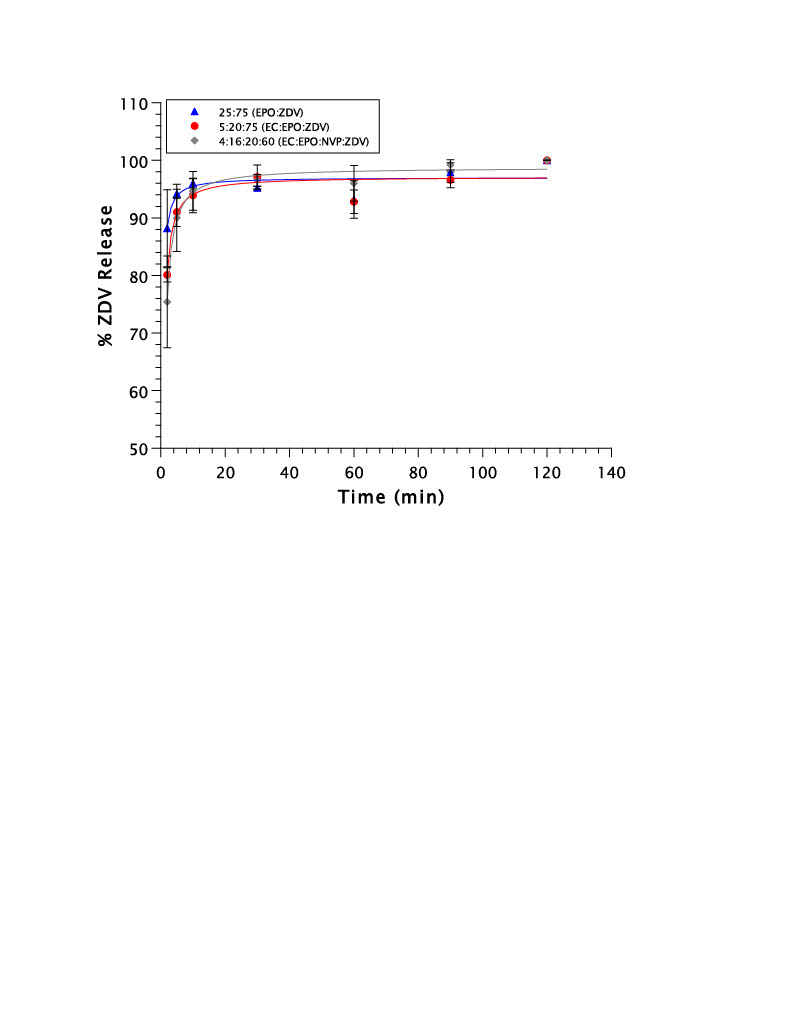 Gastric in vitro release of ZDV from 50 mM pH 4.0 acetic acid buffer was assessed to determine if the inclusion of ethylcellulose (EC) as a nonionic polymer would prevent the release of ZDV in the gastric environment significantly more than the 25:75 (EPO:ZDV) formulation, which does not include EC as a polymer.
Gastric in vitro release of ZDV from 50 mM pH 4.0 acetic acid buffer was assessed to determine if the inclusion of ethylcellulose (EC) as a nonionic polymer would prevent the release of ZDV in the gastric environment significantly more than the 25:75 (EPO:ZDV) formulation, which does not include EC as a polymer.