Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Poster Abstract
(M1130-11-74) Manufacturing of Medicated Contact Lenses Using Inkjet Printing
- IS
Iria Seoane-Viano, Ph.D.
University College London
London, England, United Kingdom - TP
Thomas Pollard, BA
University College London
LONDON, England, United Kingdom - JO
Jun Jie Ong, B.S. (he/him/his)
University College London
LONDON, England, United Kingdom 
Patricija Januskaite, M.S. (she/her/hers)
PhD student
University College London
LONDON, England, United Kingdom- SA
Sahar Awwad, Ph.D.
University College London
LONDON, England, United Kingdom - MO
Mine Orlu, Ph.D.
University College London
LONDON, England, United Kingdom - MB
Manuel Bande, M.D.
University Clinical Hospital of Santiago de Compostela
SANTIAGO DE COMPOSTELA, Galicia, Spain - AG
Alvaro Goyanes, Ph.D.
FabRx Ltd.
London, England, United Kingdom - AB
Abdul Basit, Ph.D.
University College London
London, England, United Kingdom
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Contact lenses could be utilised as drug delivery systems for local treatment in the eye. Inkjet printing is a new manufacturing paradigm that enables the deposition of drugs onto the surface of contact lenses for localised delivery and personalised dosing. To facilitate point-of-care drug dispensing onto contact lens, a non-destructive quality control method to accurately measure the amount of drug dispensed in situ is necessary. Process analytical technology (PAT) tools can perform quantitative and non-destructive analysis in real time. Near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy is a promising PAT tool for on-site quantification of drugs as it is non-destructive, rapid, and requires no sample preparation. The aim of this study was to print a drug for glaucoma, timolol maleate, onto contact lenses using a modified commercial inkjet printer and monitor drug release. NIR was used as an external validation method and was able to accurately quantify the drug dose. Overall, the combination of inkjet printing and NIR represents a novel method for point-of-care personalisation and quantification of drug-loaded contact lenses.
Methods: Preparation of timolol maleate solution ‘inks’ and inkjet printing process: To prepare a solution of timolol-loaded ink (11.2 mg/mL), timolol maleate (56.0 mg) was added to a volumetric flask (5.0 mL) with DMSO:water solution ratio of 7:3. The O2Nails V11 inkjet printer was used for printing. The contact lenses used were right 1-day disposable contact lenses. The shape printed onto the contact lens was a ring with an inner diameter of 7.1 mm and an outer diameter of 14.2 mm, equal to the diameter of the contact lens (Figure 1). Drug content and in vitro drug release: Drug loading was measured by printing 3, 5, 7, and 10 passes onto the outside face of contact lenses in triplicate. The contact lens was stirred for 24 hrs in 2 mL PBS to release all the drug and analysed via HPLC. In vitro drug release was conducted using contact lenses printed with 10 passes of timolol maleate (11.2 mg/mL) on the inner and outer face in triplicate. Release studies were conducted in an in-house flow rig model. Drug-loaded contact lenses were placed in each rig and the models were assembled, filled with phosphate buffer, and placed on a heating plate at 37 °C. The models were connected to a peristaltic pump with a 2.0 µL/min flow rate at 37 °C. Samples were collected over 48 hours and analysed via HPLC. Near infrared spectroscopy (NIR): The NIR system was a portable MicroNIR 1700ES near infrared spectrometer. Contact lenses were printed with 3, 5, 7, and 10 passes of timolol maleate (11.2 mg/mL) on the outside face in triplicates. Multivariate data analysis was performed with a python 3.10 script. The model was trained using a train:test split of 80:20 to measure the performance of the model in a real scenario on unseen data. Partial least squares (PLS) regression was performed on the datasets, with 10-fold cross validation with 3 repeats, to build calibration models. Following NIR analysis, each individual contact lens was quantitatively analysed for drug content via HPLC following the methodology described in the previous section. Light transmittance: The light transmittance (%) of unmodified, 10-pass printed drug-loaded and 10-pass printed blank contact lenses were measured using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer. Transmittance measurements were taken from 200 to 800 nm.
Results: The drug load increases linearly (R2=0.8889) with the number of passes (3, 5, 7, and 10 passes). The results also demonstrate that timolol maleate was both printable onto a contact lens and extractable. The drug concentration from the in vitro release model showed a peak in the Cmax (11.38 ± 0.19 and 8 ± 3 µg/mL for the outside and inside face respectively) at 2 h, followed by a gradual decrease in concentration (Figure 2). Several PLS models were developed with different pre-treatment filters. The selected model used a 2nd derivative (Savitzky–Golay with a filter width of 25 and a 2nd polynomial) pre-processing technique. The model showed a good linearity (R2 = 0.9120) with an RMSE of 1.1196 (Figure 3), confirming that the NIR results were proportional to timolol maleate concentration in the contact lenses in the stated range. Light transmittance of all CLs showed values above 85% in the visible range (380 to 700 nm), indicating that the drug-loaded CLs would not interfere with normal vision, and thus making them suitable for use.
Conclusion: The printing of timolol maleate onto contact lenses with an adapted commercial inkjet printer was demonstrated. In vitro results indicated that the contact lenses were capable of releasing drug over multiple hours, and NIR demonstrated to be able of performing non-destructive quality control measurements of the drug loading of inkjet printed contact lenses. Hence, the combination of inkjet printing with NIR presents a considerable opportunity for the personalised, point-of-care manufacture of glaucoma therapies.
Acknowledgements: T.D.P acknowledges the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), UK for their financial support (EP/R513143/1). I.S.-V. acknowledges Consellería de Cultura, Educación e Universidade for her Postdoctoral Fellowship (Xunta de Galicia, Spain; ED481B-2021-019). P.J. acknowledges the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) UK grant number EP/S023054/1. S.A. is grateful for funding from National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and UCL Institute of Ophthalmology, Moorfields Special Trustees, the Helen Hamlyn Trust (in memory of Paul Hamlyn), Medical Research Council, Fight for Sight and the Michael and Ilse Katz foundation.
.jpg) Figure 1. Different angles of the printed contact lens.
Figure 1. Different angles of the printed contact lens.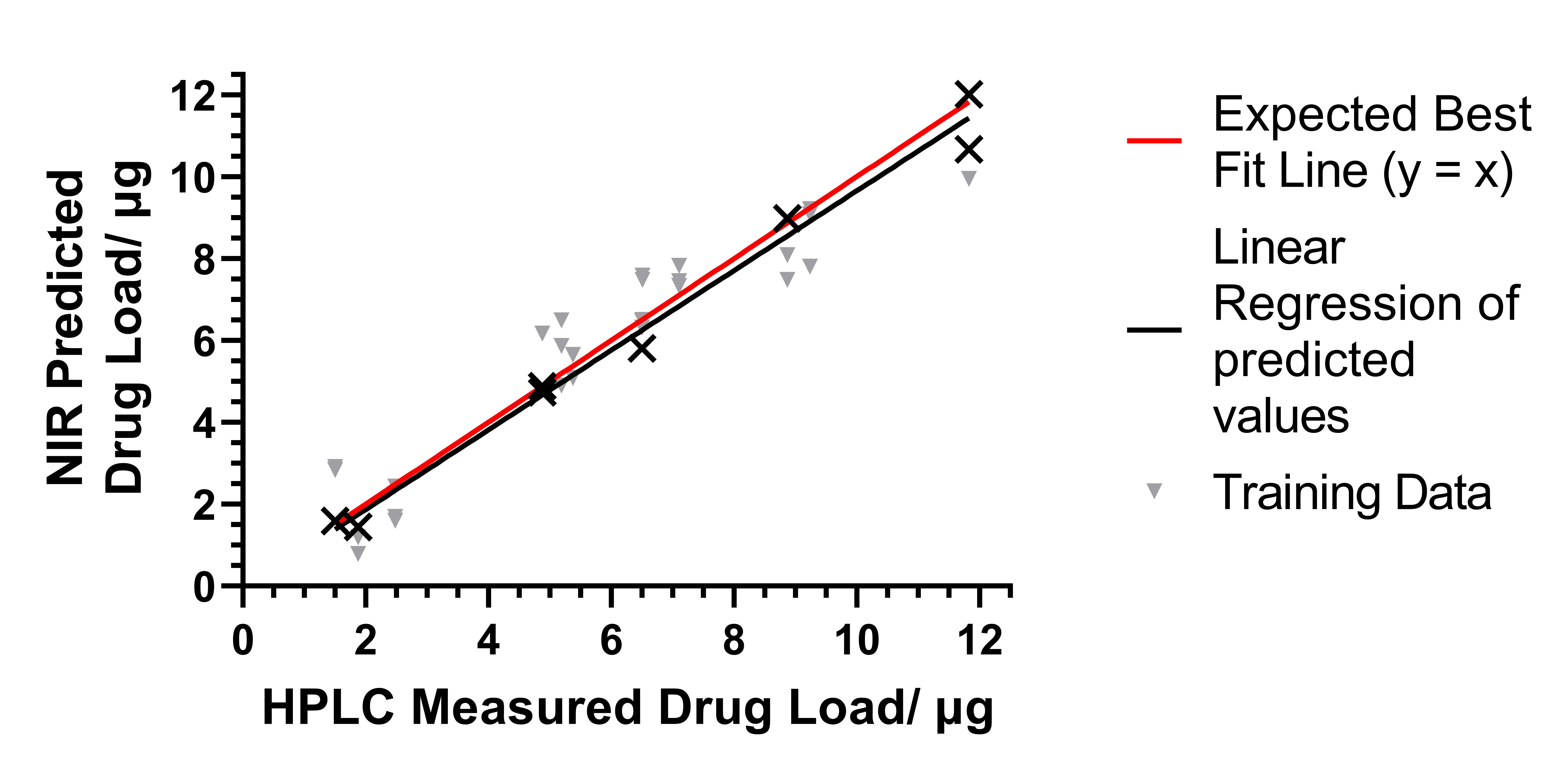 Figure 2. PLS model of NIR predicted vs. HPLC determined timolol content. The expected best fit line is for the actual concentration equal to the predicted concentration.
Figure 2. PLS model of NIR predicted vs. HPLC determined timolol content. The expected best fit line is for the actual concentration equal to the predicted concentration..jpg) Figure 3. Results from the in vitro dissolution study. Error bars are ± 1 standard deviation. A) Measurements of concentration collected over time with the drug printed on the inside face of the contact lens. Insert – plot with the concentration relative to the maximum concentration for the inside face dissolution. B) Measurements of drug concentration over time for drug printed on the outside face of the contact lens.
Figure 3. Results from the in vitro dissolution study. Error bars are ± 1 standard deviation. A) Measurements of concentration collected over time with the drug printed on the inside face of the contact lens. Insert – plot with the concentration relative to the maximum concentration for the inside face dissolution. B) Measurements of drug concentration over time for drug printed on the outside face of the contact lens.