Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Poster Abstract
(T0930-02-09) Detailed In Vivo Evaluation of Novel Bioadhesive Microemulsion-Based Long-Acting Glaucoma Eye Drops

Mohamed Moustafa Ibrahim Moustafa, PhD (he/him/his)
Assistant Professor
University of Tennessee Health Science Center
Memphis, Tennessee, United States
Mohamed Moustafa Ibrahim Moustafa, PhD (he/him/his)
Assistant Professor
University of Tennessee Health Science Center
Memphis, Tennessee, United States- DM
Doaa N. Maria, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
University of Tennessee Health Sciences Center
Memphis, Tennessee, United States - SM
Sara N. Maria, MS (she/her/hers)
University of Tennessee Health Sciences Center
Memphis, Tennessee, United States - MK
Minjae J. Kim, BS (he/him/his)
University of Tennessee Health Sciences Center
Memphis, Tennessee, United States - MJ
Monica M. Jablonski, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
University of Tennessee Health Sciences Center
Memphis, Tennessee, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: In previous study we successfully designed novel pregabalin-loaded microemulsion-based formulation for management of glaucoma. While our formulation provided excellent efficacy using single dose design, its effect after repeated dosing, its bioadhesion to ocular surface and drug tissue distribution after single or multiple dosing are still unknown. The current study was conducted to ensure that our formulation didn’t suffer from tachyphylaxis and to detect side effects after 60 days of daily use. In addition, we conducted ocular tissues drug biodistribution and ocular surface bioadhesion studies.
Methods: Efficacy of our microemulsion was previously evaluated using multiple in-vitro and in-vivo characterization tests (AAPS-2018, AAPS-2019 and Ibrahim et al 2019, ACS-Nano; 13(12):13728-13744). Some drugs may suffer from a decrease in pharmacological response upon repeated dosing that results from a decrease in their targeted receptor density and/or sensitivity. This behavior is known as tachyphylaxis, and is commonly observed among glaucoma medications. To expand on our finding and move toward a tachyphylaxis-free, safe and effective glaucoma medication, further detailed in-vivo evaluations were required. The current studies were designed as complementary evaluations for our pregabalin-loaded microemulsion. Tachyphylaxis study was conducted on Dutch belted rabbits (n=5). Each rabbit received a single daily 100μl dose of our medicated formulation in one eye and the blank formulation in the other eye for 60 successive days. Intraocular pressure (IOP) was recorded immediately before administration and at the time of maximum response (Tmax). On day 61, rabbits’ eyes were examined using fundus camera and slit-lamp biomicroscopic examination. Rabbits were euthanized and eyes as well as some internal organs were collected and evaluated for their drug contents using UPLC/MS/MS. Half of each cornea was subjected to histological examination. Another problem that may be associated with topically applied medication, is the rapid drainage from the ocular surface and short corneal contact time. Consequently, in-vivo bioadhesion study was conducted using acridine orange (fluorescent dye) loaded microemulsion to prove the ability of our formulation to remain on the eye surface for enough time to allow a prolonged IOP-lowering effect. Also, a pilot 6h-pharmacokinetics study (PK) was conducted to test pregabalin ocular distribution after a single dose of microemulsion.
Results: During tachyphylaxis study, all rabbits were calm and didn’t show any sign of discomfort. Also, all eyes failed to develop any irritation or allergic reactions. Continuous IOP monitoring demonstrated that the formulation IOP-lowering effect didn’t suffer from any diminishment. On the contrary, there was a progressive decrease in IOP until it reached its lowest value after 30 days. After 30 days, almost there was no significant difference between baseline and IOP at Tmax, such that the IOP/time curve almost became a flat line, which indicated that the IOP could be maintained at low constant value (%IOP reduction = 35-40%) after a single daily dosing of our unique formulation (Figure 1). Slit-lamp biomicroscopic examinations showed that the corneal surfaces were smooth, aqueous humor was clear, and lenses were clear and free of any abnormality. The fundus exam showing a healthy fundus conditions. Corneal histological examination demonstrated that there were no changes in the corneal histological structure regarding the shape and thickness of each layer. Drug tissue deposition study demonstrated that pregabalin was maintained within the treated eye and was distributed throughout all its tissues. Due to the bioadhesive property of the formulation that kept it on the treated eye, there was only traces of drug detected either in peripheral organs or in control eyes. In-vivo bioadhesion study demonstrated that our formulation remained on the ocular surface for up to 24h compared to the control formulation that disappeared within one hour (Figure 2). From the results of the pilot PK study, it is obvious that microemulsion improved the ocular bioavailability of pregabalin compared with the control formulation. Also, PK results showed that the systemic absorption of pregabalin from microemulsion is nearly negligible, as pregabalin plasma level during the study was below 0.1 ng/mg (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Our microemulsion didn’t suffer from tachyphylaxis or ocular side effects after 60 days of daily use. Also, our microemulsion eye drops could remain on ocular surface of the treated eyes for up to 24h which help in 2 different ways, the first is to ensure continuous drug availability on the ocular surface for absorption over 24h period and the second is to minimize systemic absorption to avoid systemic side effects. All these finding greatly support the use of our formulation as once daily IOP-lowering therapy for management of glaucoma.
References: 1- Mohamed M. Ibrahim, Doaa N. Maria and Monica M. Jablonski, Pregabalin Microemulsion Once Daily Eye Drops for Management of Glaucoma. AAPS PharmSci 360, Poster number W1030-08-058, (2018).
2- Mohamed M. Ibrahim, Doaa N. Maria and Monica M. Jablonski, In-Depth Characterization of Novel Long-Acting Glaucoma Eye drops. AAPS PharmSci 360, Poster number T1430-01-02, (2019).
3- Ibrahim MM, Maria DN, Mishra SR, Guragain D, Wang X, Jablonski MM. Once Daily Pregabalin Eye Drops for Management of Glaucoma. ACS Nano. 13(12):13728-13744. PMID: 31714057 (2019).
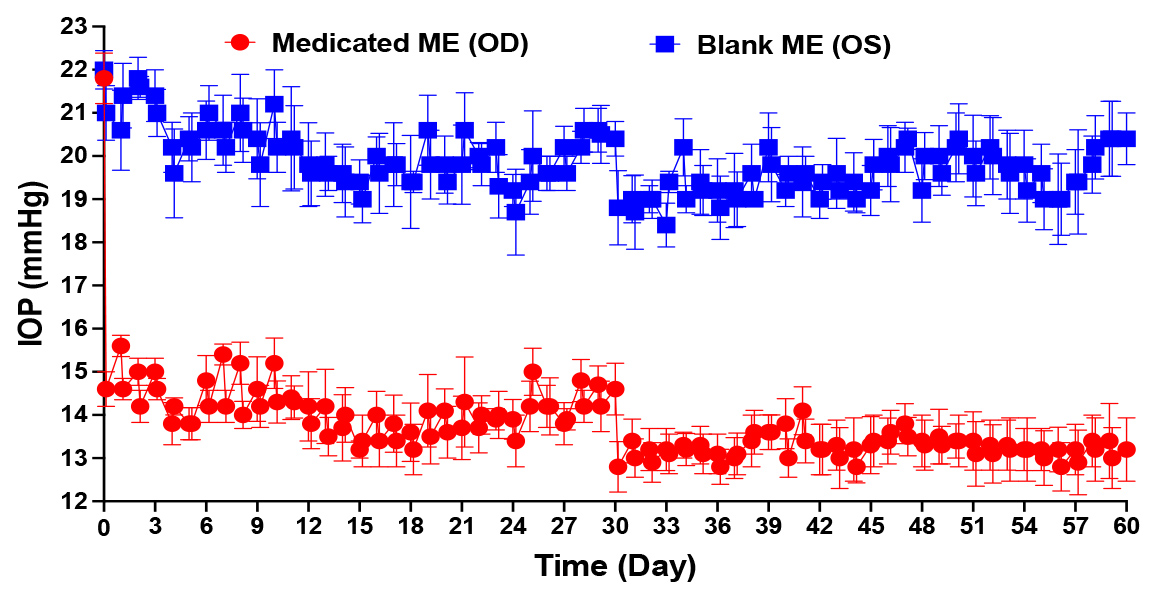 Figure 1: IOP profile of DB rabbits through 60 days of tachyphylaxis study (red; IOP of the eye received medicated microemulsion, blue; IOP of the eye received blank microemulsion)
Figure 1: IOP profile of DB rabbits through 60 days of tachyphylaxis study (red; IOP of the eye received medicated microemulsion, blue; IOP of the eye received blank microemulsion)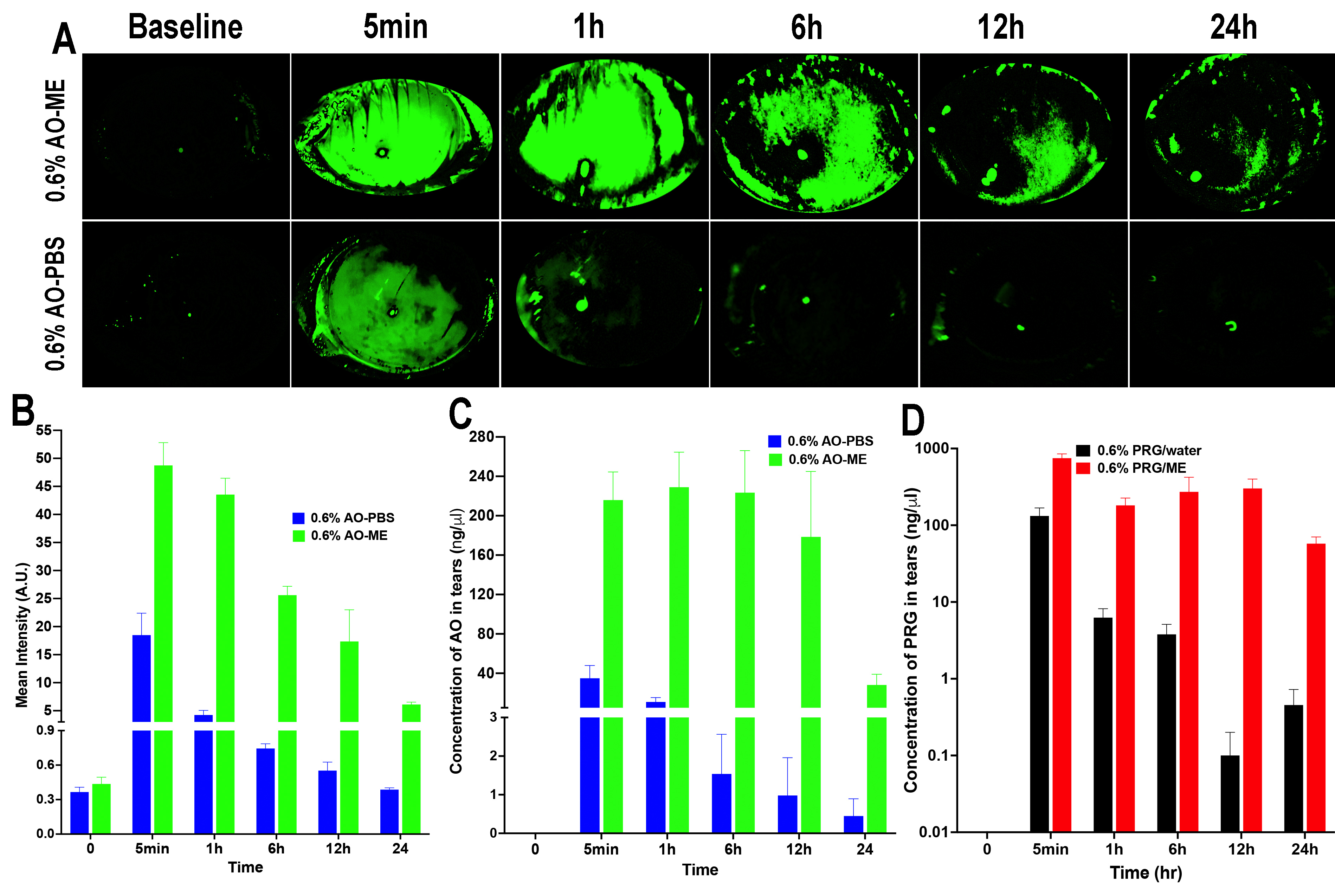 Figure 2: In-vivo bioadhesion study showed the availability of the formulation on ocular surface for up to 24h in the eye treated with microemulsion compared to the eye treated with aqueous solution. A; rabbits eye photos, B; fluorescent intensity quantification, C; acridine orange concentration in tears, D; pregabalin concentration in tears
Figure 2: In-vivo bioadhesion study showed the availability of the formulation on ocular surface for up to 24h in the eye treated with microemulsion compared to the eye treated with aqueous solution. A; rabbits eye photos, B; fluorescent intensity quantification, C; acridine orange concentration in tears, D; pregabalin concentration in tears 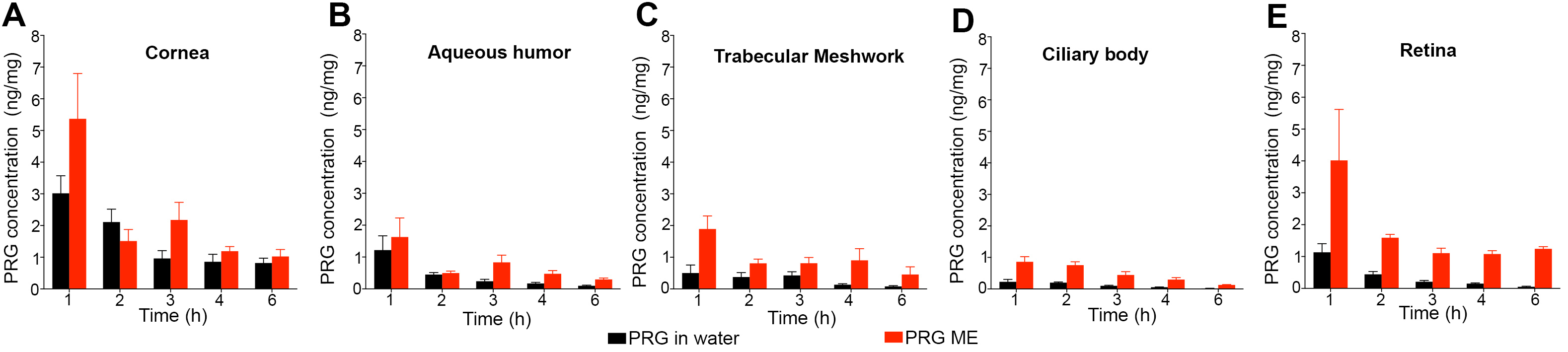 Figure 3: Ocular tissue drug content after 6h-pilot PK study showed more pregabalin availability in the eye treated with pregabalin microemulsion than the eye treated with pregabalin aqueous solution. (red bars; microemulsion, black bars; aqueous solution).
Figure 3: Ocular tissue drug content after 6h-pilot PK study showed more pregabalin availability in the eye treated with pregabalin microemulsion than the eye treated with pregabalin aqueous solution. (red bars; microemulsion, black bars; aqueous solution).