Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Poster Abstract
(T1430-11-74) Novel NanoSensoGel Engineered for Prevention of Chemotherapeutic-Induced Ototoxicity and Associated Hearing Loss
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
2:30 PM - 3:30 PM ET

Neeraj S. Thakur, PhD (he/him/his)
Postdoctoral Fellow
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States- IR
Iulia Rus, BS (she/her/hers)
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States - VA
Vibhuti Agrahari, Ph.D.
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: Cisplatin-based chemotherapies, commonly used to treat several types of cancers, but responsible for permanent inner ear hair cell damage leads to ototoxicity and hearing loss. The reported rate of cisplatin-induced hearing loss (CIHL) ranges between 11% and 97%, with an average incidence of 62%1. Hearing loss resulting from chemotherapeutic induced ototoxicity (CIO) is irreversible and there are at present no treatments available to prevent or reverse CIO; therefore, this investigation potentially provides a prophylactic cure for ototoxicity and associated hearing loss by developing an effective drug delivery system.
Methods: The novel dual stimuli-responsive nanoformulations have been investigated; A. for the synthesis of ROS-responsive polymer, B. thermos-responsive polymer and their characterization using 1H NMR. The dual drug loaded nanoformulations were optimized using DoE- Central Composite Design and NCs were prepared by nanoprecipitation method. The BUC-PPS-mPEG2000-NCs and DLT-PPS-mPEG2000-NCs were characterized using DLS and NTA Nano sight (Figure 1) and TEM images. The EE% and DL% of NCs were determined using HPLC and Ellman’s assays. The long-term storage stability over two months was checked by using DLS for size and PDI. In vitro assessments were performed on the HEIOC1 cell lines for MTT and Live-dead cell assays for biocompatibility and cellular uptake analysis, respectively. The cytoprotective effect of BUC-NCs, DLT-NCs and BUC/DLT- PPS-mPEG2000-NCs, were studied after treating with various regimens and different concentration with and without cisplatin. The ROS-Scavenging effect nanoformulation was confirmed by the ABTS+ , DCFH-DA assay, and FLICA assays. The final formulation, NanoSensoGel was characterized for its bio-responsiveness, a novel method was established to perform the in vitro drug release, and release kinetics mechanism were studied for dual drug release.
Results: The NMR spectra showed the designated proton peak of the ROS-responsive and thermos-responsive polymers successfully synthesized using multistep. The average sizes of BUC-PPS-mPEG2000-NCs, and DLT- PPS-mPEG2000-NCs, were found ~107.1 and 98.8 nm, respectively and PDI < 0.3 confirmed that most of the NPs have the same size. The NCs preparations appeared spherical and, the D10/D50/D90 values of BUC- NCs, and DLT- NCs were found to be 95.9/127.9/154.4 and 84.3/115.8/157.4 nm, respectively identified by NTA. The morphological analysis of developed NCs confirmed the spherical shape and the size of ~100 nm using NTA and TEM (Fig. 1). The EE/DL of the BUC and DLT in the respective NCs were found to be 56±4/8.38 and 87±7/12.30%. BUC-PPS-mPEG2000-NCs alone or in combination with DLT-PPS-mPEG2000-NCs have demonstrated as highly efficient as ROS scavengers in HEI-OC1 cells and could be beneficial to protect CIO (Figure 2). BUC-PPS-mPEG2000-NPs showed efficient antioxidant activity confirmed by ABTS+ radical scavenging assay. Both BUC- and DLT-loaded PPS-mPEG2000-NPs were found to be highly biocompatible with HEI-OC1 cells, therefore their cytoprotective effect after CisPt exposure . The results were further confirmed by fluorescence microscopy which confirmed that the BUC is highly responsible for the inhibition of the caspase 3/7 activation in the CisPt-exposed HEI-OC1 cells (Figure 11c). Caspase inhibition by developed BUC-entrapped NPs could be highly desirable for reduced CisPt-induced cytotoxicity and CIO, subsequently. Several characterizations of NanoSensoGel formulation were reported in figure 3 such as sol-gel state mechanism, the sample observed under the SEM showed a well-arranged honeycomb-type pattern in the structure (scale 10 µm). The release mechanism fitted well with the Korsmeyer-Peppas model (KP-model). It was observed the ‘n’ values of BUC and DLT release from Free BUC/DLT-Gel and NanoSenosGel formulations were found to be between 0.45 to 1 (0.45< n < 1) which suggests the non-Ficjkian transport.
Conclusion: The rationally designed cytoprotective novel NanoSensoGel formulation was successfully optimized, evaluated, and developed as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of the CIO and associated hearing loss. This was the first investigation engineered with dual-stimuli and dual-drug combination against irreversible inner ear hair loss. Moreover, this technology can be utilized for other inner ear diseases such as Age-related and Noise-induced hearing loss etc.
References: Vlajkovic, Srdjan M., et al. "Preventing hearing loss and restoring hearing: a new outlook." BioMed Research International 2015 .
Acknowledgements:Presbyterian Health Foundation (PHF) New Investigator Grant
Capita Foundation Auditory Research (CFAR) Grant
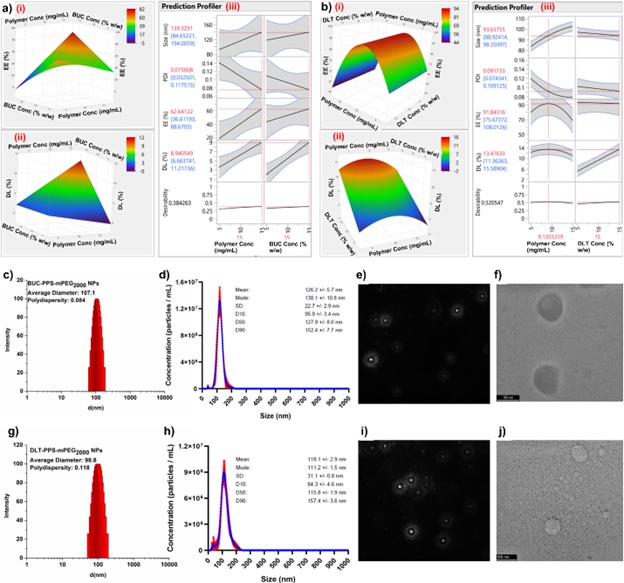 Figure 1 (a-b) DoE-CCD optimization graphs for the synthesis of (a) BUC-NCs and (b) DLT-NCs. The corresponding figures (i), (ii), and (iii), represent the encapsulation efficiency (EE%), Drug loading (DL %), and prediction profiler, respectively. (c-j) Size and morphology analysis of BUC-NCs and DLT-NCs. (c) Size distribution of BUC-NCs analyzed by DLS (d) Size distribution of BUC-NCs analyzed by NTA, (e) visual BUC-NCs under NTA Nanosight (f) TEM image of BUC-NCs showing spherical and intact shape (scale 100 nm). (g) Size distribution of DLT-NCs analyzed by DLS (h) Size distribution of DLT-NPs analyzed by NTA, (i) picture presenting the visual DLT-PPS-mPEG2000-NPs under NTA Nanosight , (j) TEM image of DLT-NCs showing spherical and intact shape (scale 100 nm).
Figure 1 (a-b) DoE-CCD optimization graphs for the synthesis of (a) BUC-NCs and (b) DLT-NCs. The corresponding figures (i), (ii), and (iii), represent the encapsulation efficiency (EE%), Drug loading (DL %), and prediction profiler, respectively. (c-j) Size and morphology analysis of BUC-NCs and DLT-NCs. (c) Size distribution of BUC-NCs analyzed by DLS (d) Size distribution of BUC-NCs analyzed by NTA, (e) visual BUC-NCs under NTA Nanosight (f) TEM image of BUC-NCs showing spherical and intact shape (scale 100 nm). (g) Size distribution of DLT-NCs analyzed by DLS (h) Size distribution of DLT-NPs analyzed by NTA, (i) picture presenting the visual DLT-PPS-mPEG2000-NPs under NTA Nanosight , (j) TEM image of DLT-NCs showing spherical and intact shape (scale 100 nm). 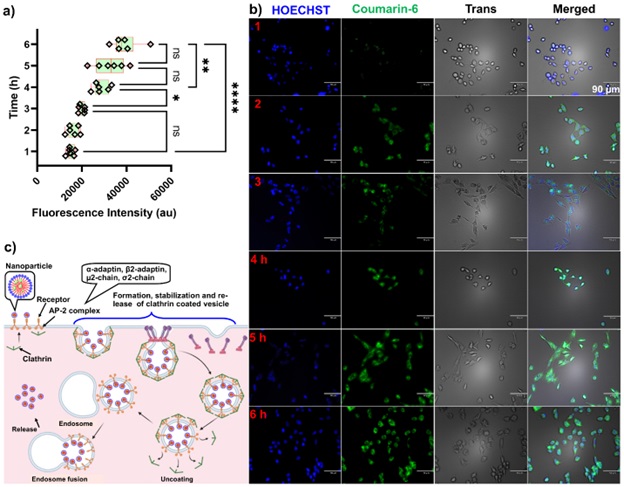 Figure 2 Cellular uptake and intracellular distribution study of NPs using C-6-PPS-mPEG2000-NCs. (a) Time required for significant cell internalization, (b) Fluorescence microscopy to confirm the cellular uptake and intracellular distribution, (c) Molecular mechanism of internalization. (The groups were compared using one-way ANOVA using Šidák’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. Asterisks: **** p < 0.0001; ** p≤ 0.005; * p≤ 0.05; ns= not significant)
Figure 2 Cellular uptake and intracellular distribution study of NPs using C-6-PPS-mPEG2000-NCs. (a) Time required for significant cell internalization, (b) Fluorescence microscopy to confirm the cellular uptake and intracellular distribution, (c) Molecular mechanism of internalization. (The groups were compared using one-way ANOVA using Šidák’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. Asterisks: **** p < 0.0001; ** p≤ 0.005; * p≤ 0.05; ns= not significant).jpg) Figure 3. Characterization of NanoSensoGel formulation. The formulation’s sol state converts to gel state at/above 33 °C, while below 33°C the formulation remains in the sol state (a). At lower temperature, the gel is present in a flowing sol state while at a higher temperature the formulation components are arranged in the micellar structure and form a nonflowing gel state (b). SEM images (c i and c ii) of hydrogel were kept below 30 °C at sol state then snap-freeze using liquid nitrogen at -196 °C and lyophilized subsequently. The sample observed under the SEM shows the un-arranged pattern in the structure (scale 10 µm). (c iii and c iv) SEM images of hydrogel were kept at 34 °C gel state then snap-freeze and lyophilized subsequently. The sample observed under the SEM showed a well-arranged honeycomb-type pattern in the structure (scale 10 µm). (d) ‘i’; the pictorial representation of well-insert that was used for the drug release study from the hydrogel. ‘ii’; the pictures captured after setting up the release experiments. (e) Graphs ‘i and ii’ are showing the percent release of BUC and DLT from NanoSensoGel and free BUC/DLT-Gel, respectively. (f) The graph showing the cytoprotective effect of NanoSensoGel compared with free BUC/DLT-Gel, free BUC/DLT-PPS-mPEG2000-NPs, and free BUC/DLT solution after the cell (HEI-OC1) exposed to CisPt.
Figure 3. Characterization of NanoSensoGel formulation. The formulation’s sol state converts to gel state at/above 33 °C, while below 33°C the formulation remains in the sol state (a). At lower temperature, the gel is present in a flowing sol state while at a higher temperature the formulation components are arranged in the micellar structure and form a nonflowing gel state (b). SEM images (c i and c ii) of hydrogel were kept below 30 °C at sol state then snap-freeze using liquid nitrogen at -196 °C and lyophilized subsequently. The sample observed under the SEM shows the un-arranged pattern in the structure (scale 10 µm). (c iii and c iv) SEM images of hydrogel were kept at 34 °C gel state then snap-freeze and lyophilized subsequently. The sample observed under the SEM showed a well-arranged honeycomb-type pattern in the structure (scale 10 µm). (d) ‘i’; the pictorial representation of well-insert that was used for the drug release study from the hydrogel. ‘ii’; the pictures captured after setting up the release experiments. (e) Graphs ‘i and ii’ are showing the percent release of BUC and DLT from NanoSensoGel and free BUC/DLT-Gel, respectively. (f) The graph showing the cytoprotective effect of NanoSensoGel compared with free BUC/DLT-Gel, free BUC/DLT-PPS-mPEG2000-NPs, and free BUC/DLT solution after the cell (HEI-OC1) exposed to CisPt.