Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(T1430-12-80) Development and Application of USP Apparatus 3 for In Vitro Drug Release from a Paclitaxel Nanocrystal Formulation
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
2:30 PM - 3:30 PM ET
- ML
Minghao Li, M.S.
Logan Instruments
Somerset, New Jersey, United States - ML
Minghao Li, M.S.
Logan Instruments
Somerset, New Jersey, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to develop and apply the USP Apparatus 3 (Reciprocating Cylinder) to evaluate the in vitro drug release profile of a paclitaxel nanocrystal formulation. The objectives were to investigate the release behavior of paclitaxel over a 120-hour period, evaluate the performance on alternative apparatus designs and address precipitation issues during dissolution testing.
Methods: Two customized adaptors for USP 3 were employed to test three different concentrations (0.6 mg/mL, 0.8 mg/mL, and 1.0 mg/mL) of the paclitaxel nanocrystal formulation. Both flat-bottom and cone-bottom nanocages were utilized. The focus was on monitoring dissolution percentages and standard deviations, and observe turbidity during the experiments over a 120-hour period. For USP apparatus parameters, 40 rpm, reciprocate distance 2 cm.
Results: Lower concentrations (0.6 mg/mL) in both flat-bottom and cone-bottom nanocages demonstrated higher dissolution percentages (96.63% for flat-bottom and 94.33% for cone-bottom). In contrast, higher concentrations resulted in lower dissolution percentages (65.52% for flat-bottom and 66.18% for cone-bottom). When comparing samples with the same concentration between the flat-bottom and cone-bottom adaptors, no significant difference in the final dissolution percentage was observed. However, the cone-bottom adaptor exhibited better standard deviations in dissolution profiles. No turbidity was observed in the lower concentration (0.6 mg/mL) for both flat-bottom and cone-bottom adaptors. However, turbidity was observed in the higher concentration (1.0 mg/mL) for the flat-bottom adaptor, while the cone-bottom adaptor showed no turbidity.
Conclusion: The findings emphasize the significance of concentration and adaptor selection for achieving optimal dissolution performance in the paclitaxel nanocrystal formulation. Lower concentrations and the use of the cone-bottom adaptor demonstrated more complete dissolution, reduced standard deviations, and minimized turbidity. These results contribute to reducing observational errors and improving the accuracy of drug release characterization during dissolution testing.
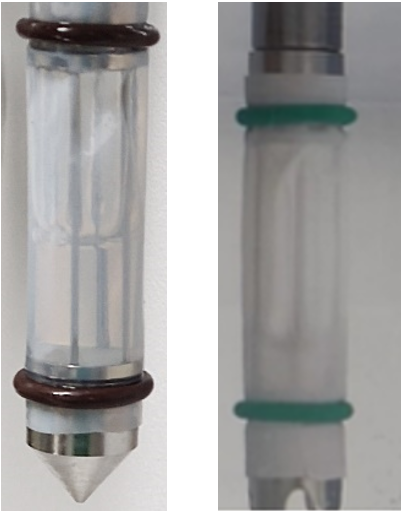 flat-bottom USP 3 adaptor and cone-bottom USP 3 adaptor
flat-bottom USP 3 adaptor and cone-bottom USP 3 adaptor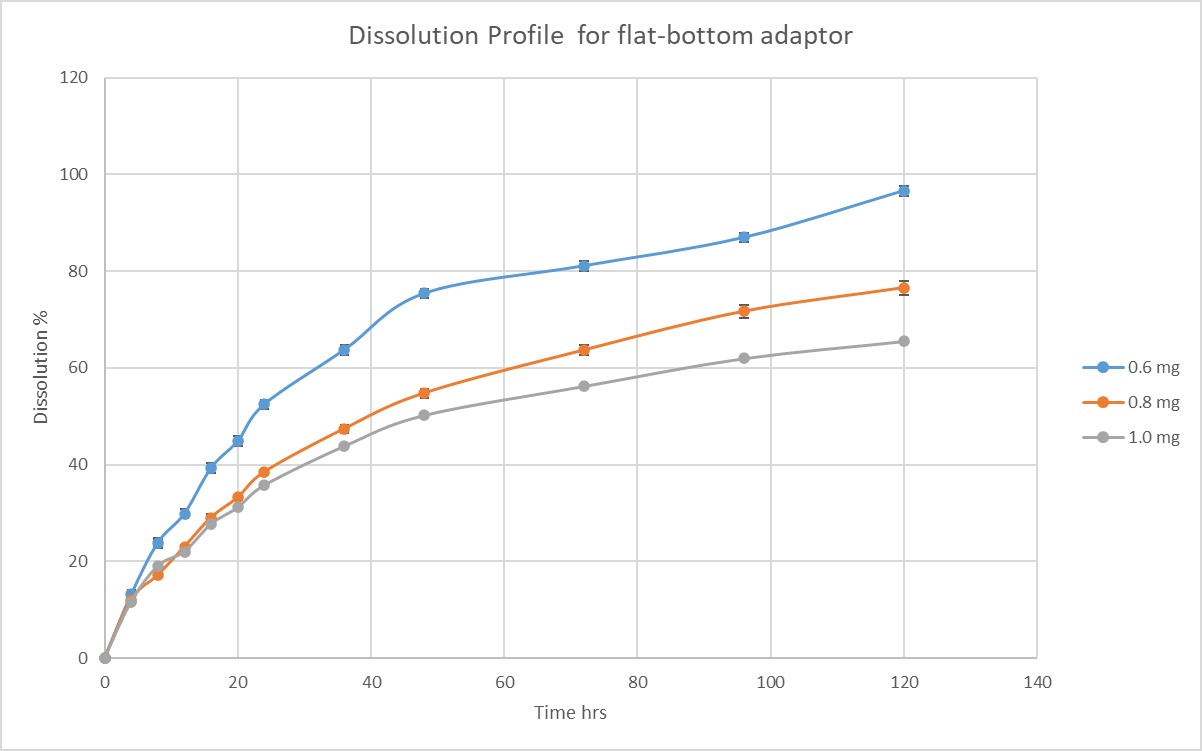 Dissolution Profile for flat-bottom adaptor
Dissolution Profile for flat-bottom adaptor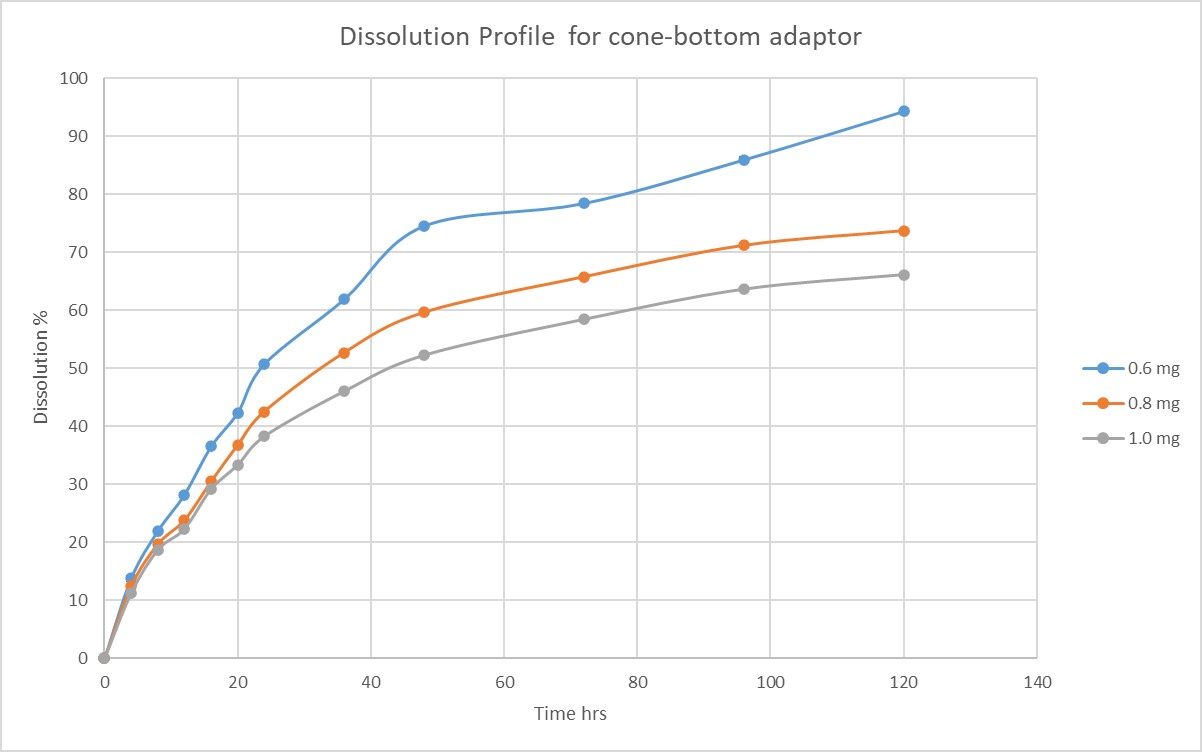 Dissolution Profile for cone-bottom adaptor
Dissolution Profile for cone-bottom adaptor