Formulation and Delivery - Biomolecular
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(M0930-03-51) Boosting Antitumor Immune Response against Breast Cancer Cells Using Doxorubicin and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Co-loaded Lipid Nanocarrier
Monday, October 23, 2023
9:30 AM - 10:30 AM ET

Hend Mohamed Abdel-Bar, PhD (she/her/hers)
Associate Professor of Pharmaceutics
University of Sadat City
Sadat City, Al Minufiyah, Egypt
Hend Mohamed Abdel-Bar, PhD (she/her/hers)
Associate Professor of Pharmaceutics
University of Sadat City
Sadat City, Al Minufiyah, Egypt- IA
Isra H. Ali, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
University of Sadat City
Sadat City, Al Minufiyah, Egypt - MH
Mohamed Hamdi, Ph.D. (he/him/his)
University of Sadat City
Sadat City, Al Minufiyah, Egypt
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Under normal circumstances there is a balance between “eat me signals” which are responsible for the ability of body to get rid of foreign materials as viruses, bacteria and dead cells. The other signal is “don’t eat me signals” which are responsible for the ability of our cells to avoid immune clearance. However, cancer cells adopt smart techniques to avoid immune recognition by disturbing this balance (1). So, the main aim of cancer immunotherapy is to upregulate eat me signals and downregulate don’t eat me signals. Doxorubicin is a widely used chemotherapeutic drug that could induce immunogenic cell death (ICD). Therefore, it triggers the host immune system to overwhelm cancer cells (2). ICD includes the over expression of calreticulin, release of ATP, Heat shock proteins (Hsps) and High mobility group box 1 protein (HMBG1). Moreover, Zinc oxide nanoparticles (nZnO) stimulates immune response and generates ICD that initiate anti-tumor immunity (3). Additionally, nZnO is reported to downregulate CD44, a cancer stem surface marker that could induce chemotherapy resistance (4). Herein, we aimed to fabricate a lipid nanocarrier co-loaded with both doxorubicin and nZnO (LNPDox-nZnO) as a combinatory immunotherapy strategy to combat breast cancer.
Methods: Different lipid nanoparticles were fabricated and optimized using D-optimal design. The optimized formulae were characterized for particle size, zeta potential and entrapment efficiency (EE%). The cellular internalization of doxorubicin and CD44 downregulation were assessed in 4T1 cells. The surface expression of calreticulin, secretion of ATP and HMGB1 secretion in 4T1 cells as well as the polarization of macrophage towards the proinflammatory M1 phenotype was also studied.
Results: The optimized cationic serum stable LNPDox-nZnO had a particle size 135.25±5.11nm and EE% > 85 % for both doxorubicin and nZnO. LNPDox-nZnO improved the cellular uptake of doxorubicin in dose and time dependent manner with augmented cytotoxicity against 4T1 cells. The proposed LNPDox-nZnO was successfully able to knockdown CD44 by approximately 60% in 48 h and consequently impeding both cell adhesion and migration. LNPDox-nZnO was able to induce macrophage polarization towards pro-inflammatory M1phenotype by upregulation of IL-6, TNF-α, CD80, CD86 and MHC II expressions on J774 macrophage cells (Figure 1 and 2). LNPDox-nZnO surface calreticulin expression, ATP and HMGB1 in 4T1 cells release over untreated cells or those treated with either monotherapy and consequently macrophage recognition and phagocytosis of the treated 4T1 cells.
Conclusion: A potent synergistic anti-tumor stimulation could be obtained by combining doxorubicin as an ICD-inducing drug with nZnO in vitro. To support the outcomes of this study, it seems to be essential to carry out in vivo antitumor efficacy and re-challenge studies.
References: (1) Abdel-Bar HM., Walters AA., Wang JT., Al-Jamal KT. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. 10(7):e2001853.
(2) Aoto K., Mimura K, Okayama H, Saito M, Chida S, Noda M, et al., Oncol Rep. 2018. 39. 151-9.
(3) Zhang Y., Guo C., Liu L., Xu J., et al., Theranostics. 2020. 10. 11197-214.
(4) Wang J, Lee J.S., Kim D., & Zhu, L. ACS Appl. Mater. 2017. 9. 39971–84.
Acknowledgements: This work has received funding from Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority, Egypt, project No. 45769
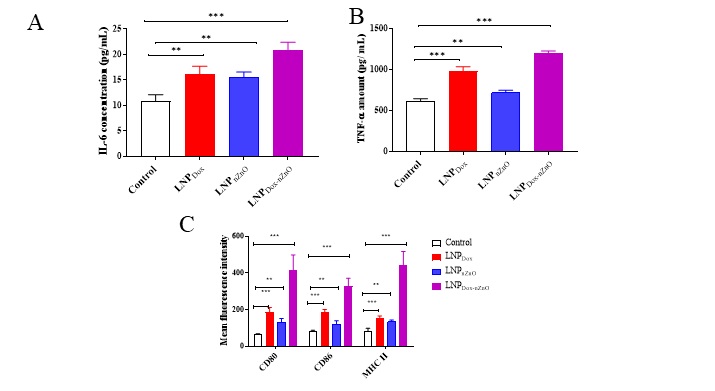 Figure 1. The co-delivery of doxorubicin and nZnO into lipid nanoparticles induced macrophage polarization. After 24h of J774 cells seeding in 24-well plate at density of 50K/ well, cells were treated with either LNPDox, LNPnZnO or LNPDox-nZnO for 24 h. Following the supernatant collection and centrifugation, the concentrations of IL-6 (A) and TNF-α (B) were measured using ELISA. Cells harvested by trypsin-EDTA were centrifuged at 1750 rpm for 3 min at 4 °C then stained with either anti-mouse CD80-FITC monoclonal antibody (1: 200 v/v), anti-mouse CD86-FITC monoclonal antibody (1: 200 v/v) or anti-mouse MHC II-FITC monoclonal antibody (1: 200 v/v) for 30 min at 4 °C. The expression of CD80, CD86 and MHC II was quantified using the fluorescence in FL1. The expression of each costimulatory marker was presented as MFI marking also higher marker values with LNPDox-nZnO (C). Data points represented mean and SD (n=3). Statistical analysis was performed using One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Figure 1. The co-delivery of doxorubicin and nZnO into lipid nanoparticles induced macrophage polarization. After 24h of J774 cells seeding in 24-well plate at density of 50K/ well, cells were treated with either LNPDox, LNPnZnO or LNPDox-nZnO for 24 h. Following the supernatant collection and centrifugation, the concentrations of IL-6 (A) and TNF-α (B) were measured using ELISA. Cells harvested by trypsin-EDTA were centrifuged at 1750 rpm for 3 min at 4 °C then stained with either anti-mouse CD80-FITC monoclonal antibody (1: 200 v/v), anti-mouse CD86-FITC monoclonal antibody (1: 200 v/v) or anti-mouse MHC II-FITC monoclonal antibody (1: 200 v/v) for 30 min at 4 °C. The expression of CD80, CD86 and MHC II was quantified using the fluorescence in FL1. The expression of each costimulatory marker was presented as MFI marking also higher marker values with LNPDox-nZnO (C). Data points represented mean and SD (n=3). Statistical analysis was performed using One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.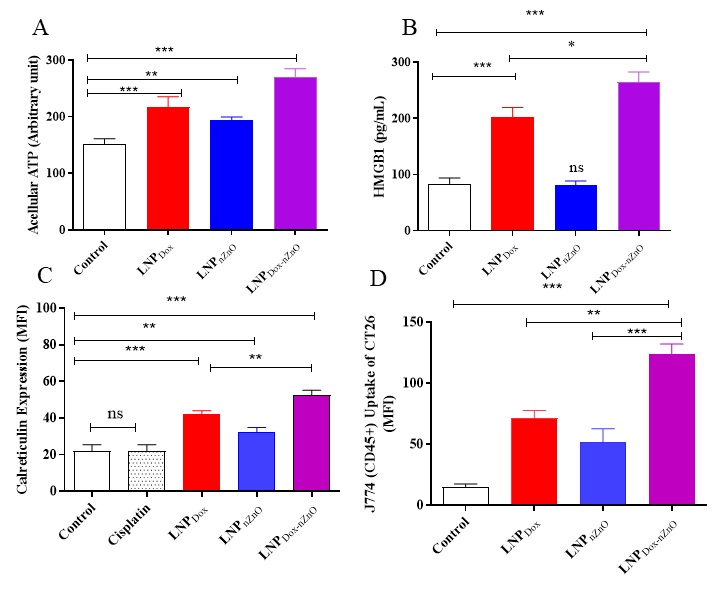 Figure 2. The co-delivery of doxorubicin and nZnO into lipid nanoparticles induced ATP, HMGB1 secretion, surface calreticulin expression and consequently macrophage phagocytosis. The effect of the proposed system on ATP and HMGB1 secretion. 4T1 cells were seeded in 24-well plate at density of 50K/ well for 24 h, then treated with LNPDox, LNPnZnO or LNPDox-nZnO for 24 h. Afterwards, the supernatant was collected and the cellular debris removed by centrifugation. The concentration of acellular ATP was measured by luciferase based ATP detection reagent (A) and HMGB1 release in the culture media was quantified using ELISA (B). Cells were collected by trypsin-EDTA, centrifuged at 1750 rpm for 3 min then stained using rabbit anti-human calreticulin antibody (1:50 v/v) followed by donkey anti-rabbit IgG-FITC secondary antibody (1:200). The fluorescence signals were measured in FL1 channel. Gates were plotted based on the isotype. Surface calreticulin expression was expressed as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) (C). The treated 4T1 cells were collected and co cultured with J774 macrophage cells for 6 h. Cells were harvested and stained with anti-mouse CD45 monoclonal before being acquired on a FACs Calibur flow cytometer. Relative MFI of CD45+ J774 cells is shown in (D). LNPDox, LNPnZnO or LNPDox-nZnO elevates ATP concentrations, calreticulin and macrophage phagocytosis over untreated cells. However, only doxorubicin loaded formulae were able to induce HMGB1 release. Data points represent mean and SD (n=3). Statistical analysis was performed using One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns nonsignificant.
Figure 2. The co-delivery of doxorubicin and nZnO into lipid nanoparticles induced ATP, HMGB1 secretion, surface calreticulin expression and consequently macrophage phagocytosis. The effect of the proposed system on ATP and HMGB1 secretion. 4T1 cells were seeded in 24-well plate at density of 50K/ well for 24 h, then treated with LNPDox, LNPnZnO or LNPDox-nZnO for 24 h. Afterwards, the supernatant was collected and the cellular debris removed by centrifugation. The concentration of acellular ATP was measured by luciferase based ATP detection reagent (A) and HMGB1 release in the culture media was quantified using ELISA (B). Cells were collected by trypsin-EDTA, centrifuged at 1750 rpm for 3 min then stained using rabbit anti-human calreticulin antibody (1:50 v/v) followed by donkey anti-rabbit IgG-FITC secondary antibody (1:200). The fluorescence signals were measured in FL1 channel. Gates were plotted based on the isotype. Surface calreticulin expression was expressed as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) (C). The treated 4T1 cells were collected and co cultured with J774 macrophage cells for 6 h. Cells were harvested and stained with anti-mouse CD45 monoclonal before being acquired on a FACs Calibur flow cytometer. Relative MFI of CD45+ J774 cells is shown in (D). LNPDox, LNPnZnO or LNPDox-nZnO elevates ATP concentrations, calreticulin and macrophage phagocytosis over untreated cells. However, only doxorubicin loaded formulae were able to induce HMGB1 release. Data points represent mean and SD (n=3). Statistical analysis was performed using One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns nonsignificant.