Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(T1430-03-15) Beyond Conventional Boundaries: New Excipients for ASD Formulation
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
2:30 PM - 3:30 PM ET
- FT
Francisco Tavares, M.S. (he/him/his)
Hovione PharmaScience SA
Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal - FT
Francisco Tavares, M.S. (he/him/his)
Hovione PharmaScience SA
Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal .jpg)
Inês Ramos, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Formulation Scientist
Hovione PharmaScience SA
Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal- SC
Sílvia Costa, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Instituto Superior Tecnico de Lisboa
Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal - VS
Vanda Serra, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Instituto Superior Tecnico de Lisboa
Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal - MP
Maria Paisana, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Hovione PharmaScience SA
Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Nearly 70% of molecules in the discovery pipeline and about 40% of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) in the market are poorly water soluble1,2. A commonly employed strategy to improve their solubility and dissolution rate consists in the formulation of amorphous solid dispersions (ASD) with hydrophilic polymeric matrices3. However, this approach does not fully address the challenges regarding APIs with high crystallization tendencies particularly at high drug loading/target doses. Recent research has been focused on leveraging natural, more sustainable carriers for the creation of ASD platforms that better address the challenges of dosage forms number/size reduction while maintaining manufacturability, improving bioavailability and enhancing in vitro/vivo performance to widen the ASD formulation design space2,4. Aligned with that trend, this work explores new excipients among naturally derived compounds (eg. proteins, polysaccharides, other natural polymers) and modified/synthetic polymers for ASD formulation for oral administration, through small scale prototyping using formulation screening techniques and spray drying (SD). Furthermore, new excipient-based formulations were tested against benchmark excipients for their ability to sustain API supersaturation, prevent API recrystallization and in vitro dissolution performance at high drug loads.
Methods: Literature search to identify new excipients was performed with emphasis on relevant features for ASD formulation (e.g. solubility in aqueous solutions/organic solvents, and sustainability). Preliminary formulation screening of new excipient matrices was conducted by solvent casting (SC), melt quenching (MQ), and supersaturation assays in fasted state simulated intestinal fluid (FaSSIF, pH 6.5), at 70% drug load and 5 times target dose, to evaluate the excipient’s influence on the API supersaturation extent. Screening results lead to SD prototyping of the most promising formulations, using a Buchi B290 (Buchi, CH). SD powders underwent a 24h post-drying process using a vacuum tray oven, followed by Karl Fisher (KF) characterization and gas chromatography (GC) monitoring to ensure low humidity and residual solvent levels below ICH limits. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to characterize the samples’ thermal transitions (e.g. Tg and melting temperatures (Tm)) and x-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) was performed to study the samples’ molecular arrangement. Furthermore, accelerated stability testing was performed by storing the SD powders in open vial conditions (40ºC and 75% relative humidity). Ongoing biorelevant dissolution testing is being conducted using a USP II dissolution apparatus (Copley Scientific, UK).
Results: Extensive literature search allowed for the creation of a database comprising over 100 new excipients and 20 APIs, from which 11 excipients (8 new and 3 benchmark selected using Hovione’s in silico screening model) and a highly challenging API, in terms of physical stability with a Tg of 36ºC, were selected. Supersaturation results revealed that five new excipients (EXC 1, 3, 4, 6, and 7) outperformed PVP/VA K28, while two more (EXC 2 and 8) surpassed HPMC. Notably, EXC 1, 3, and 7 sustained supersaturation beyond 4 hours (see Figure 1), having closely matched the results obtained for HPMC-AS M. Subsequently, new excipients soluble in solvents compatible with SD (EXC 1, 2, 3, and 4) were used for SC and MQ studies. XRPD data indicated that all SC formulations were amorphous at drug loads of 25, 50, 60, and 70%, while DSC data revealed that all MQ formulations prevented API recrystallization and subsequent melting at drug loads of 50 and 70%, except for EXC 2:API formulation at 70% drug load (see Figure 2). Based on these findings, SD prototypes at API load between 50 and 80% (see Figure 3) were produced with EXC 1, 3, and 4 and HPMC-AS M, having attained yields higher than 80% for all formulations, despite the challenging Tg. XRPD analysis indicated that all SD formulations were amorphous, except for those produced with EXC4. DSC data showed that EXC3-based SD formulations prevented API recrystallization and melting, having attained slightly higher Tg for all drug loads (50%, 70%, and 80%) compared to benchmark HPMC-AS M. Moreover, ongoing accelerated stability assays indicate that EXC3 formulations (50% drug load) remained stable under harsh storage conditions (open vial conditions). Future in vitro dissolution testing is expected to provide better insights into the excipient properties’ influence on drug product performance.
Conclusion: This study allowed for rapid screening and SD prototyping of ASD formulations using new excipients, yielding promising data regarding excipient:API compatibility at high drug loads for the model weak base API used for the proof-of-concept loads. Herein, two new excipients (EXC 1 and 3) demonstrated to have superior performances in supersaturation assays compared to benchmark excipients (PVP/VA K28 and HPMC), with EXC 3 formulations attaining comparable results to HPMC-AS M formulations regarding the stabilization of a challenging API at drug loads up to 80%. Through the integration of future biorelevant dissolution testing, this research is expected to foster a deeper comprehension on the excipient’s influence on drug product intermediate performance, thus contributing for more rational and robust development and design of ASD formulations with APIs beyond the current technology fit space.
References: 1 Nunes, P. D. et al., Mol. Pharm., 2022, 19, 51–66.
2 Pas, T. et al., Int. J. Pharm., 2018, 535, 47–58.
3 Baghel, S. et al., J. Pharm. Sci., 2016, 105, 2527–2544.
4 Xie, T. et al., J. Pharm. Sci., 2017, 106, 100–110.
Acknowledgements: This work was funded by Hovione under the doctoral fellowship PBDL/BDE/18
.jpg) Figure 1 – Supersaturation assays in fasted state simulated intestinal fluid (FaSSIF) at 70% drug load and 5 times target dose. Assays conducted with 8 different new excipients and three benchmark excipients (HPMC, HPMC-AS M, and PVP/VA K28).
Figure 1 – Supersaturation assays in fasted state simulated intestinal fluid (FaSSIF) at 70% drug load and 5 times target dose. Assays conducted with 8 different new excipients and three benchmark excipients (HPMC, HPMC-AS M, and PVP/VA K28).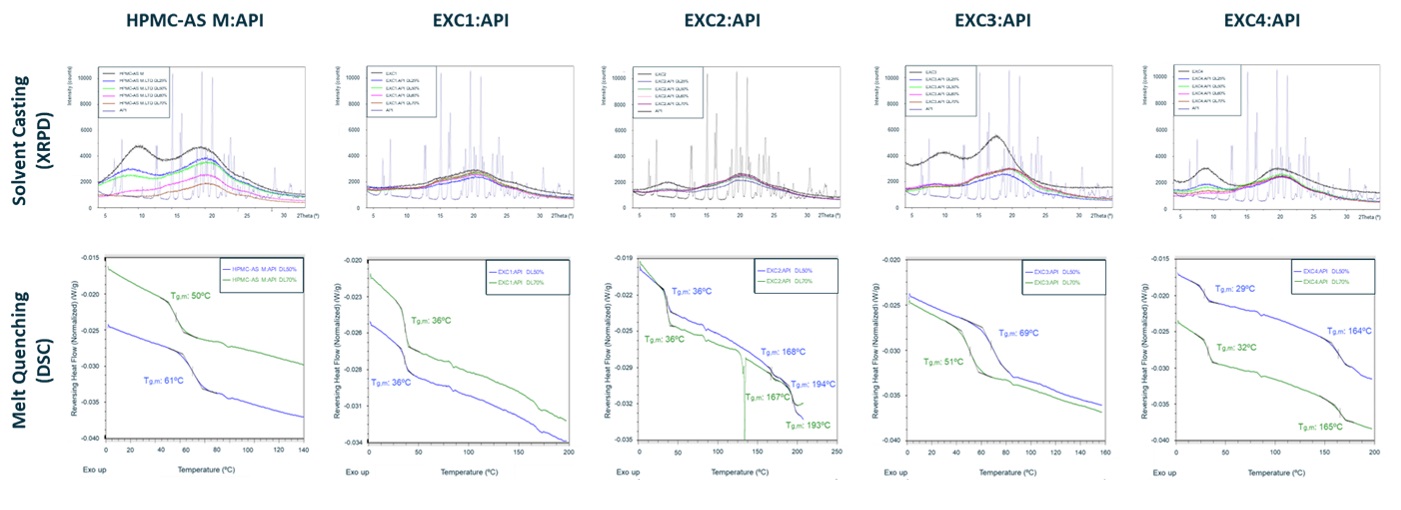 Figure 2 – XRPD results of solvent casting formulations using EXC1, 2, 3, 4, and benchmark HPMC-AS M at 25, 50, 60, and 70% drug load. DSC results for melt quenching using EXC1, 2, 3, 4, and benchmark HPMC-AS M at 25, 50, 60, and 70% drug load.
Figure 2 – XRPD results of solvent casting formulations using EXC1, 2, 3, 4, and benchmark HPMC-AS M at 25, 50, 60, and 70% drug load. DSC results for melt quenching using EXC1, 2, 3, 4, and benchmark HPMC-AS M at 25, 50, 60, and 70% drug load.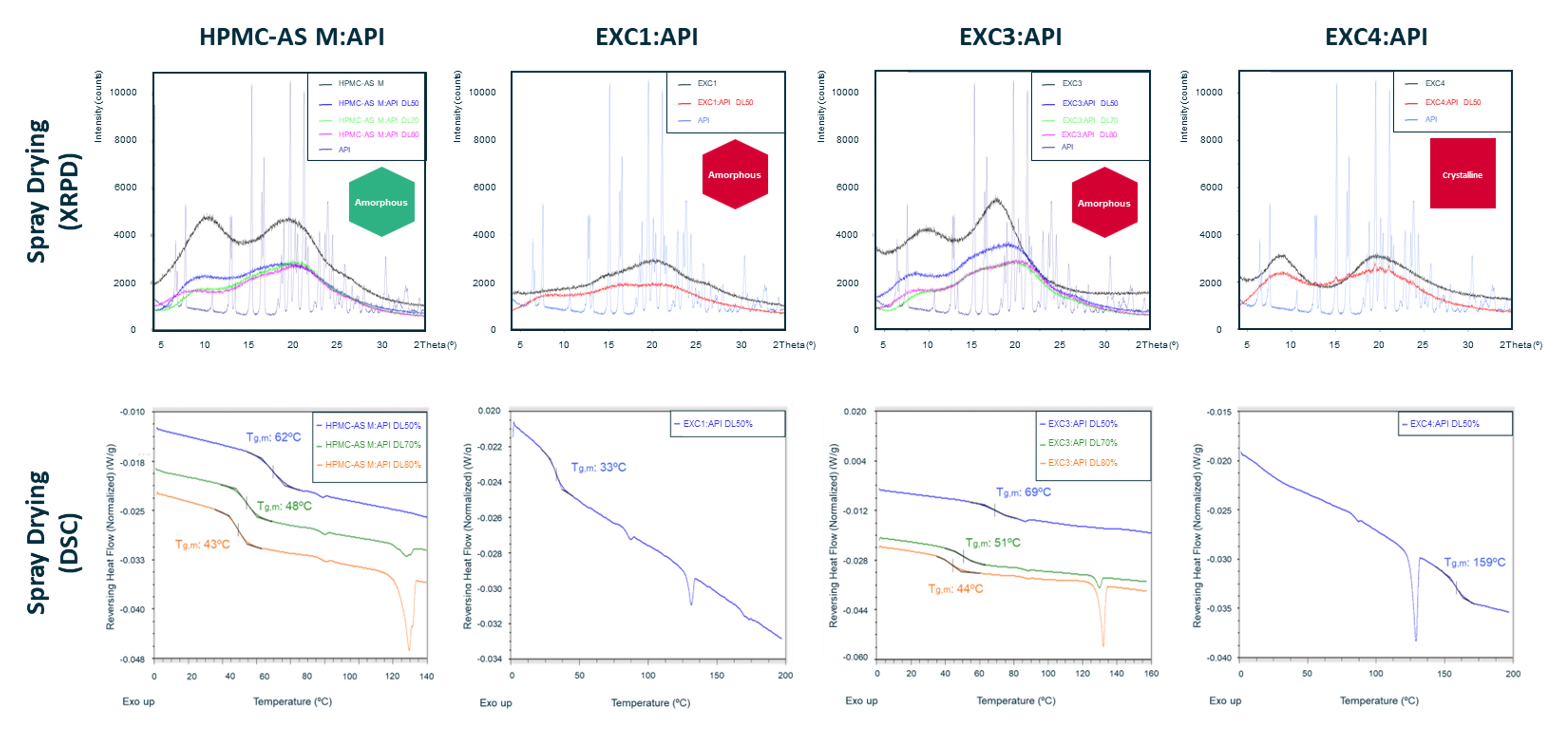 Figure 3 – X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) of spray dried formulations (drug loads between 50 and 80%) and raw materials (excipient and API) and glass transition temperature (Tg) of the same spray dried formulations based on benchmark HPMC-AS M and new excipients (EXC 1, EXC 3, and EXC 4).
Figure 3 – X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) of spray dried formulations (drug loads between 50 and 80%) and raw materials (excipient and API) and glass transition temperature (Tg) of the same spray dried formulations based on benchmark HPMC-AS M and new excipients (EXC 1, EXC 3, and EXC 4).