Manufacturing and Analytical Characterization - Biomolecular
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(M1530-09-58) Critical Manufacturing Parameters and Their Impacts on the Product Attributes of Bupivacaine Multivesicular Liposomal Formulation (Exparel®)

Ziyun Xia, M.S. (she/her/hers)
PhD Candidate in Pharmaceutical Sciences
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States
Ziyun Xia, M.S. (she/her/hers)
PhD Candidate in Pharmaceutical Sciences
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States- YL
Yayuan Liu, Ph.D.
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States - ZL
Ziyi Lu, B.S.
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States - YW
Yan Wang, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Staff Fellow
US Food and Drug Administration
Silver Spring, Maryland, United States - XX
Xiaoming Xu, Ph.D.
US Food and Drug Administration
Silver Spring, Maryland, United States - AS
Anna Schwendeman, Ph.D.
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Multivesicular liposomes (MVLs) are based on DepoFoam technology with the ability to provide a sustained drug release. The unique pomegranate-like structure of MVLs is attributed to the assembly of numerous nonconcentric liposomes within a large liposomal particle. Exparel is an MVL formulation of bupivacaine approved by FDA for local analgesia. Although Exparel is an appealing target for generic development, its complex structure and the insufficient understanding of its manufacturing process pose great challenges to not only generic developers but also regulatory authorities. To bridge these challenges, our current work focuses on identifying the critical process parameters in bupivacaine MVLs production and investigating their impact on the final product attributes.
Methods: A standard small-batch bupivacaine MVLs production process was developed using double emulsification in our lab. Briefly, an aqueous phase containing 44.9 mg/mL bupivacaine was formed by dissolving bupivacaine in deionized water containing 150 mM glucuronic acid, 15 mM hydrochloride acid, and 20 mM phosphoric acid. An organic phase was formed by dissolving 27.6 mg/mL DEPC, 15.8 mg/mL cholesterol, 6.8 mg/mL tricaprylin, and 3 mg/mL DPPG-Na in chloroform. The aqueous phase was mixed with organic phase (v:v = 1:1) and then homogenized at a speed of 15000 rpm for 9 minutes to form a water-in-oil (W/O) primary emulsion. The primary emulsion was then transferred into a second aqueous solution containing 32 mg/mL glucose and 10 mM lysine, followed with a 20-second vortex at 2000 rpm, to form a water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) secondary emulsion. The secondary emulsion was immediately transferred into a third aqueous solution containing 32 mg/mL glucose and 10 mM lysine. The mixture was then stirred at 600 rpm for 3 hours to ensure the complete evaporation of organic solvent. Finally, collected bupivacaine MVLs were resuspended in 3 mL of saline to create a final formulation with a bupivacaine concentration of 13.3 mg/mL. Several critical parameters (i.e., methods of emulsification and organic solvent evaporation, lipids concentration, and choices of amino acids) were identified and further studied by varying their settings in manufacturing. The bupivacaine MVL products were characterized and compared to commercial Exparel regarding morphology, size distribution, formulation pH, drug and lipids contents, as well as in vitro release (IVR) using the analytical methods developed in our lab previously, to investigate the impact on their product attributes. Briefly, the morphology was observed via an optical microscope, particle size was analyzed by Malvern Matersizer, and the amount of bupivacaine and lipids were quantified using ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Finally, the IVR of bupivacaine MVLs was estimated using an accelerated IVR assay based on a vertical rotator.
Results: The methods of second emulsification and organic solvent evaporation were found to be critical on forming the proper MVL structures (i.e., liposomes with nonconcentric inner vesicles) (Figure 1), and thus were essential in producing a successful MVL formulation. Lipid concentration impacted the size distribution of the MVLs product, and higher lipid concentration in the organic phase led to smaller-sized MVLs with improved stability. These results were further reflected in the IVR profiles in which higher lipids concentration led to a slower bupivacaine release from MVLs and a reduced cumulative drug release in the end (Figure 2). The choice of amino acids in the second and third aqueous solutions impacted the formulation pH, which associated with varied encapsulation efficiency (EE) and different drug and lipid recovery (Table 1).
Conclusion: All the critical process parameters (i.e., methods of emulsification and evaporation, lipid concentration, and choice of amino acids) identified in our present work exhibited prominent impact on our final product attributes. Our current results will be helpful on not only instructing generic development and authorization for Exparel but also understanding the rationale of other MVL formulation production.
References: Ye, Q., & Sankaram, M. (1996). Method for producing liposomes with increased percent of compound encapsulated.
Yu, M., Yuan, W., Xia, Z., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Xu, X., Zheng, J., & Schwendeman, A. (2023). Characterization of Exparel Bupivacaine Multivesicular Liposomes. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 639, 122952.
Exparel [package insert] Pacira Pharmaceuticals. (2018).
Acknowledgements:Funding for this project was made possible by U.S. Food and Drug Administration contract (75F40120C00127). This abstract reflects the views of the authors and should not be construed to represent FDA’s views or policies.
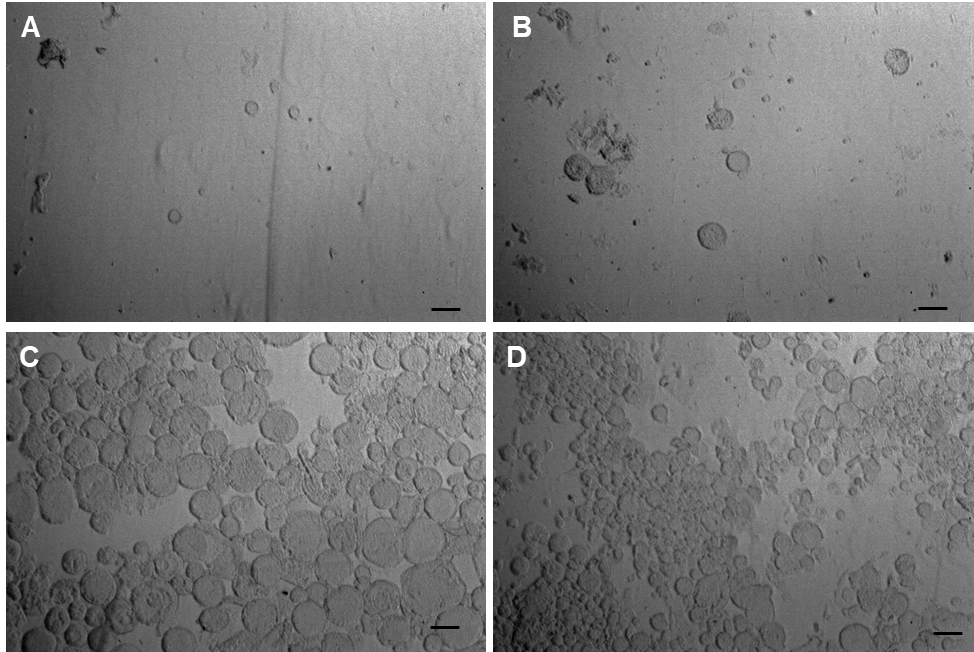 Figure 1. The morphology of bupivacaine MVLs prepared either via homogenization (A, C) or vortex (B, D) as second emulsification methods, and either via nitrogen flow (A, B) or gentle stirring (C, D) as organic solvent evaporation methods. Scale bar = 50 μm.
Figure 1. The morphology of bupivacaine MVLs prepared either via homogenization (A, C) or vortex (B, D) as second emulsification methods, and either via nitrogen flow (A, B) or gentle stirring (C, D) as organic solvent evaporation methods. Scale bar = 50 μm.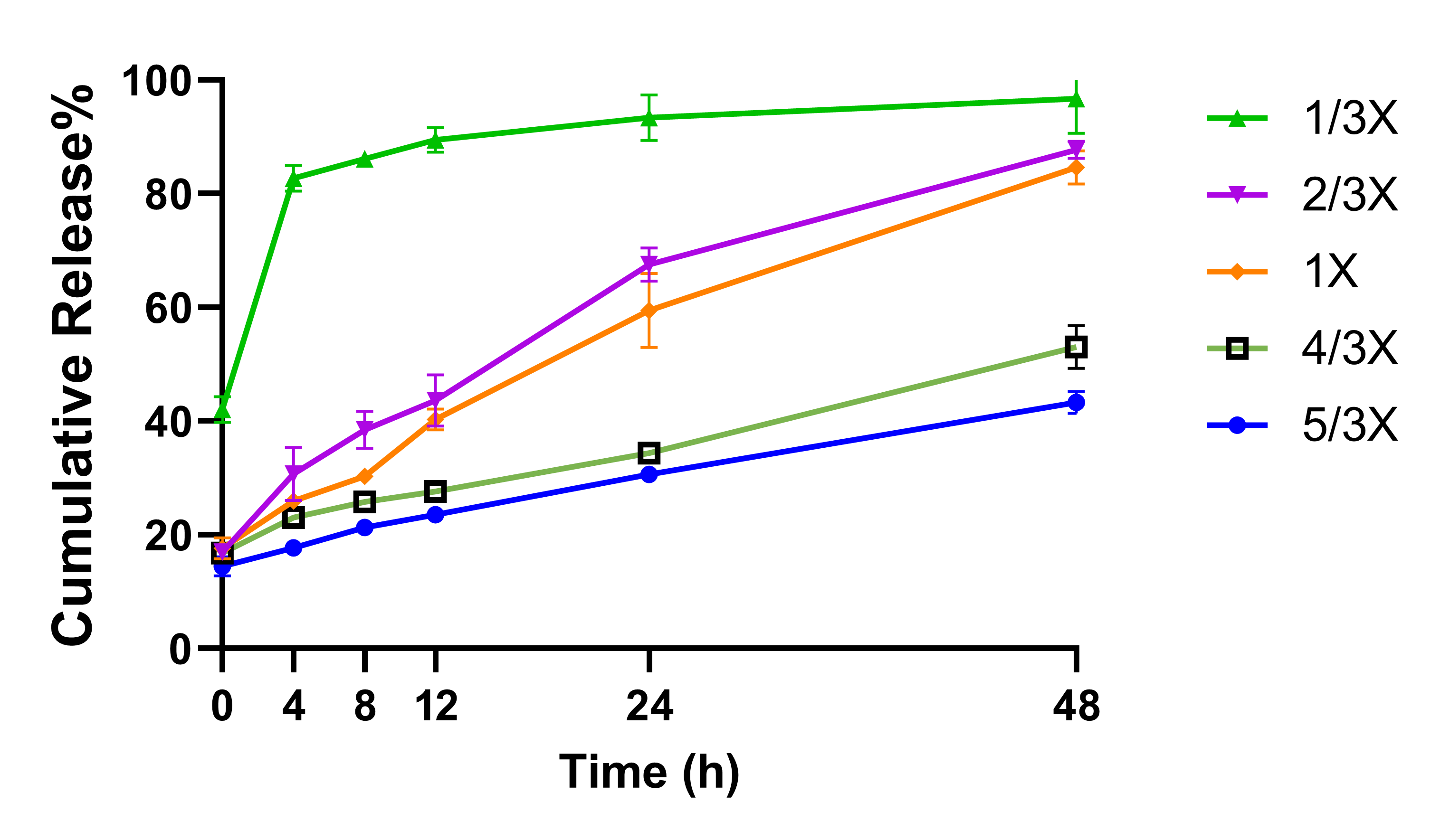 Figure 2. The in vitro release profiles of bupivacaine MVLs prepared with varied lipid concentrations in the organic phase. Lipid concentration of 1X in the original formulation served as the control.
Figure 2. The in vitro release profiles of bupivacaine MVLs prepared with varied lipid concentrations in the organic phase. Lipid concentration of 1X in the original formulation served as the control. 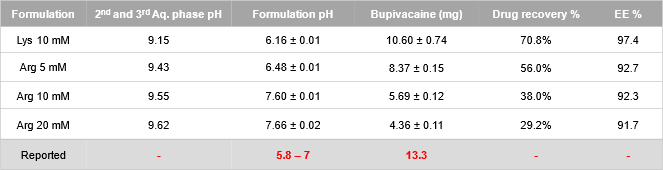 Table 1. Formulation attributes of bupivacaine MVLs prepared with different amino acids with different concentrations, and the pH value of the second and third aqueous phases used during the production
Table 1. Formulation attributes of bupivacaine MVLs prepared with different amino acids with different concentrations, and the pH value of the second and third aqueous phases used during the production