Discovery and Basic Research
Category: Late Breaking Poster Abstract
(M0930-05-32) Theoretical and Experimental Polymer-Polymer Miscibility Prediction: An Insight to In Vivo Compatibility
Monday, October 23, 2023
9:30 AM - 10:30 AM ET

Saad S. Niaz, M.S. (he/him/his)
PhD Researcher
King's College London
SLOUGH, England, United Kingdom- BR
Bahijja Raimi-Abraham, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
King's College London
London, England, United Kingdom - BR
Bahijja Raimi-Abraham, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
King's College London
London, England, United Kingdom - BF
Ben Forbes, Ph.D.
King's College London
London, England, United Kingdom - JH
James Hart, B.S.
BASF SE Pharma Solutions
Stockport, England, United Kingdom 
Lindsay M. Johnson, Ph.D.
Global Technical Marketing Manager
BASF Corporation
New York, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Polymer-polymer miscibility refers to the ability of two polymers to mix in all proportions forming a homogenous phase [1]. Knowledge of miscibility is important for tissue engineering applications – particularly in the generation of hybrid 3D printed polymeric scaffolds. Polymer-polymer miscibility can determine the complementary properties of a polymer composition [2]. Immiscibility can result in a polymer composition being very brittle, reducing the printability of a polymeric scaffold and influencing the composition’s ability to promote cell growth [3]. Typical three-dimensional (3D) printing scaffold fabrication methods include fused deposition modelling (FDM), and bioprinting. Tuning scaffold behaviour through the use of multiple miscible polymers can be advantageous. For example, polylactic acid (PLA) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) hybrid scaffolds have been shown to give enhanced Young modulus and maximum tensile strength when used in combination, and have shown to be a good material for the growth of L929 fibroblast cells [4]. This study aimed to identify miscible polymer combinations using theoretical and experimental approaches to inform polymer selection for scaffold development, and to identify the polymer combinations with optimal cell viability and biocompatibility for the generation of FDM 3D printed polymeric scaffolds.
Methods: Polymer-polymer miscibility and cell viability of PLA, Soluplus (SP), polyvinylpyrrolidone vinyl acetate (Kollidon VA64 (KV64)), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), PVP and their combinations were studied. To understand the nature of the cohesive forces between the polymers, theoretical polymer-polymer miscibility was determined by calculating the solubility parameters of the polymer combinations using the Van Krevelen and Hoftyzer, and Hoy methods. Experimental polymer-polymer miscibility and detection of hydrogen bonding were investigated using heat flux differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) (heating rate of 10ºC/min between 0 ºC and 250 ºC) and attenuated total reflection- fourier infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, respectively. The most miscible polymer combinations were used for cell viability studies in human colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells using the alamar blue cell viability assay and the resulting half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was determined via linear regression.
Results: Theoretical polymer-polymer miscibility calculations (Fig.1a) identified SP and PLA to be the most miscible polymers giving differences between solubility parameter (Δδ) values of less than 10 MPa1/2 when combined with all other polymers whilst PVA was least miscible with all other polymers except SP (Fig.1b) [5]. DSC experiments (Fig.2a) confirmed these results as SP and PLA combinations gave single glass transition (Tg) values in the range of 55°C - 66°C on cooling and PVA combinations largely gave multiple Tg’s [5]. ATR-FTIR studies (Fig.2b) of SP and PLA combinations showed little evidence of hydrogen bonding, with a slight broadening of the peak at 3500 cm-1 corresponding to interaction with the hydrogen bonding donors of SP [6]. In vitro studies (Fig.3) in Caco-2 cells of miscible combinations identified SP and KV64 in a 70/30 w/w% combination to give the highest IC50 of 10905mg/mL (Fig.3c), indicating the incredibly low inhibitory effect of the two materials making them a biocompatible combination. In many instances, Caco-2 cell viability improved greater than 100% when polymers were in combination with one another (Fig. 3a and b), e.g. SP and PVP in a 50/50 w/w% combination, however, the results were not statistically significantly greater than the control.
Conclusion: This study identified miscible polymer combinations using theoretical and experimental methods, which identified SP, PLA, KV64, and PVP combinations to be miscible whilst the majority of PVA combinations were immiscible. Heat-flux DSC miscibility studies experimentally confirmed the theoretical determined results, whilst ATR-FTIR experiments showed little evidence of hydrogen bonding amongst polymers. Caco-2 cell viability studies of miscible combinations found SP50PVP, PVA70SP, and KV6450PVP to enhance Caco-2 cell growth, however, none of the cell viability results were statistically significant compared to the control. IC50 determination of polymer combinations revealed the top five least potent polymer combinations which all contained SP. These results identify potential polymer combinations for the generation of FDM 3D printed hybrid scaffolds for tissue engineering. The top five least potent polymer combinations will be used in future work to generate FDM 3D printed hybrid scaffolds for tissue engineering.
References: [1] Carey FA. Organic Chemistry. 2000.
[2] Di Lorenzo ML. Poly(l-Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) Biobased Biodegradable Blends. Https://DoiOrg/101080/1558372420201850475 2020;61:457–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2020.1850475.
[3] Yang Z, Nollenberger K, Albers J, Craig D, Qi S. Microstructure of an immiscible polymer blend and its stabilization effect on amorphous solid dispersions. Mol Pharm 2013. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp400209w.
[4] Kruk A, Gadomska-Gajadhur A, Dulnik J, Ruśkowski P. The influence of the molecular weight of polymer on the morphology, functional properties and L929 fibroblasts growth on polylactide membranes for tissue engineering. Https://DoiOrg/101080/0091403720201798440 2020;71:45–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2020.1798440.
[5] Meng F, Dave V, Chauhan H. Qualitative and quantitative methods to determine miscibility in amorphous drug–polymer systems. Eur J Pharm Sci 2015;77:106–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJPS.2015.05.018.
[6] Mansur HS, Sadahira CM, Souza AN, Mansur AAP. FTIR spectroscopy characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel with different hydrolysis degree and chemically crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. Mater Sci Eng C 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2007.10.088.
Acknowledgements: We would like to thank the BBSRC and the London Interdisciplinary Doctoral (LiDo) programme for providing funding during this project. We express our gratitude to BASF (Pharma Solutions, USA and Pharma Ingredients and Services, UK) who supported the project and provided the required samples. A special thanks to my supervisors for their support and feedback during the project
.jpg) Fig. 1. Theoretical Polymer-Polymer Miscibility. (a) Solubility parameters (δ) of PLA, PVA, SP, KV64 and PVP. Solubility parameters, with units MPa1/2, were determined using the Hoftyzer-Van Krevelen method and Hoy method. (b) Theoretical Miscible Polymer Combinations. Miscibility was determined using the Hoftyzer-Van Krevelen method and Hoy method.
Fig. 1. Theoretical Polymer-Polymer Miscibility. (a) Solubility parameters (δ) of PLA, PVA, SP, KV64 and PVP. Solubility parameters, with units MPa1/2, were determined using the Hoftyzer-Van Krevelen method and Hoy method. (b) Theoretical Miscible Polymer Combinations. Miscibility was determined using the Hoftyzer-Van Krevelen method and Hoy method.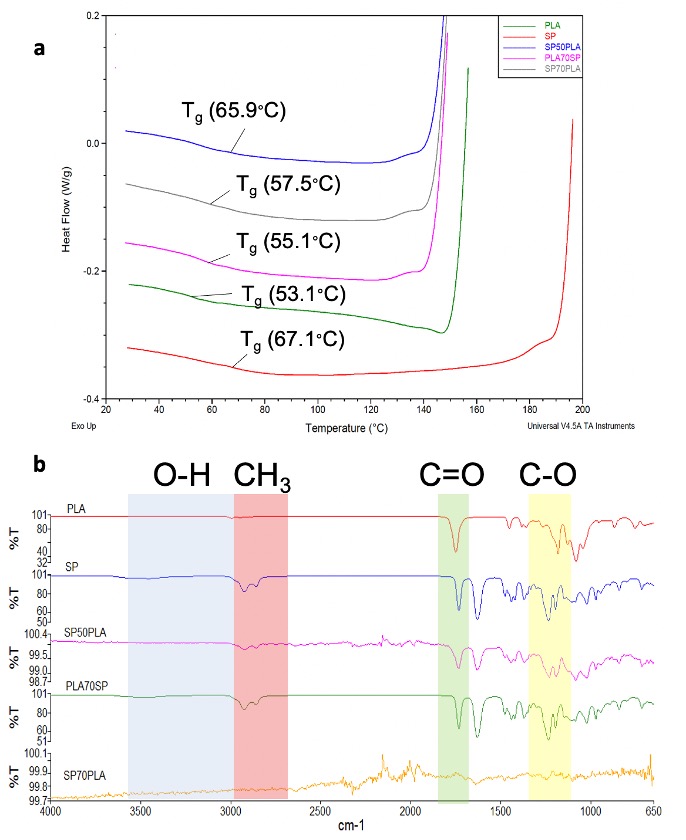 Fig. 2. Experimental Polymer-Polymer Miscibility. (a) DSC thermogram of Polylactic acid (PLA) and Soluplus (SP) combinations. This figure shows the DSC thermogram of PLA and SP in 50/50 (%w/w), 70/30 (%w/w), and 100/0 (%w/w) ratios upon cooling. DSC was performed at 10°C/min in an aluminium open pan system. (b) ATR-FTIR spectra of Polylactic acid (PLA) and Soluplus (SP) combinations. This figure shows the ATR-FTIR spectra of PLA and SP in 50/50 (%w/w), 70/30 (%w/w), and 100/0 (%w/w) ratios and shows the % transmittance (%T) against the wavelength (cm-1). ATR-FTIR was performed on the melted systems obtained from DSC.
Fig. 2. Experimental Polymer-Polymer Miscibility. (a) DSC thermogram of Polylactic acid (PLA) and Soluplus (SP) combinations. This figure shows the DSC thermogram of PLA and SP in 50/50 (%w/w), 70/30 (%w/w), and 100/0 (%w/w) ratios upon cooling. DSC was performed at 10°C/min in an aluminium open pan system. (b) ATR-FTIR spectra of Polylactic acid (PLA) and Soluplus (SP) combinations. This figure shows the ATR-FTIR spectra of PLA and SP in 50/50 (%w/w), 70/30 (%w/w), and 100/0 (%w/w) ratios and shows the % transmittance (%T) against the wavelength (cm-1). ATR-FTIR was performed on the melted systems obtained from DSC.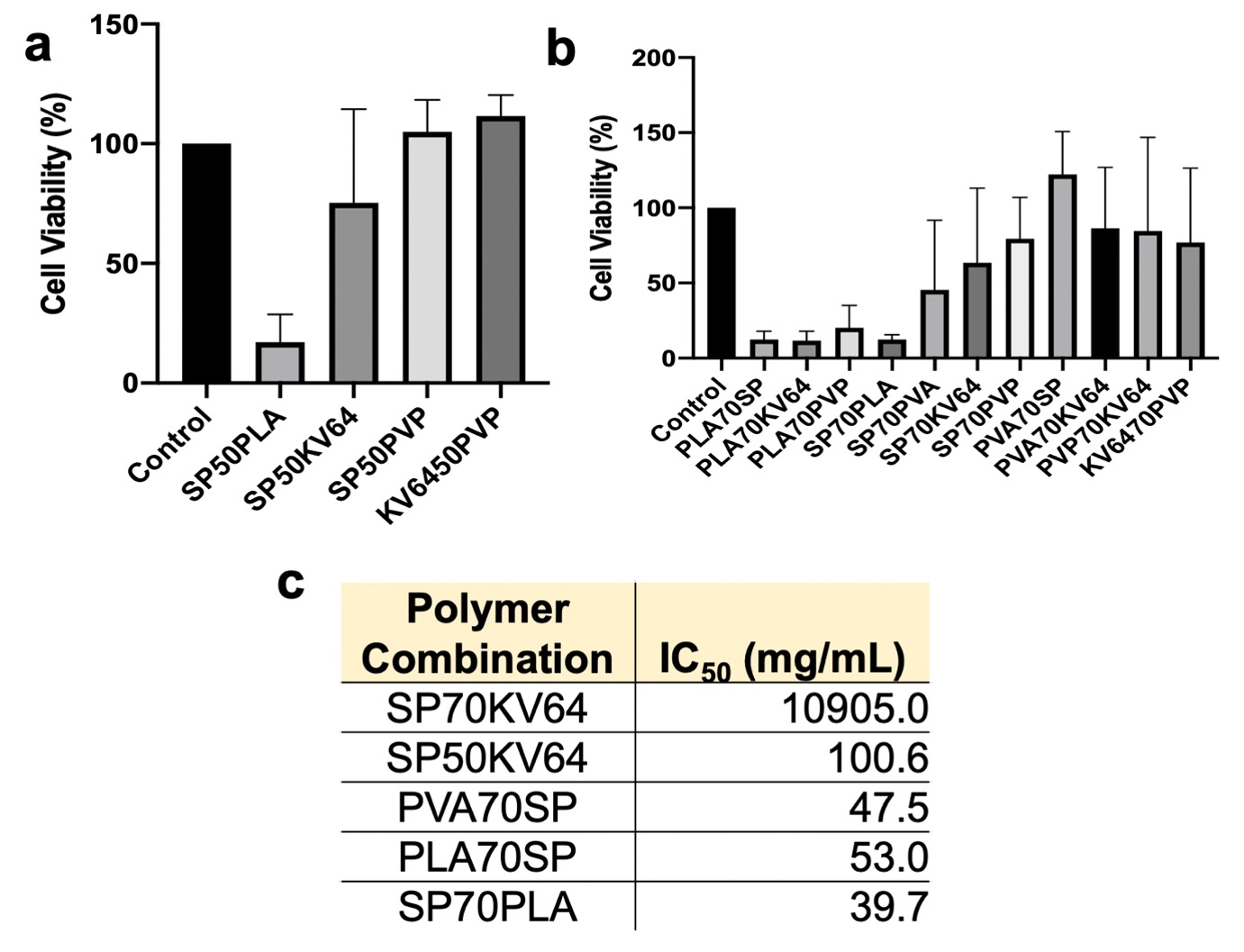 Fig. 3. In Vitro Caco-2 Cell Viability and IC50. (a) Caco-2 Cell Viability of Polymer Combinations at 5mg/mL. Viability of 50/50 (%w/w) polymer combinations. (b) Caco-2 Cell Viability of Polymer Combinations at 5mg/mL. Viability of 70/30 (%w/w) polymer combinations. (c) IC50 Values of Top Five Polymer Combinations. IC50 was determined via nonlinear regression. All data are represented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). * p ≤ 0.05 comparing with a 0mg/mL control.
Fig. 3. In Vitro Caco-2 Cell Viability and IC50. (a) Caco-2 Cell Viability of Polymer Combinations at 5mg/mL. Viability of 50/50 (%w/w) polymer combinations. (b) Caco-2 Cell Viability of Polymer Combinations at 5mg/mL. Viability of 70/30 (%w/w) polymer combinations. (c) IC50 Values of Top Five Polymer Combinations. IC50 was determined via nonlinear regression. All data are represented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). * p ≤ 0.05 comparing with a 0mg/mL control.