Discovery and Basic Research
Category: Poster Abstract
(M1230-04-27) Tangerine-Peel-Derived Nanovesicles Alleviate Hepatic Steatosis in Type 2 Diabetic Mice via Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Flora Disorder
Monday, October 23, 2023
12:30 PM - 1:30 PM ET
- JZ
Junjv Zou
Chinese University of Hong Kong
Hong Kong, Hong Kong - JZ
Junju Zou, Ph.D.
Chinese University of Hong Kong
Hong Kong, Hong Kong - ZZ
Zhong Zuo, Ph.D.
Chinese University of Hong Kong
Hong Kong, Hong Kong - QS
Qianbo Song, Ph.D.
Postgraduate Student
Chinese University of Hong Kong
Hong Kong, Hong Kong - RY
Rong Yu
Hunan University of Chinese Medicine
changsha, Hunan, China (People's Republic) - PS
Pang Chui Shaw, Ph.D.
Chinese University of Hong Kong
Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Presenter (non-author)(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Plants-release exosome-like nanovesicles (PENs) that contain miRNA, bioactive lipids, mRNAs, proteins and many other bioactive small molecules. These PENs exert antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative activities [1]. Tangerine-peel ethanol extracts have demonstrated to possess hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering effects [2, 3]. Herein, we showcased Tangerine-peel-derived nanovesicles (TNVs) isolated from fresh Tangerine-peel could restore the disordered gut microbiota community and mitigate metabolic disorders induced by Type-2 diabetes.
Methods: The TNVs was prepared by differential centrifugation of the aqueous extract of Tangerine. Three groups of male db/db mice were orally administered with 200 mg/kg TNVs (TNVs group), 250 mg/kg metformin (as a positive control) (Met group), vehicle (Model group) and one group of C57BL/6J mice were treated with vehicle (Control group) at once daily for 8 weeks (n=8/group). At the end of the treatment, the blood was collected to evaluate glucose tolerance, insulin tolerance, and blood lipid levels. The levels of key genes involved in liver fatty acid β-oxidation (Cpt1, Cpt2, FGFR4, PGC-1α, PPAR-α, UCP1, SCD-1, Tmem26) and glucose-lipid metabolism (ACC, AMPK, CD36, LXRα, PPAR-γ, SREBP-1) were measured using RT-PCR. Metabolomics analysis of liver metabolites was performed using LC/MS-MS. Gut microbiota composition, short-chain fatty acids and bile acids were monitored using 16S rRNA sequencing, GC/MS and UHPLC-MS/MS, respectively. Subsequently, effects of TNVs (200 μg/ml) on lipid accumulation and glycolysis were evaluated on 3T3-L1 cells via monitoring the expressions of PPAR-γ, SREBP1, CD36, LXR-α, ACC, G6Pase, GLUT2, PCK1, PEPCK, AMPK and PGC-1α.
Results: TNVs significantly reduced body weight (Figure 1.A, p < 0.05) together with blood lipids (TG, TC, LDL-c, HDL-c) (Figure 1.C, p < 0.01) and inhibited insulin resistance (FBG, insulin, HOMA-IR) (Figure 1.B, p < 0.01) in db/db mice. Histological examination results showed that TNVs could also significantly facilitate intestinal mucosal repair based on the crypt depth, villus length, ratio of villus crypt and quantity of goblet cells (Figure 1.D, E, p < 0.01). Additionally, TNVs regulated the dysbiosis of gut microbiota and enriched the abundance of Bacteroidota, Proteobacteria, Lactobacillus and Muribaculaceae (Figure 2.A, B, C, p < 0.01). regulated Liver ABC transporters, purine metabolism, taurine metabolism, amino acid biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism (Figure 3.A) particularly SCFA (Figure 2.D) and bile acid metabolism (Figure 2.E) were regulated as well. Furthermore, TNVs restored the expression of key genes in glucose and lipid metabolism (ACC, AMPK, CD36, LXRα, PPAR-γ, SREBP-1) (Figure 3.B, p < 0.01) while activating the expression of genes related to glycolysis (G6Pase, GLUT2, PCK1, PEPCK) ( Figure 3.C, p < 0.01). Further cell based mechanistic studies revealed that TNVs reduced lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells via regulating the genes related with glucose and lipid metabolism (UCP1, FGFR4, PRDM16, PGC-1α, Tmem26, Cpt1, Cpt2 and PPAR-α) (Figure 3.D, p < 0.01).
Conclusion: We for the first time demonstrated that TNVs could significantly improve glucose and lipid metabolism via activating the expression of genes related to fatty acid β-oxidation and glycolysis.
References: [1] Q. Yi, Z. Xu, A. Thakur, K. Zhang, Q. Liang, Y. Liu, Y. Yan, Current understanding of plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles in regulating the inflammatory response and immune system microenvironment, Pharmacol Res 190 (2023) 106733.
[2] G.H. Lee, C. Peng, S.A. Park, T.H. Hoang, H.Y. Lee, J. Kim, S.I. Kang, C.H. Lee, J.S. Lee, H.J. Chae, Citrus Peel Extract Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced NAFLD via Activation of AMPK Signaling, Nutrients 12(3) (2020).
[3] M. Hu, L. Zhang, Z. Ruan, P. Han, Y. Yu, The Regulatory Effects of Citrus Peel Powder on Liver Metabolites and Gut Flora in Mice with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), Foods 10(12) (2021).
Acknowledgements: Hong Kong Scholar program and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Li Dak Sum Yip Yio Chin R & D Center for Chinese Medicine at The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
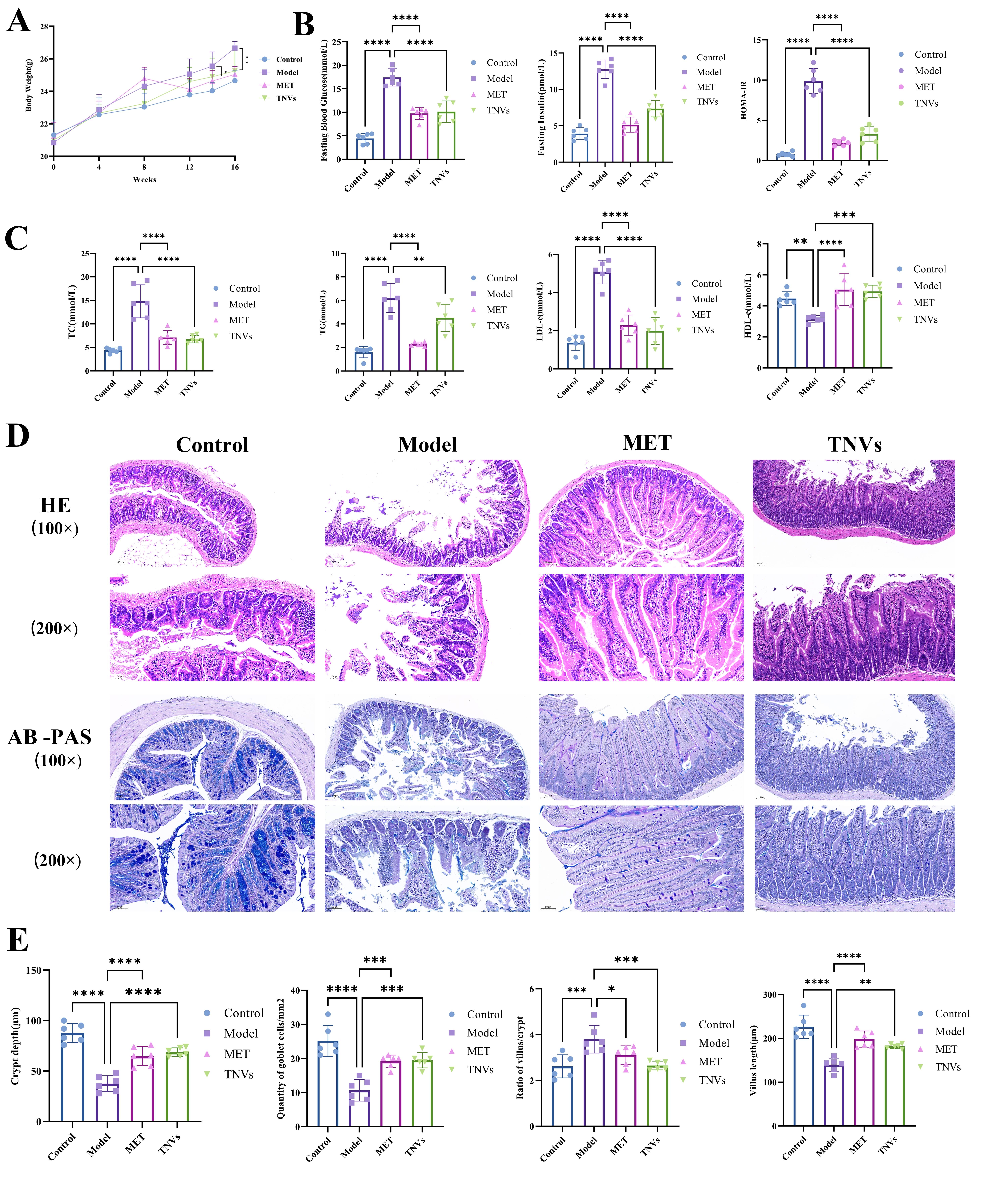 Figure 1. Effect of TNVs on colon pathology and biochemical parameters. (A) Body weight. (B) FBG, insulin, HOMA-IR levels. (C) Serum lipid levels. (D) Colon hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and Alcian Blue Periodic acid Schiff (AB-PAS) staining. (E) Crypt depth, villus length, ratio of villus crypt and quantity of goblet cells levels.
Figure 1. Effect of TNVs on colon pathology and biochemical parameters. (A) Body weight. (B) FBG, insulin, HOMA-IR levels. (C) Serum lipid levels. (D) Colon hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and Alcian Blue Periodic acid Schiff (AB-PAS) staining. (E) Crypt depth, villus length, ratio of villus crypt and quantity of goblet cells levels.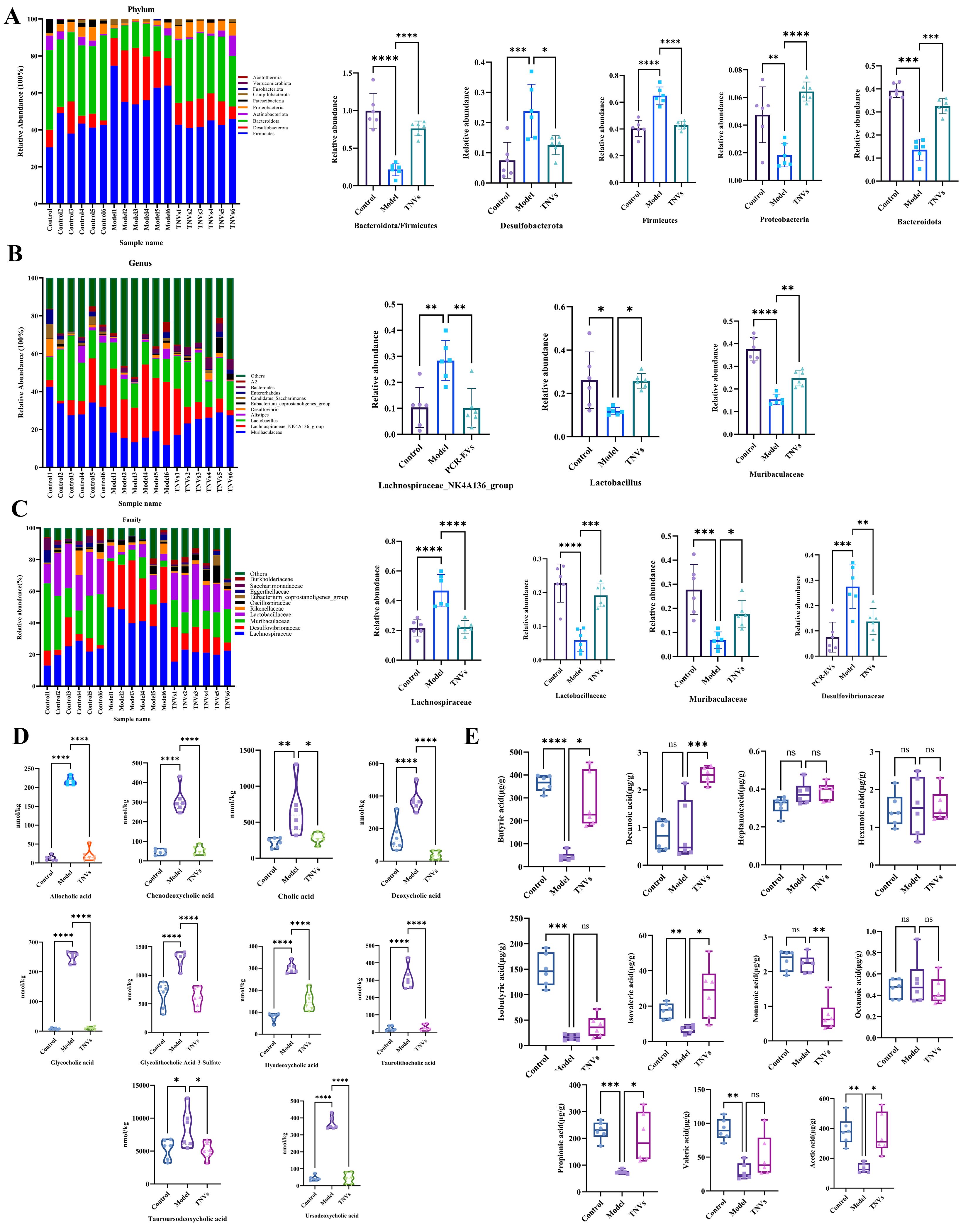 Figure 2. TNVs altered the metabolic profiles of the gut microbiota. (A) The phylum level of gut microbiota. (B) The genus level of gut microbiota. (C) The family level of gut microbiota. (D) The level of bile acids in the gut microbiota. (E) Levels of SCFAs in gut microbiota.
Figure 2. TNVs altered the metabolic profiles of the gut microbiota. (A) The phylum level of gut microbiota. (B) The genus level of gut microbiota. (C) The family level of gut microbiota. (D) The level of bile acids in the gut microbiota. (E) Levels of SCFAs in gut microbiota.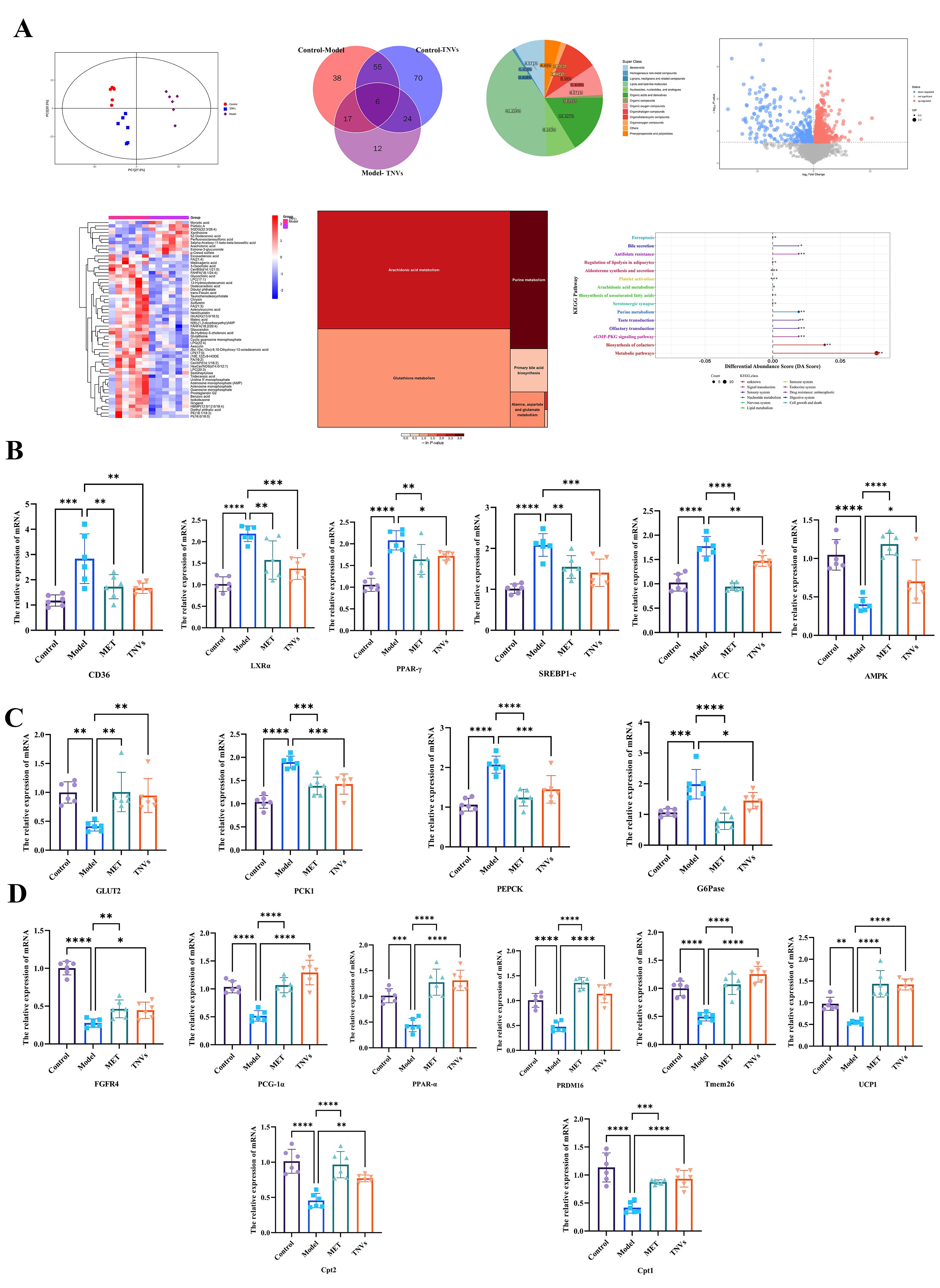 Figure 3. The effect of DOP on lipid metabolism. (A) Liver metabolomics analysis. (B) Expression levels of CD36, LXR-α, PPAR-γ, SREBP1-c, ACC and AMPK genes in liver. (C) Expression levels of GLUT2, PCK1, PEPCK and G6Pase genes in liver. (D) Expression levels of FGFR4, PCG-1α, PPAR-α, PRDM16, Tmem16, UCP1, Cpt1 and Cpt2 genes in 3T3-L1 cell.
Figure 3. The effect of DOP on lipid metabolism. (A) Liver metabolomics analysis. (B) Expression levels of CD36, LXR-α, PPAR-γ, SREBP1-c, ACC and AMPK genes in liver. (C) Expression levels of GLUT2, PCK1, PEPCK and G6Pase genes in liver. (D) Expression levels of FGFR4, PCG-1α, PPAR-α, PRDM16, Tmem16, UCP1, Cpt1 and Cpt2 genes in 3T3-L1 cell.