Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Poster Abstract
(T1230-11-73) Injectable Antibacterial Dressings for the Prevention of Bacterial Biofilm in Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS)
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
12:30 PM - 1:30 PM ET
- BY
Bhuvanesh Yathavan, MS
University of Utah
Salt Lake City, Utah, United States - BY
Bhuvanesh Yathavan, MS
University of Utah
Salt Lake City, Utah, United States - TC
Tanya Chhibber, MS
University of Utah
salt lake city, Utah, United States - DS
Douglas Steinhauff, Ph.D.
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
salt lake city, Utah, United States - AP
Abigail Pulsipher, Ph.D.
University of Utah
salt lake city, Utah, United States - JA
Jeremiah Alt, Ph.D.
University of Utah
salt lake city, Utah, United States - HG
Hamidreza Ghandehari, Ph.D.
University of Utah
salt lake city, Utah, United States - PJ
Paris Jafari, Ph.D.
University of Utah
salt lake city, Utah, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a chronic health condition that affects the nasal and paranasal sinus cavities. Currently, CRS affects approximately 11.5% of the U.S. adult population and imposes a substantial societal and economic burden. CRS is characterized by mucosal barrier disruption and epithelial cell death that can lead to opportunistic bacterial invasion, recurrent infections, and biofilm formation [1, 2]. Endoscopic sinus surgery is performed in CRS patients who fail medical management. However, bacterial biofilm formation following surgery reduces the efficacy of surgical intervention [3]. Current treatment options to prevent biofilm formation are systemic and topical antibiotics. Systemic antibiotics can be effective against planktonic bacteria but are suboptimal in eradicating bacterial biofilms. Continuous use of systemic antibiotics, moreover, is associated with antibiotic resistance. Topical antibiotics have negligible effect in preventing bacterial biofilms in patients with CRS. The main objective of this study is to develop an in-situ gelling drug delivery system that conforms to the sinonasal cavity and provides the controlled release of silver nanoparticles (AgNp) and hyaluronic acid (HA) for the prevention of bacterial biofilm in CRS.
Methods: In situ gelling delivery matrix was formulated by combining optimized doses of silver nanoparticle (AgNp) and hyaluronic acid (HA) with silk-elastinlike protein polymer (SELP) [4]. The antibacterial activity of AgNp was optimized using the macrodilution method against Pseudomonas (P.) aeruginosa and Staphylococcus (S.) aureus. The anti-inflammatory effect of the formulation was determined with the aid of an inflamed human macrophage cell line. The cytocompatibility of the formulation containing different concentrations of AgNp (125, 625, 1250 µg/ml) was tested using human nasal epithelial cells. The cytocompatible formulation containing the highest concentration of AgNp was used to determine the antibacterial property against planktonic and biofilm prevention using viable count and colony biofilm assays, respectively. Rheological properties such as viscosity, storage modulus, and loss modulus were determined to confirm if the formulation can be delivered via a catheter.
Results: The concentration for the antibacterial activity of AgNp and the anti-inflammatory activity of HA was optimized to be 125 µg/ml and 2 mg/ml, respectively. HNEpC treated with formulation containing AgNp at 625 µg/ml concentration showed 80% cell viability (Fig 1) and was selected for further experiments. The SELP formulation with AgNP showed increased cell viability compared to AgNP solution at similar concentrations enabling us to deliver higher concentrations of AgNp safely. The viable count assay showed that the formulation effectively restricted the proliferation of both strains of bacteria (Fig 1). The colony biofilm assay showed that the formulation effectively prevented biofilm formation (Fig 2). The rheological studies of the combined formulation showed that the formulation was liquid at room temperature and formed a hydrogel at physiological temperature (Fig 3), enabling a sustained release of AgNp.
Conclusion: We developed an in-situ gelling drug delivery system that can be easily administered via a catheter and has an in-vitro antibacterial activity to prevent bacterial biofilm formation.
References: (1) Schleimer. Annu Rev Pathol. (2017) 12: 331-357.
(2) Stevens et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol, (2015) 136(6): 1442-1453.
(3) Hsu and Peters. Am J Rhinol Allergy, (2011) 25(5): 285-290.
(4) Jensen et al. Journal of Controlled Release 263 (2017) 46–56.
Acknowledgements:Financial support for this project was provided by the University of Utah Center for Clinical and Translational Sciences Seed Grant and University of Utah College of Pharmacy Skaggs Fellowship.
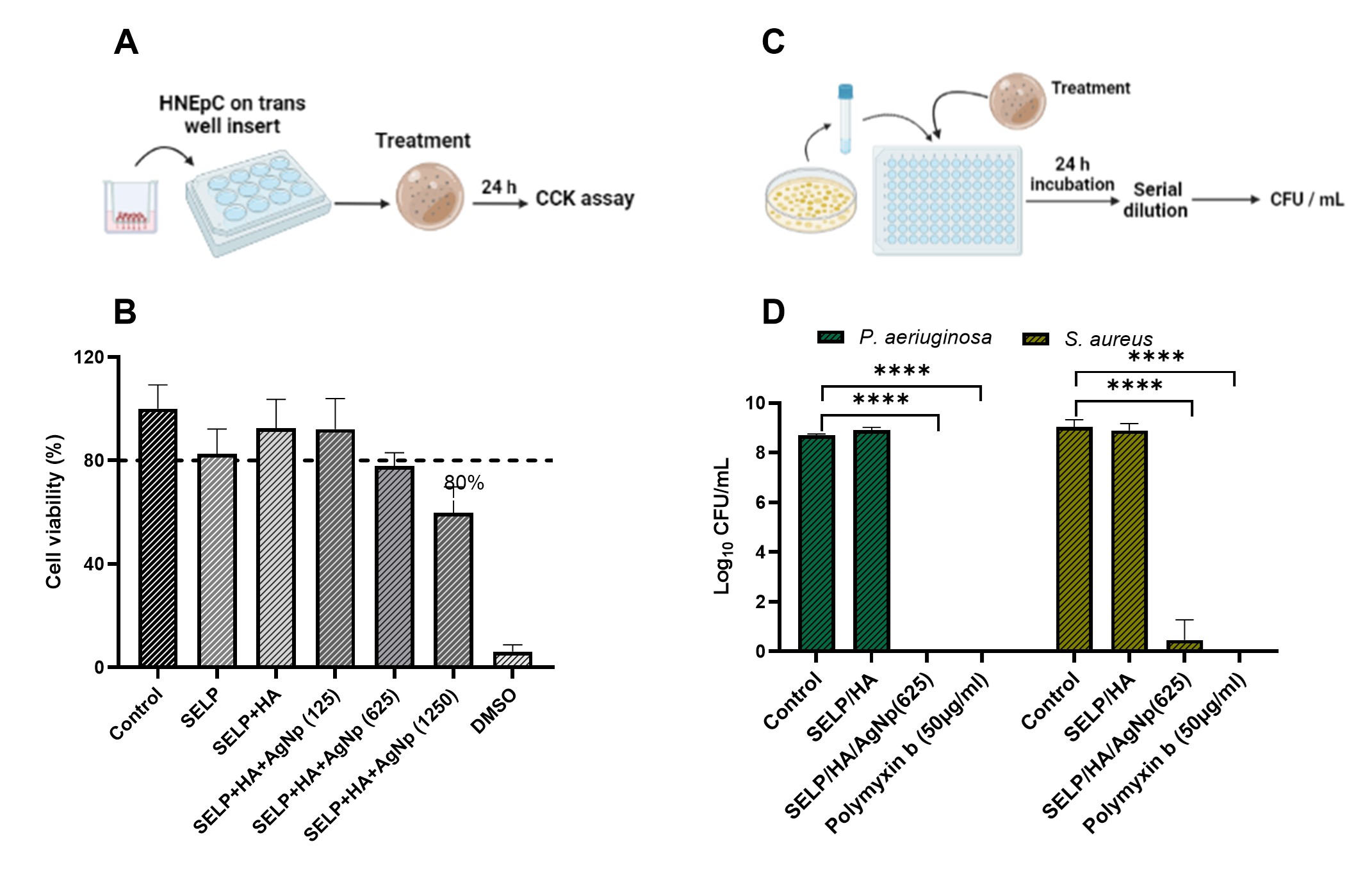 Fig 1: Cytocompatibility and cell viability assay. A) Schematic illustration of cytocompatibility experiment. B) Cell Viability % of HNEpCs after 24-hour treatment with different formulations. C) Schematic illustration of cell viability experiment. D) Impact on log CFU/ml due to treatment with different formulations. N ≥ 3, Data is represented as the mean ± SD. (****p < 0.0001). Human nasal epithelial cells (HNEpC), silk-elastinlike protein polymer (SELP), hyaluronic acid (HA), silver nanoparticle (AgNp), colony forming units (CFU).
Fig 1: Cytocompatibility and cell viability assay. A) Schematic illustration of cytocompatibility experiment. B) Cell Viability % of HNEpCs after 24-hour treatment with different formulations. C) Schematic illustration of cell viability experiment. D) Impact on log CFU/ml due to treatment with different formulations. N ≥ 3, Data is represented as the mean ± SD. (****p < 0.0001). Human nasal epithelial cells (HNEpC), silk-elastinlike protein polymer (SELP), hyaluronic acid (HA), silver nanoparticle (AgNp), colony forming units (CFU). 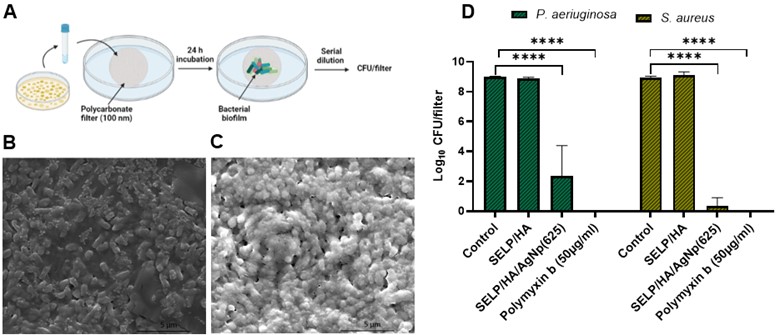 Fig 2: SELP formulation with HA and AgNP significantly reduced biofilm formation. A) Schematic illustration of colony biofilm experiment. B) P. aeruginosa biofilm formation on control filters. C) S. aureus biofilm formation on control filters. D) Influence on CFU / filter due to treatment with different formulations. N ≥ 3, Data is represented as the mean ± SD. (****p < 0.0001). Silk-elastinlike protein polymer (SELP), hyaluronic acid (HA), silver nanoparticle (AgNp), colony forming units (CFU).
Fig 2: SELP formulation with HA and AgNP significantly reduced biofilm formation. A) Schematic illustration of colony biofilm experiment. B) P. aeruginosa biofilm formation on control filters. C) S. aureus biofilm formation on control filters. D) Influence on CFU / filter due to treatment with different formulations. N ≥ 3, Data is represented as the mean ± SD. (****p < 0.0001). Silk-elastinlike protein polymer (SELP), hyaluronic acid (HA), silver nanoparticle (AgNp), colony forming units (CFU).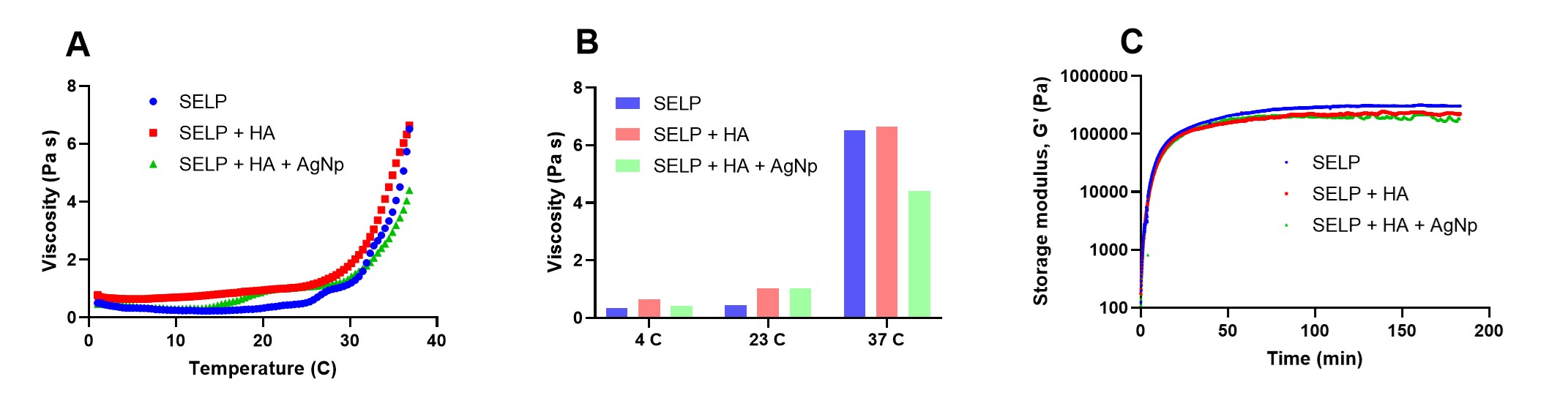 Fig 3: Rheological properties of the formulation. A) Viscosity as a function of temperature. B) Viscosity at different temperatures. C) Storage modulus of the formulation. Silk-elastinlike protein polymer (SELP), hyaluronic acid (HA), silver nanoparticle (AgNp), colony forming units (CFU).
Fig 3: Rheological properties of the formulation. A) Viscosity as a function of temperature. B) Viscosity at different temperatures. C) Storage modulus of the formulation. Silk-elastinlike protein polymer (SELP), hyaluronic acid (HA), silver nanoparticle (AgNp), colony forming units (CFU).