Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Poster Abstract
(W1030-11-70) Biodegradable Cationic Nanoparticles Prepared with Methylmethacrylate Copolymers Derivatives for Immune Activation and Cancer Immunotherapy
Wednesday, October 25, 2023
10:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
- AL
Alf Lamprecht, Ph.D. (he/him/his)
University of Bonn
Bonn, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany - AC
Angel Castaneda Ruiz, MS (he/him/his)
University of Bonn
Bonn, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany - MS
Maryam Alsadat Shetab Boushehri, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
University of Bonn
Bonn, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany - MA
Mohamed Ehab Ali, Ph.D.
University of Bonn
Bonn, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany - TF
Thilo Faber (he/him/his)
University of Bonn
Bonn, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Given their specific size, nanoparticles (NPs) are often identified by the immune system and interact therewith. The outcome depends on factors e.g. NP size, surface charge, hydrophobicity, morphology and the state of immune system’s activity [1]. Particularly, there are reports of cationic NPs activting the immune response. A previous study in our lab has demonstrated the immunostimulatory properties of cationic ammonio methacrylate copolymer NPs (AMCNPs) to be exploitable for drug-free cancer immunotherapy [2]. An important issue however, was the non-biodegradability of AMCNPs, and whether their immunotherapeutic potentials could be translated in context of a biodegradable system. The present study sought to address this problem through the synthesis of biodegradable cationic NPs using methylmethacrylate copolymer derivatives. These were then investigated in terms of physicochemical properties, in vitro biodegradability, interactions with immune cells and immunotherapeutic potentials in vivo.
Methods: NPs were prepared using methyl methacrylate (MMA) and cationic trimethylammoniumethylmethacrylate (TMAEMC) monomers (Figure 1-A) through modified free radical polymerization [3]. Briefly, 2,4-dimetheyl-6-tert-butylpehol and hydroquinone monomethyl ether were base- and acid-extracted from MMA and TMAEMC, respectively. For NP synthesis, a constatntly stirred polymerization medium (78 °C) containg distilled H2O and (CH3)2CO was used. MMA and TMAEMC monomers were added in succession and polymerization was initiated using pre-tempered 0.03% (w/v) aquoeus ammonium persulfate solution. The reaction was terminated after 24 h, and the mixture was dialyzed for 72 h against distilled H2O using a 50 kDa dialysis membrane under constant stirring. NPs were characterized in term of size, zeta potential (Nanoparticle Analyzer SZ-100; Horiba) and morphology (focused ion beam-scanning electron microscope; FEI). To evaluate in vitro biodegradability, freeze-dried nanoparticles were redispered in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH=7.4) along with trypsin (0.2 mg/mL), esterase (1 mg/mL), or pepsin (0.5 mg/mL). Samples were incubated at 37 °C for different periods, following which the debris was removed by centrifugation and particle size was measured. Using Quanti BlueTM (Invivogen) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (Thermofisher Scientific), the ability of NPs to induce nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) and tumor necrosis alpha (TNF-a) in murine macrophage-like cells J774-DualTM (Invivogen) and J774-A1 (Sigma) was investigated. NP toxicity was determined using tetrazolium (MTT) assay. Finally, the immunotherapeutic potentials of NPs was investigated in vivo. 6-week-old male BALB/c mice were injected with 3x105 C26 colorectal cancer cells (NCI) in their right flank. Treatment began once the tumor approached 40-50 mm3 as biweekly peritumoral injections of PBS or NPs (10 mg/mL). Tumor volume was calculated biweekly. Treatment was terminated once the tumor volume surpassed 1000 mm3, upon complete remission, a body condition score of 1 combined with poor hair coat and severe lethargy, or more than 15% weight loss.
Results: The size and zeta potential of the synthesized NPs were 179±7.3 nm (PDI=0.177) and 31.7±3.5 mV, respectively. Nanoparticles had a round morphology (Figure 1-B). In vitro biodegradation studies revealed that while the size of NPs did not change significantly on their own, co-incubation with esterase and pepsin led to a complete disintegration of the particles as soon as 4 h, while tripsin only marginally reduced the particle size after 24 h (Table 1). The results of the cell culture experiments demonstrated that MMA-TMAEMC NPs could stimulate macrophages, and induce TNF-α secretion through NF-κB activation (Figures 1-C and 1-D). In both cases, the immunostimulatory properties of NPs were most potent at high concentrations. Given the NP toxicity for J774.A1 cells at 3000 µg/mL (LC50=399±17 µg/mL), TNF-α induction at this concentration was negligible. Yet NPs could significantly induce cellular NF-κB prior to the loss of viability.3 in less than 35 days post-tumor inoculation, only one animal in NP-treated group surpassed this threshold on day 85. Experiments on four animals was terminated due to localized immunological reactions, but only after receiving at least 10 doses (1 mg NP/dose). Furthermore, one animal underwent complete lasting remission. The mean survival estimation for the NP-treated group was significantly longer than that of control group (72.6 vs. 32 days, respectively; Figure 2-B).
Conclusion: In this work, methacrylate copolymer derivatives MMA and TMAEMC could be used to successfully synthesize biodegradable cationic NPs. Under physiological conditions, NPs were quickly broken down by esterase and pepsin. Comparatively, tripsin could change the particle size much more slowly. NPs could activate NF-κB and lead to the secretion of TNF-α from unpolarized macrophages. Peritumoral injection of NPs led to a significant retardation of tumor growth and even complete remission. However, further research should be dedicated to the optimization of the inflammatory properties of MMA-TMAEMC NPs by chaning the ratio of the cationic monomer to reduce the localized inflammatory side effects. Furthermore, the biodegradability of the NPs should be investigated in vivo.
References: [1] B.S. Zolnik, Á. González-Fernández, N. Sadrieh, M.A. Dobrovolskaia, Minireview: Nanoparticles and the Immune System, Endocrinology. 151 (2010) 458–465. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-1082.
[2] M.A. Shetab Boushehri, V. Stein, A. Lamprecht, Cargo-free particles of ammonio methacrylate copolymers: From pharmaceutical inactive ingredients to effective anticancer immunotherapeutics, Biomaterials. 166 (2018) 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.02.053.
[3] F. Hoffmann, J. Cinatl, H. Kabicková, J. Kreuter, F. Stieneker, Preparation, characterization and cytotoxicity of methylmethacrylate copolymer nanoparticles with a permanent positive surface charge, Int. J. Pharm. 157 (1997) 189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-5173(97)00242-1.
Acknowledgements:The authors have no conflict of interests to report.
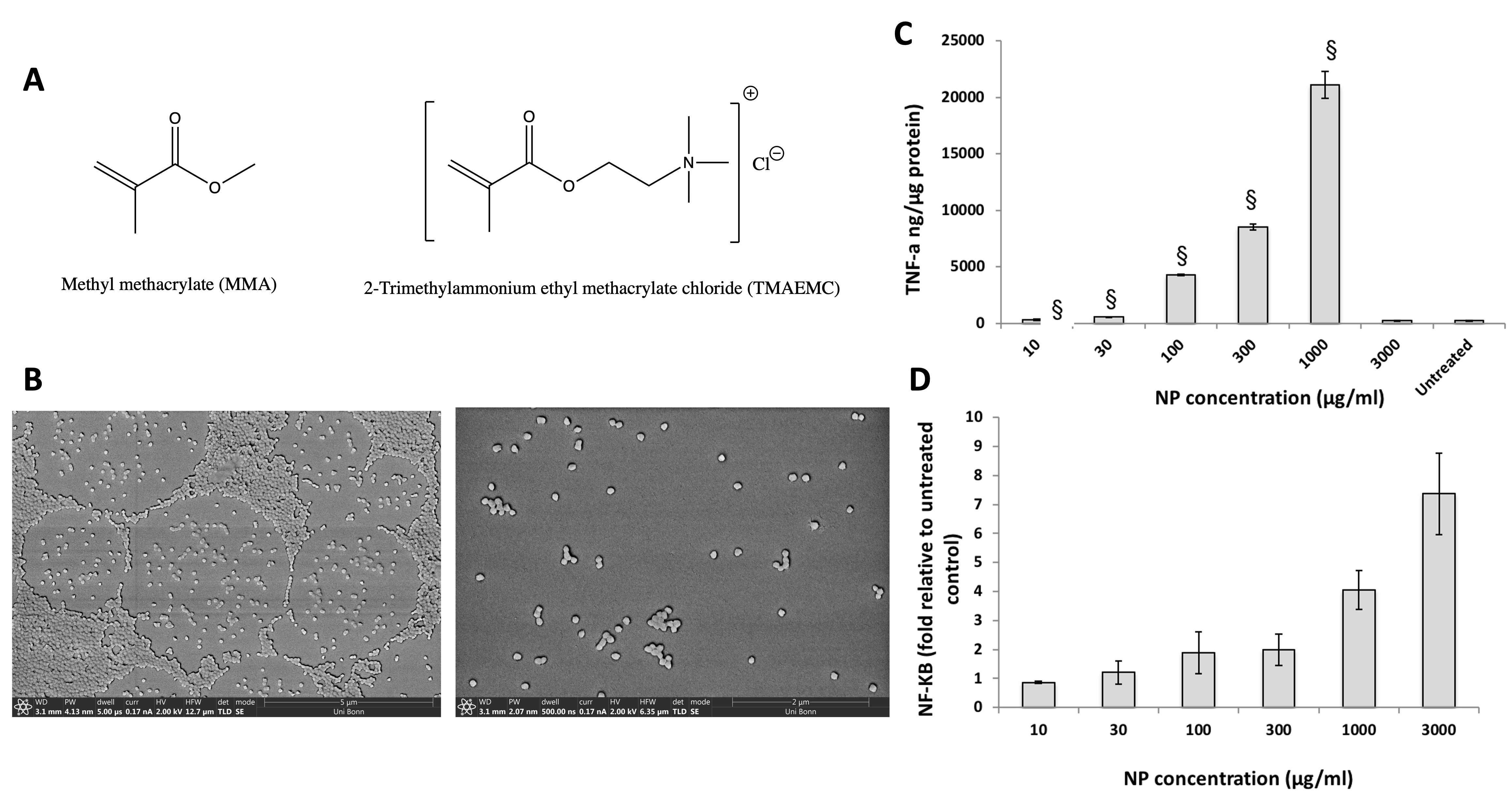 Figure 1- (A) Chemical structure of the monomers used for the synthesis of MMA-TMAEMC cationic nanoparticles (NPs), (B) Scanning electron microscopic images of the developed NPs revealing a spherical morphology, (C) NP-mediated induction of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF- and (D) the inflamma-tory mediator NF-B in J774 macrophage-like cells. § p < 0.05 compared to untreated control.
Figure 1- (A) Chemical structure of the monomers used for the synthesis of MMA-TMAEMC cationic nanoparticles (NPs), (B) Scanning electron microscopic images of the developed NPs revealing a spherical morphology, (C) NP-mediated induction of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF- and (D) the inflamma-tory mediator NF-B in J774 macrophage-like cells. § p < 0.05 compared to untreated control.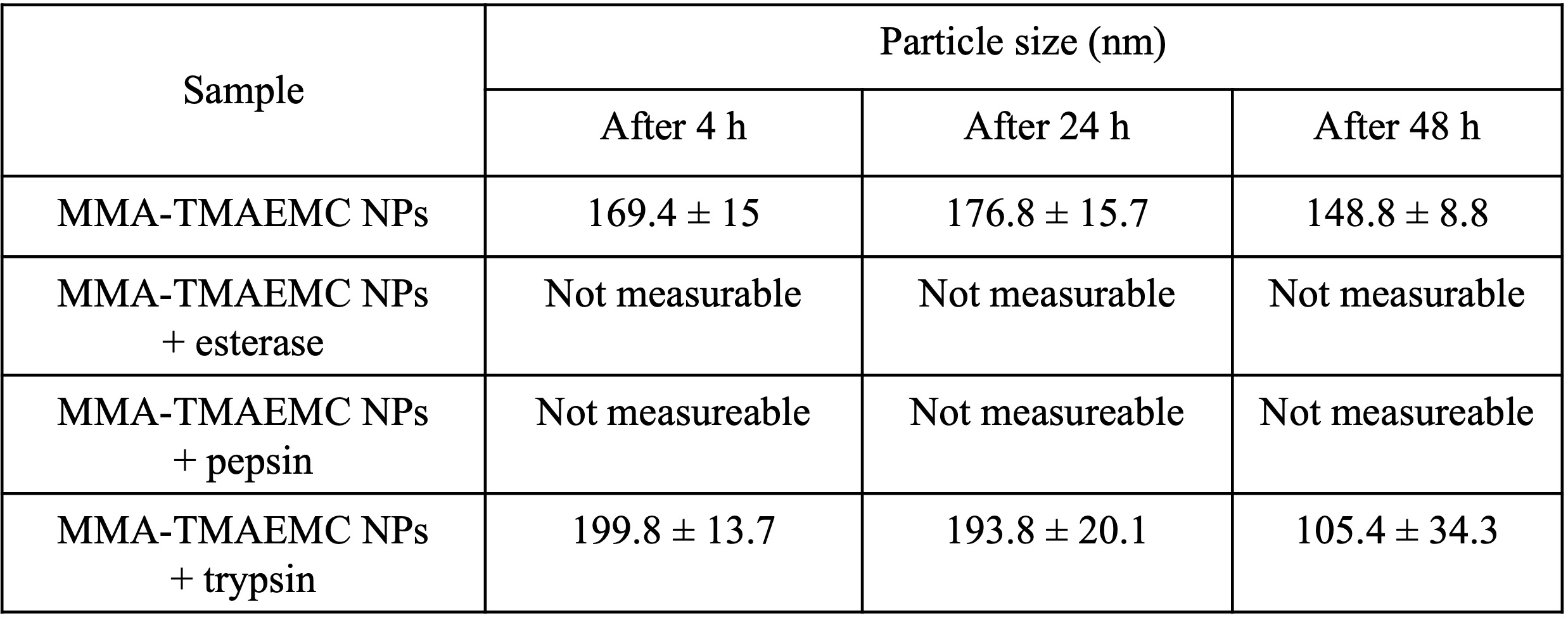 Table 1- Change in NP size following incubation in the absence and presence of different enzymes (es-terase, pepsin and trypsin) under biorelevant conditons (pH=7.4, T=37 °C)
Table 1- Change in NP size following incubation in the absence and presence of different enzymes (es-terase, pepsin and trypsin) under biorelevant conditons (pH=7.4, T=37 °C)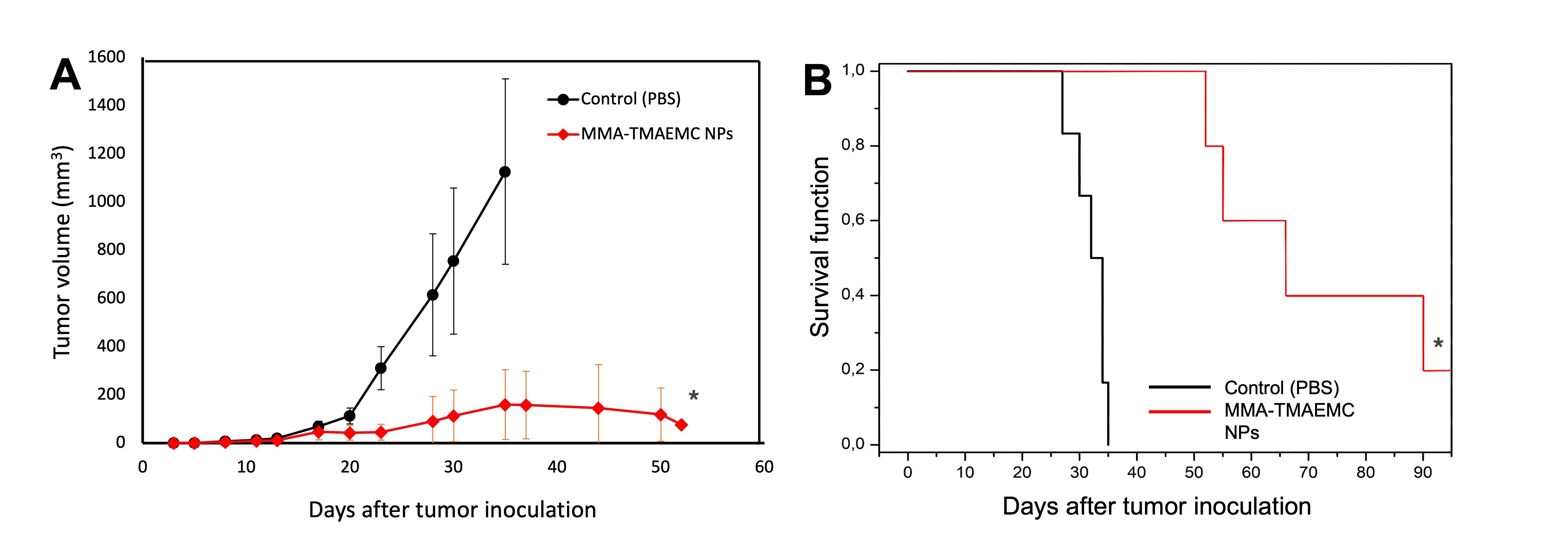 Figure 2- (A) Tumor volume (n=6) and (B) survival analysis of C26 tumor-bearing mice having received biweekly peritumoral injections of PBS or MMA-TMAEMC NPs. Log-rank analysis revealed a signifi-cant increase in the mean survival of the mice following NP treatment (p < 0.05)
Figure 2- (A) Tumor volume (n=6) and (B) survival analysis of C26 tumor-bearing mice having received biweekly peritumoral injections of PBS or MMA-TMAEMC NPs. Log-rank analysis revealed a signifi-cant increase in the mean survival of the mice following NP treatment (p < 0.05)