Formulation and Delivery - Biomolecular
Category: Poster Abstract
(M1030-11-70) Controlled Release Edaravone Nanosuspension: A Translational Therapeutic Approach for the Prevention of Preterm Birth
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
- SS
Sruthi Sarvepalli, MS (she/her/hers)
Doctoral Fellow
St. John's University
newark, New Jersey, United States - SS
Sruthi Sarvepalli, MS (she/her/hers)
Doctoral Fellow
St. John's University
newark, New Jersey, United States - KP
Ketan Patel, Ph.D.
St. John's University
Jamaica, New York, United States - SR
Sandra Reznik, M.D., Ph.D.
St. John's University
Queens, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Preterm birth is when a baby is born too soon before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Each year, 15 million preterm births are predicted to occur worldwide and is the leading cause of infant mortality and long-term disability in children. Among various risk factors, infection associated with oxidative stress and inflammation is the major reason for which a strong association to induce spontaneous parturition is established at the molecular level (Fig 1a). Unfortunately, there is no FDA approved therapy available for this. Present management to delay the preterm labor include antibiotics, progesterone, antenatal corticosteroids and tocolytic agents. Thus, there is a critical need for novel therapies. With this background, we are motivated to investigate edaravone, an FDA approved molecule that has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It has also been reported to reduce lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced inflammation. To delay the preterm labor, it is also important to maintain the drug concentrations in the blood within the desired range. For this, translatable controlled release nanosuspension formulation is considered since high drug loading is required pairing with less invasive subcutaneous route of administration. Thus, the purpose of this research is to develop novel, stable, injectable edaravone nanosuspension and establish its efficacy and safety for the prevention of preterm birth.
Methods: Edaravone nanosuspension is prepared using NETZSCH DeltaVita® 1 (NETZSCH Premier Technologies, LLC. PA, USA) dual centrifugation (DC) nano-milling method. In brief, edaravone is dispersed in the distilled water containing parenteral grade stabilizers including bovine serum albumin (BSA), lecithin, poloxamer-407 and hyaluronic acid alone and in different combinations. Nano milling was carried out at 0.3 mm milling beads at -15 °C with 1h of milling at 1500 rpm (Fig 1b). To improve the stability of edaravone, lowering of the pH to 4.5 that reduces the formation of edaravone anion in aqueous medium and solidifying by freeze-drying approaches are considered. Based on the stability and physical characteristics of the nanosuspensions including particle size, poly dispersity index (PDI), %nano yield, final formulation is optimized. Further formulation studies include differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), powdered x-ray diffraction (PXRD), in vitro release, stability and injectability are performed. In vitro biological efficacy and safety of the formulation are tested by studying the oxidative stress and inflammatory markers like reactive oxygen species (ROS), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), interleukins (IL-1β, IL-6) and cell viability in LPS treated murine macrophages (RAW264.7) and human placental trophoblasts (HTR-8/SVneo). Further to confirm its in vivo efficacy LPS induced preterm labor model in CD1 pregnant mice is in progress.
Results: The nanosuspension formulations stabilized by hyaluronic acid and poloxamer resulted in phase separation. BSA alone and in combination with lecithin gave stable nano suspension formulations. Since, BSA forms aggregates at acidic pH, to further improve edaravone’s stability, all the stable nano suspensions are solidified by freeze drying with mannitol. Formulations containing lecithin are precipitated upon redispersion after freeze drying, while BSA alone stabilized batches are easily re-dispersible. Further considering the particle size (281.1nm, Fig 1d) and percent nano yield, the final optimized formulation that is stabilized by 10% BSA was selected for further studies. Controlled release of edaravone (44.7 ±4.5%) is observed from the nanosuspension within 24h with no burst release. By the end of Day 4, 82.88±6.85% of edaravone is recovered in the release medium (Fig 1e). Higuchi kinetic model is the best fitted model for this profile indicating that, the release is following the Fickian diffusion. The final formulation is found to be injectable through 181/2G till 26G that are suitable for subcutaneous route applications. Formulation is found to be stable when stored under refrigerated (4⁰C) conditions for at least one month and further investigation is ongoing at 2- and 3-month time points as well as at room temperature conditions. The final formulation as well as the pure drug have reduced LPS induced ROS levels in RAW264.7 (Fig 2a) and HTR-8/SVneo cells (Fig 3a) and TNF-α levels in RAW264.7 cells (Fig 2b) with chronic exposure giving the better outcome compared to the acute exposure at 5 (p < 0.001) and 10 µM. These concentrations are found to be safe in HTR-8/SVneo cells from cell viability study (Fig 3b). Further inducible nitric oxide levels and inflammatory markers and in vivo studies are under progress.
Conclusion: Overall, our research provides convincing evidence of the BSA stabilized edaravone nanosuspension in preventing infection associated inflammation induced preterm labor through in vitro assays in RAW264.7 and HTR-8/SVneo cells. This is the very first research work involving developing the controlled release injectable edaravone nanosuspension formulation and establishing its efficacy to prevent preterm labor. While in vitro biological assay results are promising, further in vivo studies are under investigation to support the proof of concept.
References: 1. Frey HA, Klebanoff MA, The epidemiology, etiology, and costs of preterm birth, Seminars in Fetal & Neonatal Medicine (2016).
2. Atallah, M., Yamashita, T. & Abe, K. Effect of edaravone on pregnant mice and their developing fetuses subjected to placental ischemia. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 19, 19 (2021).
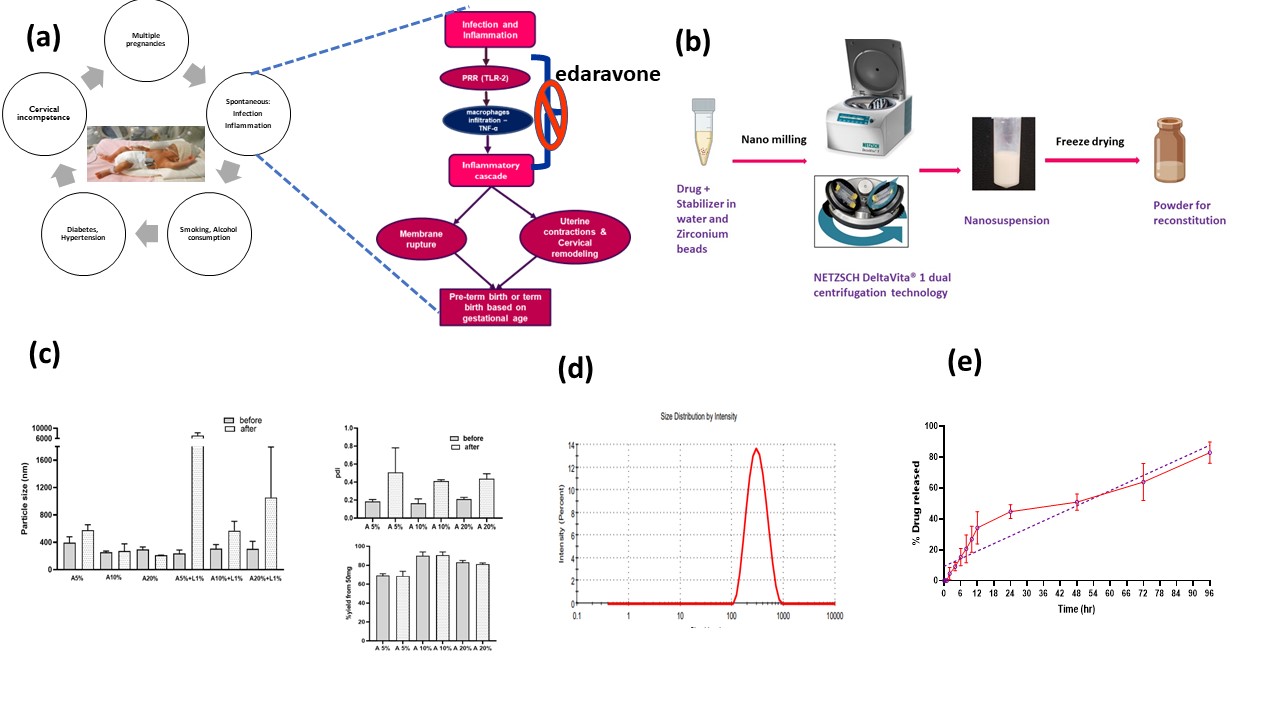 Fig 1. Preterm labor pathophysiology, Development and characterization of Edaravone Nanosuspension. (a) preterm birth causes and pathophysiology (b) Schematic presentation of formulation preparation. (c) Characterization including particle size, pdi, %nano yield of all the 6 shortlisted formulations before and after freeze drying. (d) Dynamic light scattering graph illustrating unimodal particle size distribution of the final formulation that is stabilized by BSA 10%. (e) Cumulative % in vitro release profile of final formulation demonstrating controlled release of edaravone.
Fig 1. Preterm labor pathophysiology, Development and characterization of Edaravone Nanosuspension. (a) preterm birth causes and pathophysiology (b) Schematic presentation of formulation preparation. (c) Characterization including particle size, pdi, %nano yield of all the 6 shortlisted formulations before and after freeze drying. (d) Dynamic light scattering graph illustrating unimodal particle size distribution of the final formulation that is stabilized by BSA 10%. (e) Cumulative % in vitro release profile of final formulation demonstrating controlled release of edaravone.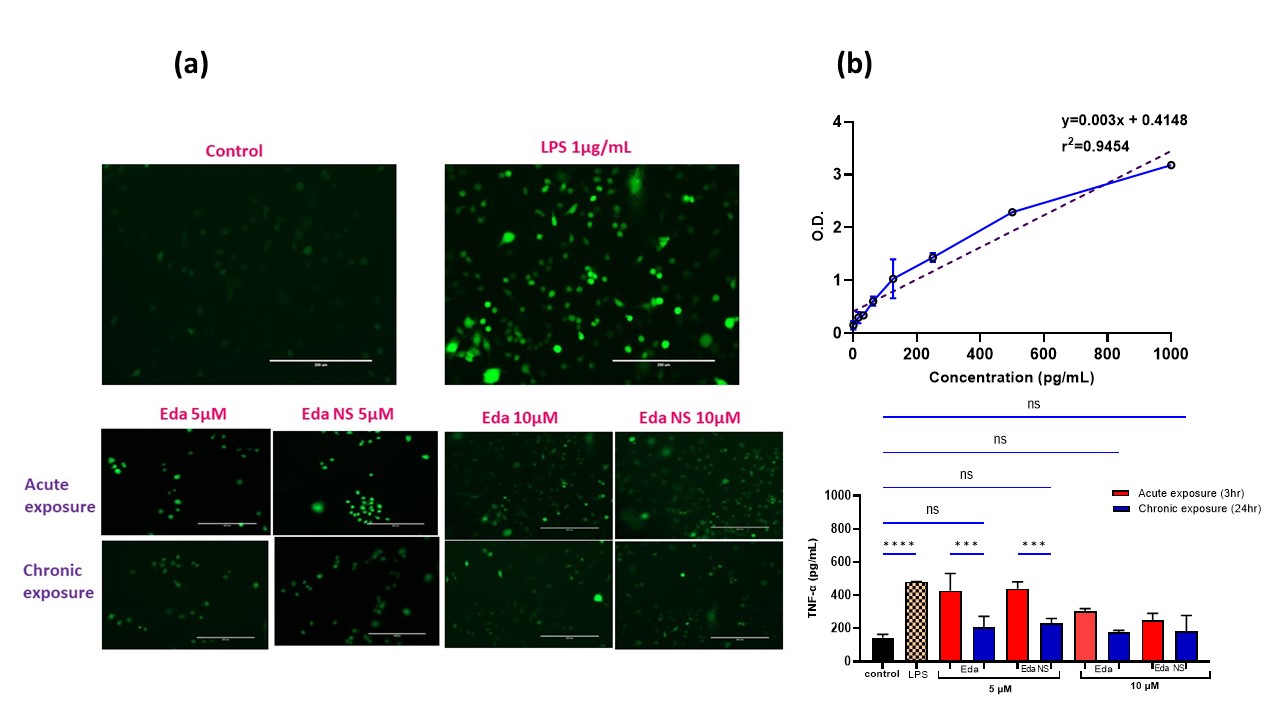 Fig 2. In vitro biological efficacy studies of the Eda NS in RAW 264.7 cells. (a) Pictures representing reduction in LPS induced ROS associated fluorescence with treatments upon ROS sensitive staining [by Chloromethyl derivative of dihydro dichloro fluorescein diacetate, acetyl ester (CM-H₂DCFDA)] of the cells. (b) TNF-α linearity, reduction in LPS induced TNF-α levels, [significant with chronic exposure than acute (at 5µM, p < 0.001)] with treatments - ELISA study.
Fig 2. In vitro biological efficacy studies of the Eda NS in RAW 264.7 cells. (a) Pictures representing reduction in LPS induced ROS associated fluorescence with treatments upon ROS sensitive staining [by Chloromethyl derivative of dihydro dichloro fluorescein diacetate, acetyl ester (CM-H₂DCFDA)] of the cells. (b) TNF-α linearity, reduction in LPS induced TNF-α levels, [significant with chronic exposure than acute (at 5µM, p < 0.001)] with treatments - ELISA study.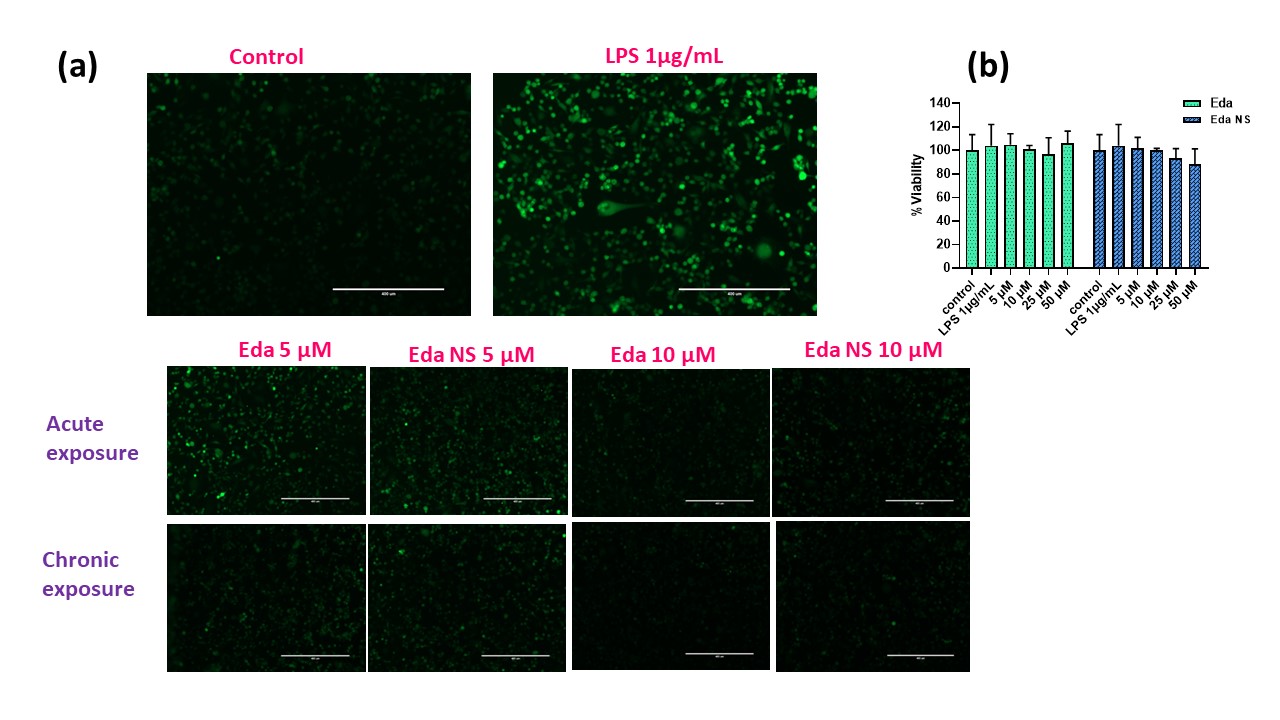 Fig 3. In vitro biological efficacy studies of the Eda NS in HTR-8/SVneo cells. (a) Pictures representing reduction in LPS induced ROS associated fluorescence with treatments upon ROS sensitive staining (CM-H₂DCFDA) of the cells. (b) Safety profile of the pure drug and Eda NS with >85% cell viability is proven by MTT study.
Fig 3. In vitro biological efficacy studies of the Eda NS in HTR-8/SVneo cells. (a) Pictures representing reduction in LPS induced ROS associated fluorescence with treatments upon ROS sensitive staining (CM-H₂DCFDA) of the cells. (b) Safety profile of the pure drug and Eda NS with >85% cell viability is proven by MTT study.