Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
Category: Poster Abstract
(W0930-02-13) Size-Dependent Drug Loading, Gene Complexation, Cell Uptake, and Transfection of a Novel Dendron-Lipid Nanoparticle for Drug/Gene Co-delivery
- KJ
Kaila Javius-Jones, BS (she/her/hers)
University of Wisconsin Madison
Madison, Wisconsin, United States - AN
Ashita Nair, Ph.D.
University of Wisconsin Madison
Madison, Wisconsin, United States - JB
Jiyoon Bu, Ph.D.
University of Wisconsin Madison
Madison, Wisconsin, United States - JB
Jason Bugno, Ph.D.
University of Illinois Chicago
Chicago, Illinois, United States - PR
Piper Rawding, BS
University of Wisconsin Madison
Madison, Wisconsin, United States - LK
Luke Kubiatowicz, BS
University of Wisconsin Madison
Madison, Wisconsin, United States - WJ
Woo-jin Jeong, Ph.D.
University of Wisconsin Madison
Madison, Wisconsin, United States - SH
Seungpyo Hong, Ph.D.
University of Wisconsin Madison
Madison, Wisconsin, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Dendron micelles are particularly promising nanocarriers for drug/gene co-delivery due to their unique molecular properties. Dendrons, which are singular branches of dendrimers, are nonimmunogenic, have high degrees of monodispersity, and are thermodynamically stable.1,2 In this study, we have developed a dendron-based NP system using poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendron-phospholipid hybrid conjugates (DL) for effective micellar drug/gene co-delivery. Two DLNP systems were synthesized using generation 2 (D2; 4 terminal amine groups) and generation 3 (D3; 8 terminal amine groups) DL conjugates. We assessed three hypotheses: (1) the encapsulation of doxorubicin (DOX) inside DLNPs will form stable drug-loaded micelles, which can evade chemoresistance mechanisms. (2) DLNPs from a higher dendron generation will help in complexation with DNA plasmid. (3) The cellular uptake of DLNPs will be affected by their physiochemical properties. By verifying these hypotheses, we aim to provide design cues that could help advance the engineering of multifunctional dendron-based drug delivery platforms in the context of combination therapies across multiple cancer types.
Methods: Dendron-lipids were synthesized via conjugation of alkyne-functionalized dendrons with azide-functionalized lipid, 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE), using copper-catalyzed click chemistry. Final DL products were further characterized using 1H NMR and FTIR spectroscopy. DLNPs were formed via thin-film hydration method, enabling internal loading of hydrophobic compounds, while the external surface was complexed with plasmids expressing green fluorescent protein (pGFP) or luciferase (pLuc). The physiochemical properties of DLNPs were measured using nanoparticle tracking analysis and Zetasizer. The gene delivery potential was tested by observing gene complexation efficiency using gel electrophoresis. While gene transfection of pGFP or pLuc was monitored using fluorescent microscopy or analysis of cell lysates. To understand the drug delivery potential of DLNPs, DOX loaded DLNPs were tested in human glioblastoma (U87) cells. Finally, the mechanism of cellular uptake for these nanocarriers was investigated in U87 cells.
Results: Conjugation of dendrons to DOPE was confirmed using 1H NMR and FTIR. The appearance of the triazolyl hydrogen 1H NMR spectroscopy signal (8.3 ppm) and the disappearance of the FT-IR signal associated with azide stretching (~2600 cm-1) indicated successful conjugation. Post micelle-assembly, D3LNPs were found to have a significantly smaller hydrodynamic diameter than D2LNPs (182 ± 20 nm vs 250 ± 15 nm). Additionally, D3LNPs exhibited a higher ζ-potential of ~23 mV, compared to D2LNPs (~10 mV). These differences in charge density translated to higher gene complexation efficiency as D3LNPs could condense pGFP at a minimal N/P = 5:1 compared to 20:1 for D2LNPs. Pre-treatment of U87 cells with the endocytosis inhibitor, Chlorpromazin, inhibited cellular uptake of D2LNPs by 52%. Whereas cell uptake of D3LNPs was reduced 23%. Efficienct endosomal escape of D3LNP translated to observable transfection of GFP at an N/P > 10:1 as monitored by GFP fluorescence. Similarly, in delivery of pLUC, a 12-fold higher transfection efficiency (p = 0.031) was observed for D3LNPs compared to D2LNPs. The delivery of DLNPs encapsulating DOX to U87 cells indicated a ~46% and 31% reduction in cell viability for DOX-D3LNPs and DOX-D2LNPs, respectively, compared to free DOX (~21%).
Conclusion: Herein, we presented a new design of a dendron-lipid NP with demonstrated capability of stably co-delivering a chemotherapy drug and pDNA for cancer treatment. Our DLNPs took advantage of the unique properties inherent to dendrons for enhanced cellular uptake and co-delivery of multiple cancer therapeutics. Two different NPs were designed from different dendron generations, D2 and D3, and the effect of the dendron generation on drug delivery, gene complexation, and cellular uptake was investigated. Our results confirmed our first hypothesis that higher generation dendrons improved the delivery of DOX to glioblastoma cells. Additionally, the second hypothesis confirmed DLNPs formed from higher generation dendrons demonstrated a greater amount of external pGFP complexed on the surface due to their higher number of positively charged groups. Finally, the differences in dendron generation affecting the efficiency of cellular uptake, confirmed the third hypothesis. As a result, D3LNPs demonstrated the ability to potentially co-deliver multiple chemotherapeutic payloads to cancer cells using a singular nanoplatform.
References: 1. Myung, et al; Dendrimer-Mediated Multivalent Binding for the Enhanced Capture of Tumor Cells. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 11973– 11976.
2. Jeong, et al. Nanoparticle Conjugation Stabilizes and Multimerizes β-Hairpin Peptides to Effectively Target PD-1/PD-L1 β-Sheet-Rich Interfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 1832– 1837.
Acknowledgements: This study was partially supported by NSF (DMR1808251 and DMR-1741560), Milton J. Henrichs Endowed Chair fund and the University of Wisconsin Head and Neck SPORE grant (P50DE026787).
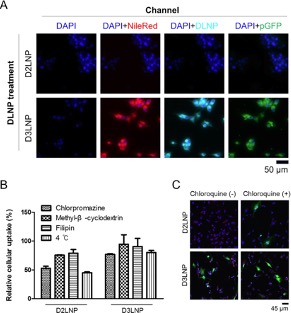 Figure 1. Cellular uptake of DLNPs by U87 cells. (a) In vitro Nile Red and pGFP co-delivery of DLNPs. (b) Cellular internalization mechanism of DLNPs. U87 cells were preincubated with inhibitors (chlorpromazine, methyl-β-cyclodextrin, or filipin) or under 4 °C for 30 min, followed by incubation with DLNPs. (c) GFP expression of cells after 48 h transfection with DLNPs in the presence or absence of chloroquine.
Figure 1. Cellular uptake of DLNPs by U87 cells. (a) In vitro Nile Red and pGFP co-delivery of DLNPs. (b) Cellular internalization mechanism of DLNPs. U87 cells were preincubated with inhibitors (chlorpromazine, methyl-β-cyclodextrin, or filipin) or under 4 °C for 30 min, followed by incubation with DLNPs. (c) GFP expression of cells after 48 h transfection with DLNPs in the presence or absence of chloroquine.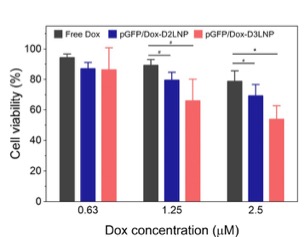 Figure 2. In vitro cytotoxicity of Dox-loaded DLNPs on U87 cells. Significance levels are indicated as #p < 0.10 and *p < 0.05.
Figure 2. In vitro cytotoxicity of Dox-loaded DLNPs on U87 cells. Significance levels are indicated as #p < 0.10 and *p < 0.05.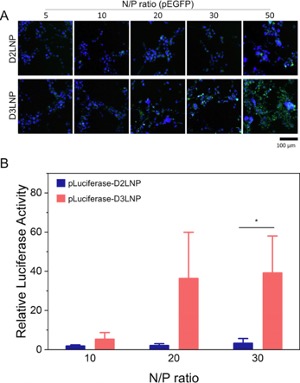 Figure 3. Gene transfection efficiency of DLNPs on U87 cells. (a) Transfection efficiency of pGFP plasmid complexed with D2LNP and D3LNP on U87 cells. The transfection was determined by the expression of green fluorescent protein in the cells. (b) Transfection efficiency of luciferase plasmid complexed with D2LNP and D3LNP on U87 cells. The transfection was measured by the luciferase activity of the cell lysates. Significance levels are indicated as *p < 0.05.
Figure 3. Gene transfection efficiency of DLNPs on U87 cells. (a) Transfection efficiency of pGFP plasmid complexed with D2LNP and D3LNP on U87 cells. The transfection was determined by the expression of green fluorescent protein in the cells. (b) Transfection efficiency of luciferase plasmid complexed with D2LNP and D3LNP on U87 cells. The transfection was measured by the luciferase activity of the cell lysates. Significance levels are indicated as *p < 0.05.